MYT1
-
Official Full Name
myelin transcription factor 1 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a family of neural specific, zinc finger-containing DNA-binding proteins. The protein binds to the promoter regions of proteolipid proteins of the central nervous system and plays a role in the developing nervous system. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MYT1;myelin transcription factor 1;MTF1;MYTI;NZF2;PLPB1;ZC2HC4A;C20orf36;myelin transcription factor I;proteolipid protein binding protein;proteolipid protein-binding protein;neural zinc finger transcription factor 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Wheat Germ
- His
- T7
- Non
- GST
Background
What is MYT1 protein?
MYT1 gene (myelin transcription factor 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 20 at locus 20q13. MYT1 is a transcription factor that is mainly enriched in brain tissue, especially in the cerebellum. It is involved in regulating the expression of genes associated with myelination and is essential for maintaining the integrity of myelin in the central nervous system. The protein encoded by the MYT1 gene contains multiple transcription factor active domains that bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate transcription of downstream genes. In addition, MYT1 protein also has the activity of Wee1 kinase, which can phosphorylate the Thr14 site of Cdc2, a key cell cycle regulator, thereby inhibiting Cdc2 kinase activity and controlling the cell cycle transition from G2 phase to M phase. In the cytoplasm, MYT1 protein may also be associated with the cell membrane and is involved in cell cycle regulation and cellular stress response. The MYT1 protein is consisted of 1121 amino acids and MYT1 molecular weight is approximately 122.3 kDa.
What is the function of MYT1 protein?
MYT1 protein has the dual function of transcription factor and kinase, and plays an important role in nervous system development and disease. It is involved in regulating the expression of genes associated with myelination and is essential for maintaining the integrity of myelin in the central nervous system. MYT1 kinase is another functional aspect of MYT1 protein. Regulation of MYT1 kinase activity is essential for precise regulation of the cell cycle and for preventing cells from entering mitosis prematurely. MYT1 plays a role in neurodevelopment, affecting the proliferation and differentiation of neural precursor cells. The activity of MYT1 kinase is also associated with the process of apoptosis, and its inhibitors may fight cancer by promoting apoptosis. In oligodendrocyte progenitors, MYT1 influences the development of oligodendrocyte lineages by regulating the OP proliferative response associated with terminal differentiation and myelin gene expression.
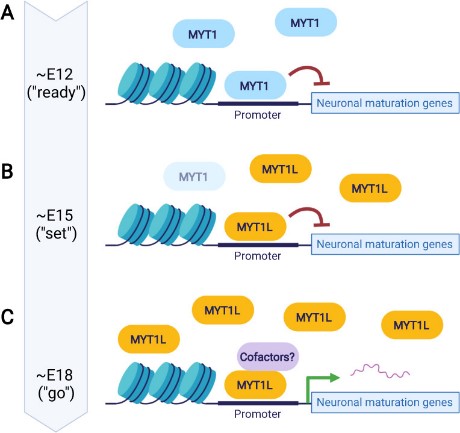
Fig1. Speculative "ready-set-go" model of MYT TFs during neuronal differentiation. (Jiayang Chen, 2022)
MYT1 Related Signaling Pathway
MYT1 kinase and Wee1 kinase belong to the Wee family, and Wee1 kinase mainly phosphorylates the Thr14 site of Cdk1. Upregulation of MYT1 is one way cancer cells develop resistance to Wee1 inhibition. Akt promotes cell cycle progression of G2/M conversion through Wee1 inactivation, and Akt down-regulates PKMYT1 activity. Myt1 and MYT1L (Myelin Transcription Factor 1 and myT1-like) can directly inhibit the expression of YAP1 coactivators, change the output of Hippo signaling pathway, and affect cell proliferation and differentiation.
MYT1 Related Diseases
The protein encoded by the MYT1 gene has been implicated in a variety of diseases, particularly cell cycle control and cancer development. The MYT1 protein, a member of the Wee1 kinase family, is highly expressed in a variety of cancers and less expressed in most normal tissues. For example, abnormal expression of MYT1 is associated with breast cancer, gynecological cancers (including ovarian, endometrial, and cervical cancers), hepatocellular carcinoma, glioma, and neuroblastoma. In addition, MYT1 inhibition and CCNE1 amplification constitute a synthetic lethal effect, suggesting that it plays a key role in cell cycle regulation and provides a drug development strategy for the treatment of CCNE1-amplified tumors. In neurodevelopmental disorders, loss of function of MYT1L (a myT1-like protein) has been associated with intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorders, while duplication of MYT1L has been observed in patients with schizophrenia.
Bioapplications of MYT1
Due to its high expression in a variety of cancers, MYT1 is considered a potential target for cancer therapy, especially for tumors with CCNE1 amplification. Based on the potential of MYT1 as a therapeutic target, MYT1 inhibitors are being developed that may be effective in the treatment of breast cancer, gynecological cancer, etc. Variations in the gene MYT1L, which is related to MYT1, have been linked to neurodevelopmental disorders such as intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders, and schizophrenia, so MYT1L could serve as an important biomarker for studying these disorders. MYT1 can be used as a target for drug screening to discover new compounds or biomolecules using high-throughput screening methods. As an effective tool, develop more MYT1 antibody, etc.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Tiffany A Melhuish, 2018
Myelin transcription factor 1 (Myt1) and Myt1l (Myt1-like) are zinc finger transcription factors that regulate neuronal differentiation. Reduced Myt1l expression has been implicated in glioblastoma (GBM), and the related St18 was originally identified as a potential tumor suppressor for breast cancer. Researchers previously analyzed changes in gene expression in a human GBM cell line with re-expression of either Myt1 or Myt1l. This revealed largely overlapping gene expression changes, suggesting similar function in these cells. Here this study shows that re-expression of Myt1 or Myt1l reduces proliferation in two different GBM cell lines, activates gene expression programs associated with neuronal differentiation, and limits expression of proliferative and epithelial to mesenchymal transition gene-sets. Consistent with this, expression of both MYT1 and MYT1L is lower in more aggressive glioma sub-types. Examination of the gene expression changes in cells expressing Myt1 or Myt1l suggests that both repress expression of the YAP1 transcriptional coactivator, which functions primarily in the Hippo signaling pathway. Expression of YAP1 and its target genes is reduced in Myt-expressing cells, and there is an inverse correlation between YAP1 and MYT1/MYT1L expression in human brain cancer datasets.
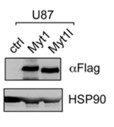
Fig1. Expression of Myt1 and Myt1l in U87 cells.
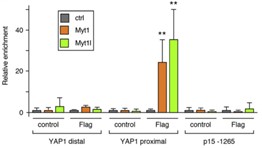
Fig2. Binding of Myt1 and Myt1l was analyzed by ChIP-qPCR.
Case Study 2: J P H Chow, 2013
Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) by phosphorylation is a key regulatory mechanism for both the unperturbed cell cycle and the DNA damage checkpoint. Although both WEE1 and MYT1 can phosphorylate CDK1, little is known about the contribution of MYT1. Researchers found that in contrast to WEE1, MYT1 was not important for the normal cell cycle or checkpoint activation. Time-lapse microscopy indicated that MYT1 did, however, have a rate-determining role during checkpoint recovery. The acceleration of checkpoint recovery in MYT1-depleted cells was due to a lowering of threshold for CDK1 activation. The kinase activity of MYT1 was high during checkpoint activation and reduced during checkpoint recovery. Importantly, although depletion of MYT1 alone did not affect long-term cell growth, it potentiated with DNA damage to inhibit cell growth in clonogenic survival and tumor xenograft models.
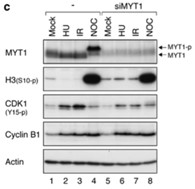
Fig3. MYT1 is not required for the activation of various checkpoints.
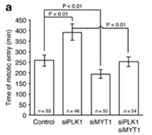
Fig4. Depletion of MYT1 accelerates entry into mitosis during checkpoint recovery.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MYT1-5868H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MYT1-3004H)
Involved Pathway
MYT1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MYT1 participated on our site, such as G1 to S cell cycle control,Integrated Breast Cancer Pathway,Integrated Pancreatic Cancer Pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MYT1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Integrated Breast Cancer Pathway | BACH1,RPP38,EDAR,DAG1,ANXA1,USP15,GRN,AHR,NAB1,NOXA1 |
| Integrated Pancreatic Cancer Pathway | GPRC5A,DAXX,JUND,FST,FKBP1B,NOXA1,AGA,MST1,LEFTY1,FKBP3 |
| G1 to S cell cycle control | E2F6,ATF6B,TFDP1B,CDKN1C |
Protein Function
MYT1 has several biochemical functions, for example, enhancer sequence-specific DNA binding,transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding,zinc ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MYT1 itself. We selected most functions MYT1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MYT1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| zinc ion binding | RNF220,ADAM18,C6AST3,PHF11,SIRT5,RNF152,ZSWIM2,PHEX,FHL1A,TRIM39 |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | ZFP382,PA2G4,ZNF773,PPARAA,FOXC1,GATA1A,ZNF480,ZFP746,RORAB,ZFP13 |
| enhancer sequence-specific DNA binding | ISL1,YY1,XBP1,GATA1,GATA4,TFAP2B,KLF7B,LMO4,TWIST1B,GATA5 |
Interacting Protein
MYT1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MYT1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MYT1.
CDK1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Martin, NG; McAndrew, PC; et al. Phosphorylation of cyclin dependent kinase 4 on tyrosine 17 is mediated by Src family kinases. FEBS JOURNAL 275:3099-3109(2008).
- Rohe, A; Erdmann, F; et al. In vitro and in silico studies on substrate recognition and acceptance of human PKMYT1, a Cdk1 inhibitory kinase. BIOORGANIC & MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS 22:1219-1223(2012).


