PABPC4
-
Official Full Name
poly(A) binding protein, cytoplasmic 4 (inducible form) -
Overview
PolyA-binding protein (PABP) is a ubiquitous RNA binding protein that contains 4 RNA recognition motifs and a proline-rich C-terminal domain responsible for protein-protein interaction. It is an important regulator of mRNA stability and translation. PABPC -
Synonyms
PABPC4;poly(A) binding protein, cytoplasmic 4 (inducible form);polyadenylate-binding protein 4;APP 1;iPABP;PABP-4;poly(A)-binding protein 4;activated-platelet protein 1;inducible poly(A)-binding protein;APP1;APP-1;PABP4;FLJ43938
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PABPC4-1504H | Recombinant Human PABPC4 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 285-631 aa | |
| PABPC4-11444Z | Recombinant Zebrafish PABPC4 | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| PABPC4-1271HCL | Recombinant Human PABPC4 cell lysate | Human | Non |
|
||
| PABPC4-4390H | Recombinant Human PABPC4 protein | E.coli | Human | Non | 1-644aa |
|
Background
What is PABPC4 Protein?
PABPC4, short for poly(A) binding protein cytoplasmic 4, is one of several proteins in the PABP family that play a crucial role in managing mRNA within cells. This protein primarily hangs out in the cytoplasm, where it binds to the poly(A) tails at the end of mRNA molecules. This binding is essential for stability and translation of mRNA, basically helping the cell make proteins from the genetic instructions it receives. Beyond just lending a hand in protein production, PABPC4 is also involved in regulating mRNA decay, ensuring that faulty or excess mRNA molecules are broken down when they're no longer needed. It’s like a quality control manager ensuring everything runs smoothly. Researchers are still exploring its specific roles in different tissues and conditions, but it’s clear PABPC4 is an important player in keeping our cells functioning properly.What is the Function of PABPC4 Protein?
The PABPC4 protein, part of the poly(A) binding protein family, mainly does its work in the cell's cytoplasm. Its main job is to latch onto the poly(A) tails at the ends of mRNA molecules. By doing so, it keeps these mRNAs stable and ready for translation, helping turn genetic codes into proteins. Think of it like a helper making sure the instructions for protein-building don’t fall apart before the job is done. Beyond just aiding in protein production, PABPC4 plays a part in controlling how long these mRNA molecules stick around, breaking down the extras or faulty ones. This control helps keep the cell’s protein production line running smoothly without hiccups. Although there’s still much to learn about its specific roles across different cell types, PABPC4’s function is vital for maintaining cellular harmony.PABPC4 Related Signaling Pathway
PABPC4 is a key player in the complex web of cellular signaling pathways, particularly in regulating mRNA stability and translation. When mRNA gets its poly(A) tail, PABPC4 binds to it, acting like a shield that keeps the mRNA intact and ready for protein synthesis. This connection is crucial because it influences how efficiently a cell can produce proteins when responding to signals. In immune cells, for instance, PABPC4 plays a significant role in managing how quickly certain proteins are made, impacting immune responses. Furthermore, by being involved in signaling pathways, PABPC4 affects cell growth, response to stress, and metabolism shifts, potentially playing a part in how cells react to different conditions. Scientists are digging into these pathways to understand more about PABPC4’s broader impact, as altering this pathway might offer insights into treating diseases linked to immune system dysfunction or improper cell signaling.PABPC4 Related Diseases
PABPC4, though not the most famous protein, is linked to several important health conditions because of its role in mRNA regulation. In cancer, changes in how PABPC4 functions might lead to uncontrolled cell growth by messing with protein production. It's like when the instructions for stopping cell division don’t get through, leading to tumors. In the immune system, PABPC4 helps regulate how quickly immune cells respond to invaders. If something's off with PABPC4, it might mean immune responses are either too weak or too aggressive, contributing to autoimmune diseases or problems fighting infections. There's ongoing research to see exactly how PABPC4 changes might be involved in these diseases, as understanding this could lead to new treatment options. So, while it works quietly in the background, PABPC4 has a big impact when things go awry.Bioapplications of PABPC4
PABPC4, or Poly(A) Binding Protein Cytoplasmic 4, serves a key role in binding mRNA in the cytoplasm, contributing significantly to gene expression by influencing mRNA stability and translation. Its involvement in immune response modulation suggests potential in therapeutic advances, particularly for enhancing immune functions and cancer treatments. Additionally, PABPC4's interactions within cellular mechanisms present exciting possibilities in bioengineering, such as drug screening and developing targeted therapies. Overall, PABPC4's multifaceted role positions it as a crucial element in advancing medical and bioengineering fields.Case Study
Case Study 1: Kumar GR. et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2011
Studies show PABPC can switch roles based on its location. In the cytoplasm, it boosts protein production, but stress sends it to the nucleus, blocking mRNA export. It's not clear how this happens, but RNA seems to keep it in the cytoplasm. Viral proteins or a deadenylase can trigger its move by using its RNA recognition motifs to bind importin α for nuclear entry. Poly(A) RNA blocks this, keeping PABPC in the cytoplasm under normal conditions.-
 Fig1. HEK293T cells were transfected with empty vector or plasmids expressing SOX or muSOX for 24 h.
Fig1. HEK293T cells were transfected with empty vector or plasmids expressing SOX or muSOX for 24 h. -
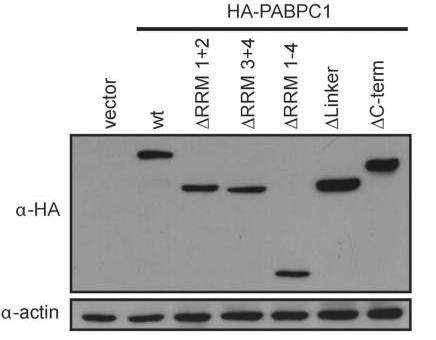 Fig2. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated wild-type and mutant HA-PABPC1 plasmids for 24 h.
Fig2. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated wild-type and mutant HA-PABPC1 plasmids for 24 h.
Case Study 2: Bhattacharjee RB. et al. PLoS One. 2012
In vertebrates, PABPs mainly stay in the cytoplasm, except for PABPN1, found in the nucleus where it helps set the poly(A) tail length of mRNA. While PABP1 is well-studied, others aren’t. After reducing PABPN1 in HeLa and HEK293 cells, mRNA tail length and export remained unchanged, but PABP5 levels went up and PABP4 moved to the nucleus, associating with pre-mRNA and CPSF. However, losing PABPN1 hurt cell survival, increasing apoptosis markers like phosphorylated p53 and PUMA, and the ER stress marker GRP78.-
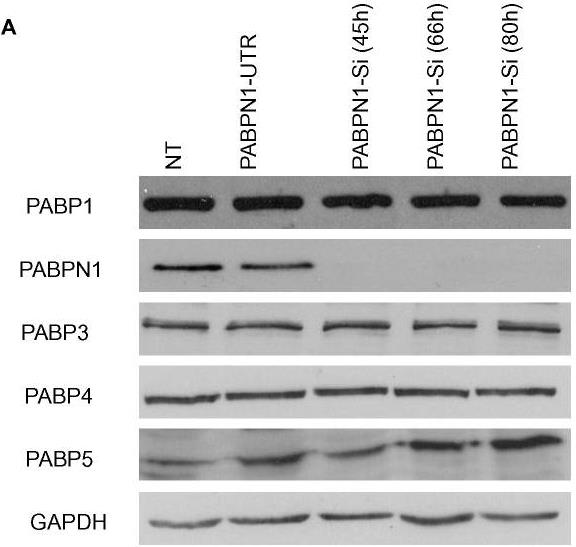 Fig3. Level of different cellular PABPs in PABPN1 depleted cells.
Fig3. Level of different cellular PABPs in PABPN1 depleted cells. -
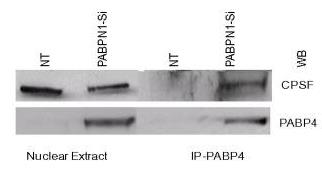 Fig4. The agarose bead eluted (IP-PABP4) and cell equivalent amount of the input nuclear extract were used for western blotting.
Fig4. The agarose bead eluted (IP-PABP4) and cell equivalent amount of the input nuclear extract were used for western blotting.
Involved Pathway
PABPC4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PABPC4 participated on our site, such as RNA transport,mRNA surveillance pathway,RNA degradation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PABPC4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA degradation | ENO1B,PAPD7,EXOSC6,HSPD1,CNOT4B,CNOT6L,PABPC1B,CNOT10,EXOSC4,PABPC1 |
| RNA transport | EIF2S1B,DDX39B,RPP25L,EIF4EBP3L,EIF3E,NUP133,EIF3EB,RPP40,NXF2,EIF4EBP2 |
| mRNA surveillance pathway | PPP2R5EA,SYMPK,PPP2R2D,FIP1L1,PPP1CBL,CSTF2T,PPP2R1B,SMG7,GSPT1L,MSI2 |
-
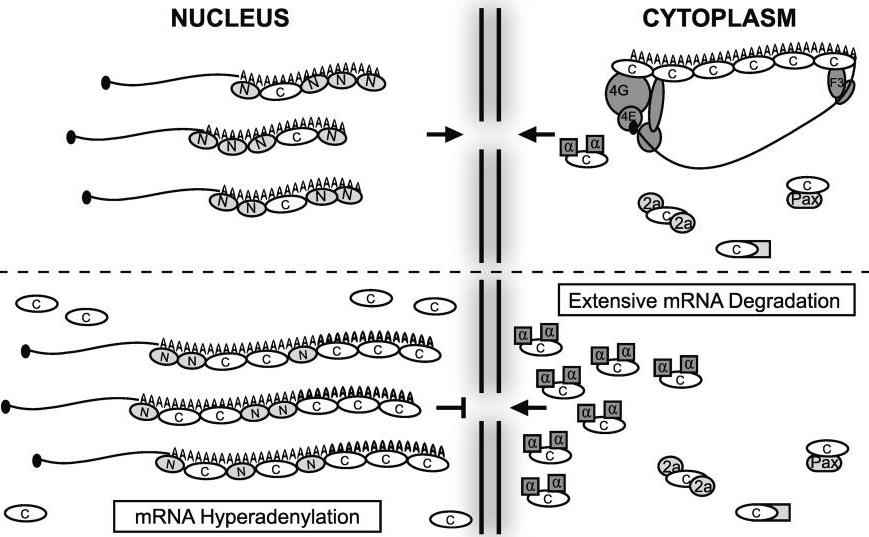 Fig1. Model depicting mRNA turnover-induced nuclear accumulation of PABPC. (G Renuka Kumar, 2011)
Fig1. Model depicting mRNA turnover-induced nuclear accumulation of PABPC. (G Renuka Kumar, 2011) -
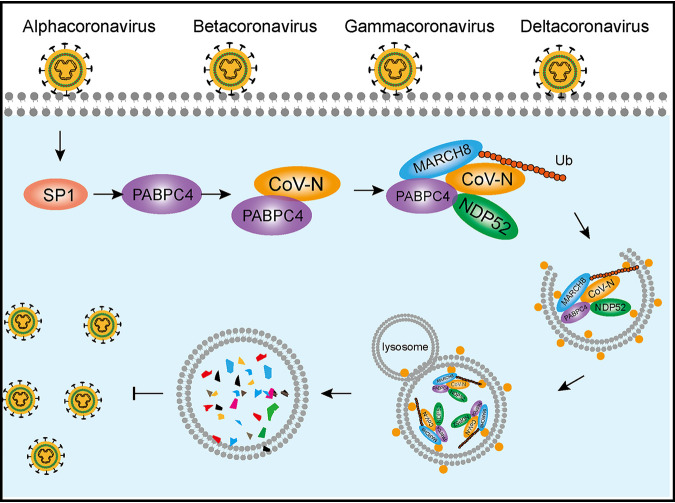 Fig2. A proposed working model to illustrate the PABPC4-MARCH8-NDP52 axis broadly inhibits coronavirus replication. (Yajuan Jiao, 2021)
Fig2. A proposed working model to illustrate the PABPC4-MARCH8-NDP52 axis broadly inhibits coronavirus replication. (Yajuan Jiao, 2021)
Protein Function
PABPC4 has several biochemical functions, for example, nucleotide binding,poly(A) RNA binding,poly(A) binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PABPC4 itself. We selected most functions PABPC4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PABPC4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| nucleotide binding | RBM5,FIGN,GTF2F2B,U2AF1,TDRD12,ADCY1B,TIA1L,ARF1L,TARDBP,SNRPA |
| protein binding | CCDC43,NRSN1,HSF1,BMI1,WWTR1,GATA3,DPH3,C19orf44,ECH1,SNRPE |
| poly(A) RNA binding | NKAP,MYBBP1A,IMMT,RPL10,TCP1,NGRN,SURF6,RPL22,RPS27.1,TPD52L2 |
| poly(U) RNA binding | KHDRBS2,KHDC1A,PABPC1,HNRNPH1,PATL2,MSI2,DIS3L2,RBM11,PATL1,PNPT1 |
| poly(A) binding | PABPC3,KHDRBS1,PAIP2B,TIA1,PABPN1,HNRNPDL,PABPC1,ZC3H14,HNRPDL,SYNCRIP |
Interacting Protein
PABPC4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PABPC4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PABPC4.
YWHAZ;PHLDA1;SRPK2;PPM1B;HNF4A;ARF6;IKBKE;Klc1;PINX1;TNFRSF10D;PUF60;SMAD9;XRN1;15-deoxy-delta(12,14;midostaurin;NS1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



