ODC1
-
Official Full Name
ornithine decarboxylase 1 -
Overview
Ornithine Decarboxylase (ODC) is the first and rate limiting enzyme of the polyamine biosynthesis pathway which catalyzes ornithine to putrescine. ODC activity is induced by numerous agents known to promote cell proliferation including growth factors, mit -
Synonyms
ODC1;ornithine decarboxylase 1;ornithine decarboxylase;ODC
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
- Flag
Background
What is ODC1 Protein?
ODC1, or ornithine decarboxylase 1, is a key player in promoting cell growth and development. It acts as an enzyme that converts ornithine into putrescine, kicking off the production of polyamines, which are essential for cells to divide and grow. This process is vital for things like tissue repair and a healthy immune response. In areas where rapid cell growth occurs—like in developing tissues or cancer—ODC1 tends to be more active. That's why it's a focus in research, as regulating ODC1 might offer ways to address diseases marked by uncontrolled cell growth. Essentially, ODC1 functions like a growth accelerator in the body, vital for development and maintenance.What is the Function of ODC1 Protein?
ODC1, or ornithine decarboxylase 1, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in cell growth and division. It kickstarts the process of converting ornithine into putrescine, which is the first step in making polyamines. Polyamines are essential for cells because they help with DNA stabilization and support cell division—basically, they’re fundamental for cell life and function. Without ODC1 doing its job, cells would struggle to grow and divide properly, affecting everything from healing wounds to maintaining healthy tissues. This function makes ODC1 particularly important in rapidly growing cells, such as those found in embryonic development and cancer. Scientists are interested in ODC1 because controlling its activity might help manage diseases where cell growth is excessive or abnormal.ODC1 Related Signaling Pathway
ODC1, or ornithine decarboxylase 1, plays a pivotal role in pathways that drive cell growth by initiating polyamine production. As the first step in this pathway, ODC1 converts ornithine to putrescine, paving the way for generating key polyamines necessary for DNA stability and cell division. Through this action, ODC1 influences critical growth pathways like mTOR, which governs cell growth and protein synthesis. Variations in ODC1 activity can affect how these signals are managed within cells, making it particularly significant in cancer research, where growth signals often go haywire. Researchers are exploring how tweaking ODC1's function could offer new strategies for diseases marked by excessive cell growth.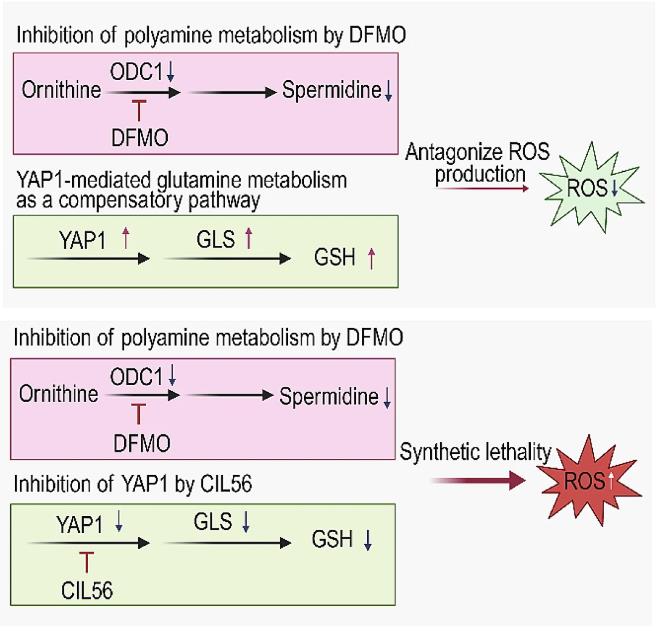
Fig1. Tumor growth curves for in vivo PDX models following combined treatment of DFMO with CB-839. (Hongsheng Wang, 2024)
ODC1 Related Diseases
ODC1, or ornithine decarboxylase 1, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the polyamine biosynthesis pathway, important for cell growth and differentiation. While ODC1 itself sounds pretty technical, its malfunction can lead to several human diseases which have very real impacts. For instance, one significant disorder connected with ODC1 is Snyder-Robinson Syndrome, a rare X-linked recessive condition characterized by intellectual disability, muscle tone abnormalities, and developmental delays. Moreover, abnormal activity of ODC1 has been linked to certain cancers. This is because polyamines, promoted by ODC1, are essential for rapid cell growth, and unchecked activity can foster tumorigenic processes. Additionally, elevated levels of ODC1 have been observed in colorectal cancer and bladder cancer. Alterations in ODC1 levels or activity can serve as both a marker and a potential therapeutic target for these conditions. Despite being less known to many, the ripple effects of its dysfunction remind us how intricate and finely tuned our genetic makeup really is, and how a single enzyme can dramatically influence health.Bioapplications of ODC1
ODC1, or ornithine decarboxylase 1, might not pop up in your everyday chat, but it's making waves in the world of science. This enzyme is great at churning out polyamines, the tiny molecules that keep cells growing and running smoothly. In the lab, ODC1 is a bit of a superstar, especially when it comes to cancer research. Scientists dive into its workings to uncover new ways to tackle tumor growth or even spot cancers earlier. But it’s not just about medicine; agriculture is also getting in on the action. By tweaking ODC1, researchers are exploring how to help crops grow stronger, faster, and stand up to challenges like tough weather or pesky bugs. So, while ODC1 might not make the news, it's a behind-the-scenes player with a hand in shaping health and farming solutions that touch all our lives.Case Study
Case Study 1: Li YP. et al. J Proteome Res. 2024
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a prevalent cancer where autophagy, the cell's recycling process, often gets disrupted. There's a pressing need to identify new autophagy-related factors in NSCLC. Here pirin levels are elevated in NSCLC and linked to worse outcomes. High pirin inhibits autophagy and boosts cancer cell growth. Using advanced proteomics, pirin influences various proteins, notably increasing ornithine decarboxylase 1 (ODC1). Reducing ODC1 counteracts the effects of high pirin, restoring autophagy and slowing cell proliferation. Both pirin and ODC1 are highly expressed in NSCLC tissues, and patients with high levels of both have a poorer survival prognosis.-
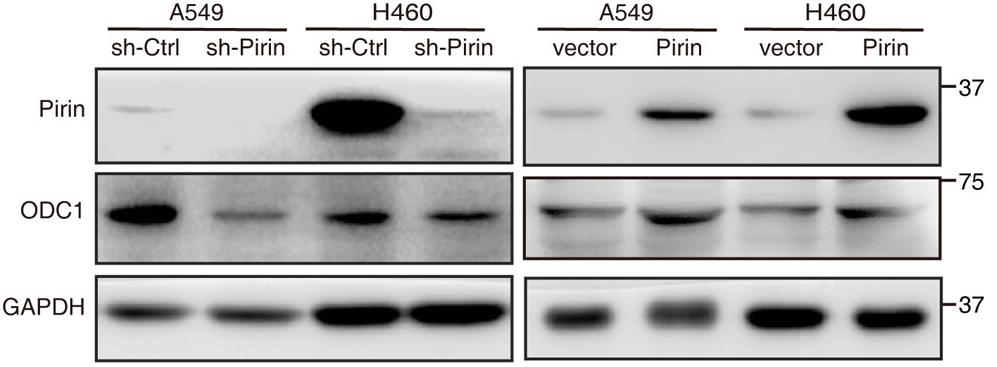 Fig1. The expression of ODC1 in pirin-knockdown or pirin-overexpressing NSCLC cells (A549 and H460) was detected by Western blotting.
Fig1. The expression of ODC1 in pirin-knockdown or pirin-overexpressing NSCLC cells (A549 and H460) was detected by Western blotting. -
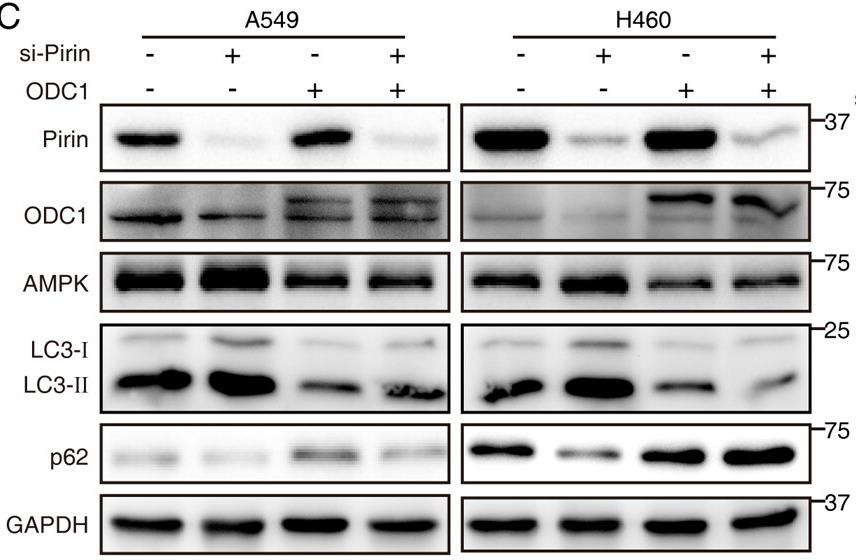 Fig2. The expression of AMPK, LC3, and p62 in NSCLC cells with manipulated pirin and/or ODC1 expression was detected by Western blotting.
Fig2. The expression of AMPK, LC3, and p62 in NSCLC cells with manipulated pirin and/or ODC1 expression was detected by Western blotting.
Case Study 2: Keller T. et al. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2022
The RS1 protein regulates glucose uptake in the intestine by affecting the SGLT1 transporter. It does this by blocking vesicle release at the trans-Golgi network. RS1's antidiabetic role involves ODC1, which converts ornithine to putrescine, promoting vesicle release. This report examines the interaction between ODC1 and RS1-reg using techniques like SPR, SAW, and ITC, revealing small differences in binding across setups. A significant finding is a 100-fold increase in binding affinity with biological membranes, which may be crucial for RS1's role and future antidiabetic drug development.-
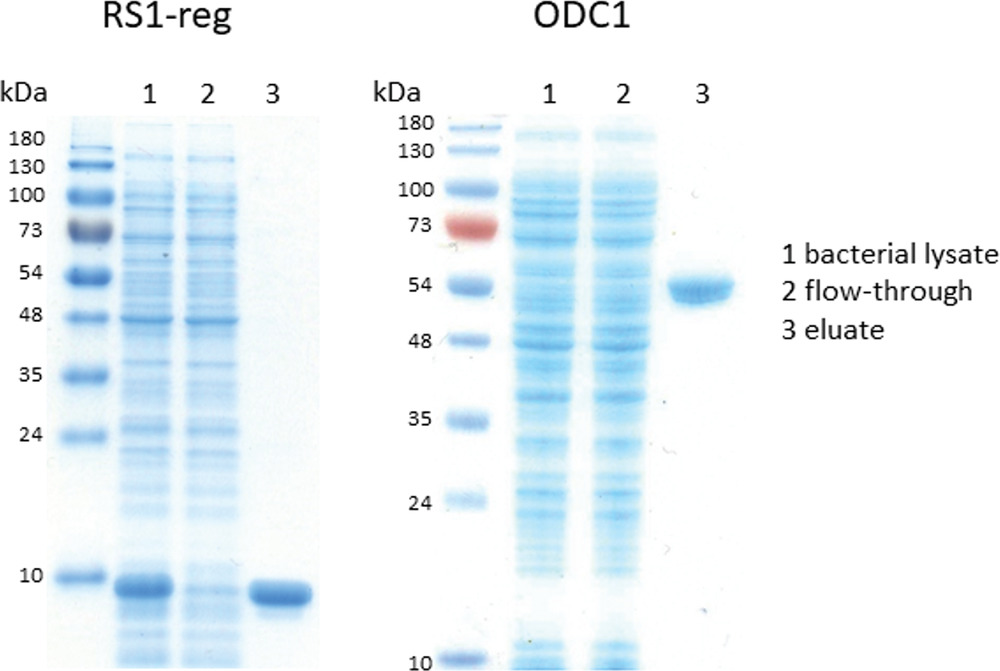 Fig3. SDS–PAGE showing purification of recombinant hRS1-reg(S20E) and hODC1 produced in E. coli.
Fig3. SDS–PAGE showing purification of recombinant hRS1-reg(S20E) and hODC1 produced in E. coli. -
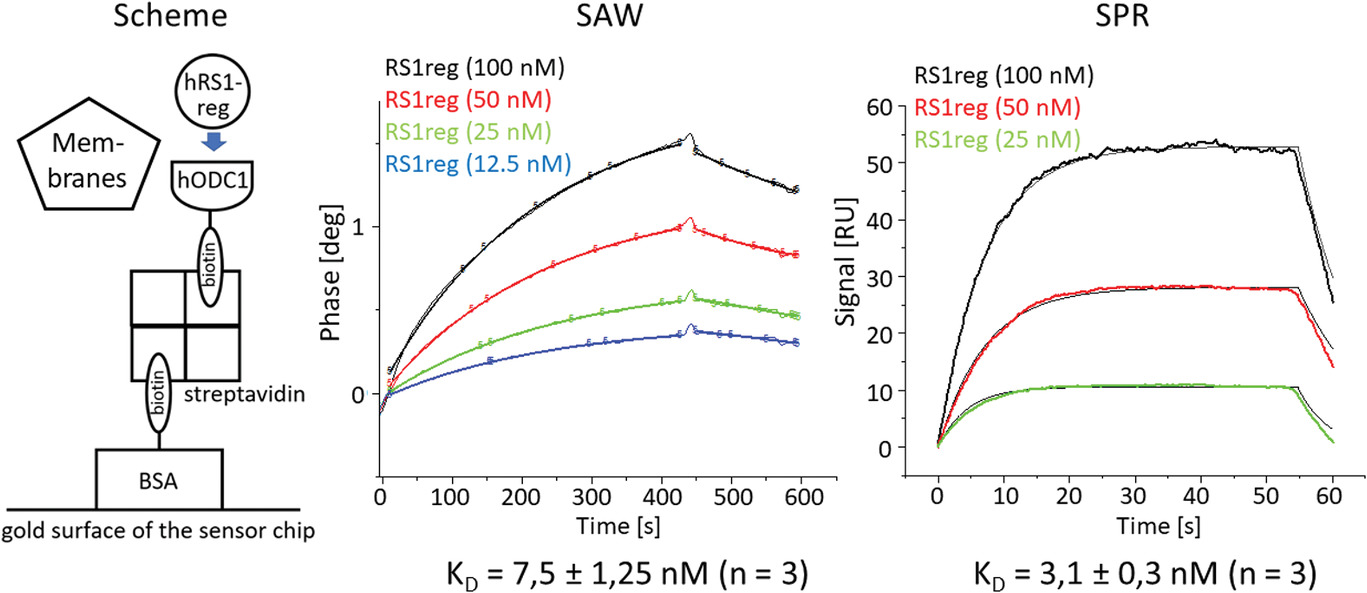 Fig4. SAW and SPR experiments involving coating of the sensor chip surface with biotinylated BSA.
Fig4. SAW and SPR experiments involving coating of the sensor chip surface with biotinylated BSA.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ODC1-6826R)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ODC1-6826R) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ODC1-1883R)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ODC1-1883R)
Involved Pathway
ODC1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ODC1 participated on our site, such as Arginine and proline metabolism,Glutathione metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ODC1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Glutathione metabolism | GGT1A,GSTM,GSTA1,MGST1.2,GSTM7,GSTA2,TXNDC12,ANPEPB,GGT1,MGST1.1 |
| Arginine and proline metabolism | CARNS1,DAO.1,P4HA1B,CKMT2,DAO1,CKMT1A,ALDH2,PYCR1A,AZIN2,CKM |
| Metabolic pathways | B3GNT3,UROC1,UGT1A9,AKR1B1L,GM5506,PYCR1A,NDUFB11,NAT,BTD,CYP7A1A |
-
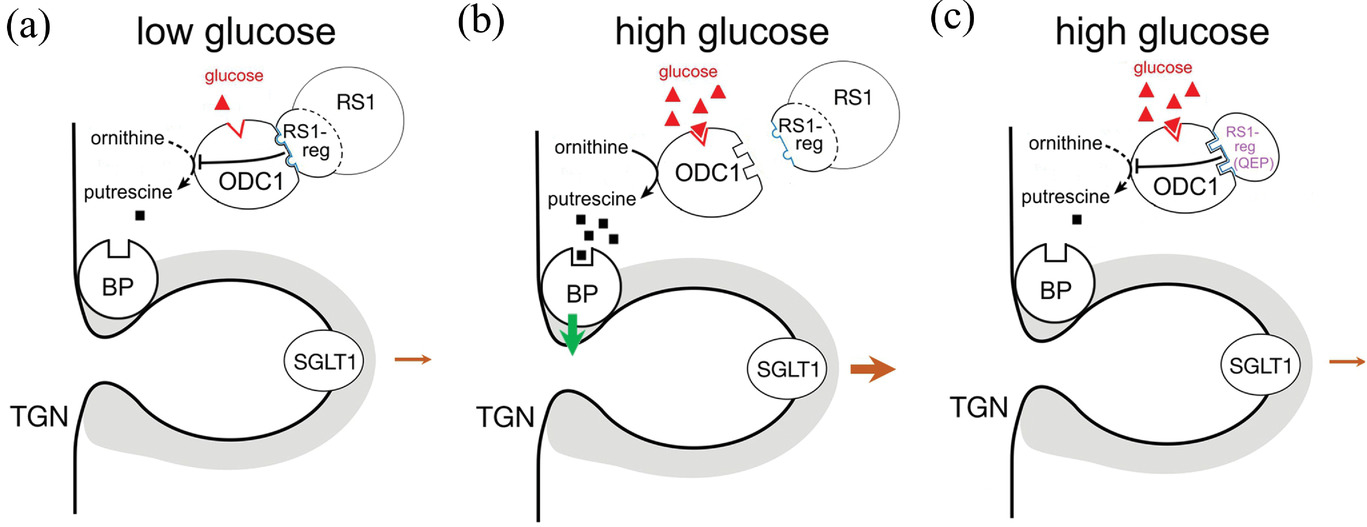 Fig1. Scheme of the suggested mode of action of RS1 for upregulation of SGLT1 in small intestine after glucose ingestion with food and the effect of an RS1-reg variant that blocks the glucose-mediated upregulation. (Thorsten Keller, 2022)
Fig1. Scheme of the suggested mode of action of RS1 for upregulation of SGLT1 in small intestine after glucose ingestion with food and the effect of an RS1-reg variant that blocks the glucose-mediated upregulation. (Thorsten Keller, 2022) -
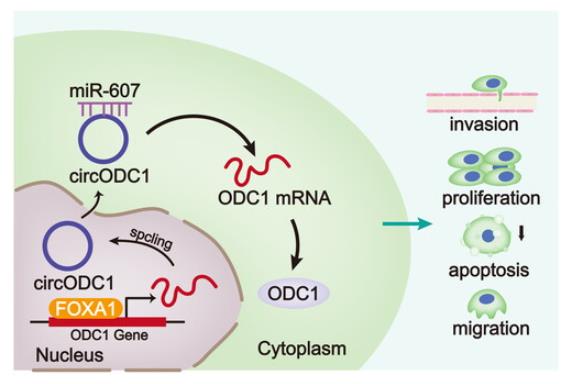 Fig2. Transcription factor FOXA1 binds to circODC1 promoter and activates circODC1 transcription. (Rong Jin, 2024)
Fig2. Transcription factor FOXA1 binds to circODC1 promoter and activates circODC1 transcription. (Rong Jin, 2024)
Protein Function
ODC1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ornithine decarboxylase activity,protein binding,protein homodimerization activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ODC1 itself. We selected most functions ODC1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ODC1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | AGGF1,ELK4,ALPL,HTR1A,SPSB1,FGF21,NUP62L,KLC3,DRD1,TRPV6 |
| protein homodimerization activity | BCL2L1,ACOT7,CHEK2,EPHX2,FOXP3,NR2C1,NR6A1B,CADM2,AMICA1,IKBKB |
Interacting Protein
ODC1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ODC1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ODC1.
KAT5;GORASP2;OAZ3;OAZ2;TK1;TMOD1;SSR1;STX17;CSNK2B;MAP2K1;BAAT;TSTD2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


