NEU2
-
Official Full Name
sialidase 2 (cytosolic sialidase) -
Overview
This gene belongs to a family of glycohydrolytic enzymes which remove sialic acid residues from glycoproteins and glycolipids. Expression studies in COS7 cells confirmed that this gene encodes a functional sialidase. Its cytosolic localization was demonstrated by cell fractionation experiments. -
Synonyms
NEU2;sialidase 2 (cytosolic sialidase);sialidase-2;N acetyl alpha neuraminidase 2;SIAL2;Cytosolic sialidase;MGC129579;N-acetyl-alpha-neuraminidase 2;NEUR2_HUMAN;Neuraminidase 2;OTTHUMP00000164374;Sialidase 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Human
- Chinese hamster
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- Yeast
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- T7
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Myc
- DDK
- Flag
Background
What is NEU2 protein?
NEU2 gene (neuraminidase 2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q37. It functions to remove sialic acid residues from glycoproteins and glycolipids. NEU2 is involved in the catabolism of complex carbohydrates and plays a role in various biological processes, including cell-cell interactions and immune responses. NEU2 protein is expressed in various species and can be found in different cellular locations, including the cytosol, indicating its diverse functions within the cell. It is also known to have specificity for certain types of sialic acid linkages, such as α-(2->3)-sialylated GD1a and GT1B gangliosides, and it prefers α-(2->3) over α-(2->8)-sialylated GD1b. The NEU2 protein is consisted of 380 amino acids and NEU2 molecular weight is approximately 42.3 kDa.
What is the function of NEU2 protein?
NEU2 plays a key role in the metabolism of complex carbohydrates by catalyzing the removal of terminal sialic acid residues from glycoconjugates. It is involved in various biological processes, including cell differentiation, cell-cell interactions, and immune responses. NEU2 is particularly important for the differentiation of myoblasts and neurons. The activity of NEU2 is crucial for maintaining the balance of sialic acid levels in the body, which is important for proper cellular function and communication.

Fig1. Schematic diagram outlining the overexpressed Neu2. (Eswara Murali Satyavarapu, 2021)
NEU2 Related Signaling Pathway
Upregulation of NEU2 can inhibit the PI3K-AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, which is one of the major pathways regulating cell physiology, angiogenesis and proliferation. Neu2-overexpressed cells showed higher levels of Fas/CD95 death receptor, FasL, FADD, and Bid cleavage, confirming exogenous pathways mediated apoptosis. Fmod protein regulates the expression of genes related to muscle atrophy by regulating TGF signaling pathway to reduce muscle atrophy. NEU3, as a homologous protein of NEU2, is involved in tumorigenesis through EGFR/Src signaling pathway and may be a potential target for inhibiting EGFR.
NEU2 Related Diseases
The NEU2 protein has been implicated in a variety of diseases, especially those related to metabolism and cell function. Mutations or abnormal expression of the NEU2 gene are associated with certain types of lipoma, a soft tissue tumor that presents as an abnormal proliferation of fat cells. In addition, NEU2 is associated with influenza and Glycoproteinosis. The surface of influenza viruses contains sialic acid, and NEU2 acts as a sialase that may play a role in viral replication and host immune response. Glycoproteinosis is a genetic disease caused by abnormal sialic acid metabolism in cells. The dysfunction of NEU2 may affect the normal modification and degradation of glycoproteins on the cell surface, resulting in the disease.
Bioapplications of NEU2
The application of NEU2 protein is mainly concentrated in the field of medical research and therapy. Because NEU2 plays a role in regulating sialylation levels of glycoproteins on the surface of cells, it has important implications in studying biological processes such as cell recognition, signaling, and immune responses. In addition, functional studies of NEU2 could help develop treatments against viral diseases such as influenza, which rely on sialylation molecules on the surface of host cells for infection. The regulation of NEU2 activity may also be relevant to the treatment of certain inherited metabolic diseases, such as glycoproteinosis. In drug development, NEU2 can be used as a drug target to influence the progression of related diseases by inhibiting or activating its activity. In addition, the expression level and activity of NEU2 can also be used as biomarkers for disease diagnosis and treatment response.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Shalini Nath, 2020
In this study, researchers have addressed the role of sialylation in regulating stemness-like properties of pancreatic cancer sphere-forming cells (PCS) through modulation of the Hedgehog (Hh) pathway. The status of CD133/CD44/surface-sialylation was checked by flow cytometry and effects of Neu2 overexpression in PCS were compared using qPCR, immunoblotting, co-immunoprecipitation and also by colony-formation assays. Neu2 and Shh status in patient tissues were examined by immunohistochemistry. PCS showed higher Hh-pathway activity and sialylation with reduced cytosolic-sialidase (Neu2). Neu2 overexpression caused desialylation of Shh, thereby reducing Shh-Patched1 binding thus causing decreased Hh-pathway activity with lower expression of Snail/Slug/CyclinD1 leading to reduction of stemness-like properties. Neu2-overexpression also induced apoptosis in PCS. Additionally, Neu2-overexpressed PCS demonstrated lower mTORC2 formation and inhibitory-phosphorylation of Gsk3β, reflecting a close relationship with reduced Hh pathway.

Fig1. qPCR analysis of all four sialidases, namely Neu1, Neu2, Neu3 and Neu4.

Fig2. Co-immunoprecipitation of Neu2 and Shh showed higher association in N-PCS than PCS.
Case Study 2: Dianne E van der Wal, 2020
Neuraminidases (NEU) are responsible for desialylation and so far, however, the role of NEU in healthy platelets is currently unknown. Aim of the study was to study the role of NEU1 and NEU2 in platelet signalling. Membrane association of platelet attached glycans, NEU1 and NEU2 was measured following activation with agonists using flow cytometry. Adhesion on fibrinogen, aggregation and fibrinogen-binding were assessed with/without the NEU-inhibitor, 2-deoxy-2-3-dide-hydro-N-acetylneuraminic acid. Cellular localisation of NEU1 and NEU2 was examined by fluorescence microscopy. Desialylation occurred following GPIbα-clustering by VWF. Membrane associated NEU2 increased two-fold upon VWF-binding, while inhibition/removal of GPIbα reduced the majority of membrane associated NEU1 and NEU2. High shear and addition of fibrinogen increased membrane NEU1 and NEU2.

Fig3. Membrane association of NEU2 were measured by flow cytometry.
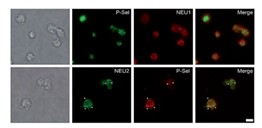
Fig4. Unstimulated (non-) permeabilised washed platelets were stained for NEU2 (green).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NEU2-95HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Neu2-1189R)
Involved Pathway
NEU2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NEU2 participated on our site, such as Other glycan degradation,Sphingolipid metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NEU2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Sphingolipid metabolism | PPM1LA,SPTLC3,SMPD1,GAL3ST1,ACER1,ARSI,SMPD3,UGT8A,PPAP2CB,ARSA |
| Other glycan degradation | NEU3,ENGASE,MAN2B2,NEU3.5,ENG-1,NEU3.1,GBA,MANBA,MAN2C1,NEU4 |
Protein Function
NEU2 has several biochemical functions, for example, exo-alpha-(2->3)-sialidase activity,exo-alpha-(2->6)-sialidase activity,exo-alpha-(2->8)-sialidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NEU2 itself. We selected most functions NEU2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NEU2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| exo-alpha-(2->6)-sialidase activity | NEU3,NEU1,NEU4 |
| protein binding | CRLF3,CTSH,NPLOC4,CYBB,CRKL,TGM1,TATDN1,TXNDC16,PPIL1,RPLP0 |
| exo-alpha-(2->8)-sialidase activity | NEU4,NEU3,NEU1 |
| exo-alpha-(2->3)-sialidase activity | NEU3,NEU4,NEU1 |
Interacting Protein
NEU2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NEU2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NEU2.
NOTCH2NL
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Tomin, A; Dumych, T; et al. Desialylation of dying cells with catalytically active antibodies possessing sialidase activity facilitate their clearance by human macrophages. CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL IMMUNOLOGY 179:17-23(2015).
- Vicari, D; Foy, KC; et al. Engineered Conformation-dependent VEGF Peptide Mimics Are Effective in Inhibiting VEGF Signaling Pathways. JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 286:13612-13625(2011).


