MR1
-
Official Full Name
major histocompatibility complex, class I-related -
Overview
Mediates B-cell proliferation in the absence of co-stimulus as well as IgE production in the presence of IL-4. Involved in immunoglobulin class switching. Release of soluble CD40L from platelets is partially regulated by GP IIb/IIIa, actin polymerization, and an matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) inhibitor-sensitive pathway. -
Synonyms
MR1;major histocompatibility complex, class I-related;HLALS, major histocompatibility complex, class I like sequence;major histocompatibility complex class I-related gene protein;Class I histocompatibility antigen like protein;HLALS;Major histocompatibility complex class I like sequence;Major histocompatibility complex class I related;Major histocompatibility complex class I related isoform CRA a;Major histocompatibility complex class I related isoform CRA c;Major histocompatibility complex class I related isoform CRA d;MHC class I like antigen MR 1;MHC class I like antigen MR1;MHC class I related protein 1 isoform B;MHC class I related protein 1 isoform C;MR 1;Mr1 protein;MR1B;MR1C;OTTHUMP00000033129;OTTHUMP00000033130;OTTHUMP00000033131;MHC class I-like antigen MR-1;MHC class I-related gene protein;MHC class-I related-gene protein;class I histocompatibility antigen-like
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- GST
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is MR1 Protein?
MR1 is a protein akin to MHC class I molecules but instead of attaching to peptide antigens like the traditional MHC class I, MR1 binds specifically to microbial metabolites, particularly those from the vitamin B2 synthesis pathway. It presents these small molecules to a unique subset of T cells called mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, activating them. MAIT cells are crucial in mucosal areas like the gut, where they help manage certain bacterial populations. MR1’s antigen presentation involves unique cellular routes through organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum and endosome-lysosome system. Beyond infection defense, MR1 plays a key role in immune responses and is linked to diseases like cancer and autoimmunity.What is the Function of MR1 Protein?
MR1's main job is to present microbial metabolites to MAIT cells. Unlike typical MHC class I, MR1 binds small molecule metabolites from microbial vitamin B2 synthesis instead of peptides. Once MR1 presents these metabolites, it activates MAIT cells, prompting them to release pro-inflammatory cytokines like IFN-γ and TNF-α and kill infected cells directly. Inside the cell, MR1 loads these metabolites at organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum and endosome-lysosome, moving them to the surface during infection. MR1 also plays a role in immune responses related to cancer and autoimmune diseases, potentially by presenting specific tumor antigens.MR1 Related Signaling Pathway
MR1 protein's signaling pathway involves presenting microbial metabolites to MAIT cells. Inside the cell, MR1 mainly binds with β2-microglobulin in the endoplasmic reticulum and uses molecules like tapasin or TAPBPR to load antigens. These metabolites, often intermediates in the vitamin B2 synthesis pathway like 5-OP-RU, form stable complexes with MR1. These complexes are then transported to the cell surface via the secretion pathway and recognized by MAIT cells. Activation of MAIT cells triggers immune responses, releasing cytokines such as IFN-γ and TNF-α, and directly kills infected cells. MR1 also helps regulate other MR1-restricted T cells, playing significant roles in diseases like cancer and autoimmunity.
Fig1. Illustration showing early endosomal Toll‐like receptor 9 (TLR9)‐dependent signalling in the control of MR1‐mediated bacterial antigen presentation in antigen‐presenting cells. (Jianyun Liu, 2017)
MR1 Related Diseases
MR1 protein is linked to various diseases, mainly impacting immune responses through its interaction with MAIT cells. In infectious diseases, MR1 helps in immune defense against bacterial infections by activating MAIT cells via microbial metabolite presentation, such as in tuberculosis. It's also connected to cancer, where MR1-restricted T cells might have a role in immune surveillance for different cancers. In autoimmune diseases, MR1 influences immune responses in conditions like multiple sclerosis. Additionally, MR1 impacts skin conditions like atopic dermatitis by regulating MAIT cell activity, affecting disease progression.Bioapplications of MR1
MR1 protein finds uses in research, industrial production, and clinical studies. In research, it helps us understand its role in the immune system, especially in activating MAIT cells. MR1 is also promising for cancer immunotherapy, as MR1-restricted T cells can recognize various cancer cells without being restricted by human leukocyte antigen (HLA), making them ideal for broad cancer treatment development. Industrially, the preparation of MR1-T cells can be standardized for clinical treatments, offering ready-made cell products. Clinically, MR1-T cell immunotherapy is being explored for cancer treatment, with its unique mechanism potentially reducing side effects like cytokine release syndrome. Moreover, MR1 research may open new avenues for vaccines and treatments for infectious diseases.Case Study
Case Study 1: Ashley CL. et al. Front Immunol. 2023
Researchers identified MR1’s role in presenting vitamin B2-related bacterial metabolites to MAIT cells. They examined changes in MR1 expression during human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infections while using an MR1 ligand. Utilizing methods like coimmunoprecipitation, mass spectrometry, and recombinant adenovirus, they studied whether HCMV proteins, such as gpUS9, affect MR1 levels. Tests with engineered Jurkat cells and primary MAIT cells assessed MR1's importance during HCMV infection. They confirmed MR1’s role by applying a neutralizing antibody and conducting CRISPR/Cas9 MR1 knockouts. The researchers found that HCMV infection decreases MR1 on cell surfaces and overall. The viral gpUS9 protein alone could achieve this reduction, and analysis of a US9 deletion mutant indicated multiple viral strategies targeting MR1. Functional assays confirmed HCMV's capacity to block MR1-dependent MAIT cell activation using both neutralizing antibodies and MR1 knockout approaches.-
 Fig1. Downregulation of total cellular MR1 protein by multiple strains of HCMV.
Fig1. Downregulation of total cellular MR1 protein by multiple strains of HCMV. -
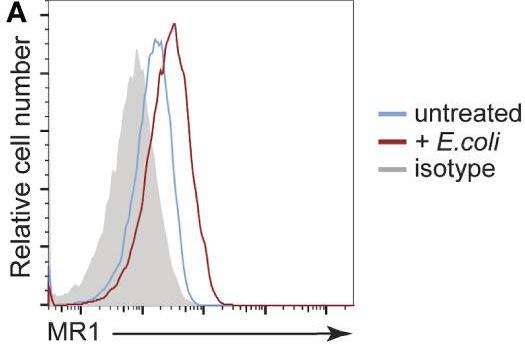 Fig2. Primary HFs were treated with 1000 CFU/cell of partially fixed E. coli or left untreated for 18 h before being stained for analysis of cell surface MRI by flow cytometry.
Fig2. Primary HFs were treated with 1000 CFU/cell of partially fixed E. coli or left untreated for 18 h before being stained for analysis of cell surface MRI by flow cytometry.
Case Study 2: Lim HJ. et al. J Cell Biol. 2022
Researchers found that MR1, a conserved immune detection system in mammals, grabs vitamin B-related antigens from different microbes to present them to MR1-restricted lymphocytes like MAIT cells. This process helps maintain balance through defense and tissue repair. However, the details of how MR1 is regulated on the cell surface were not clear. They discovered that human MR1 has a tyrosine-based motif in its cytoplasmic domain that binds with the AP2 complex, an endocytic adaptor protein. This interaction influences how quickly MR1 is internalized from the cell surface, reducing its recycling. They suggest that MR1 uses AP2 endocytosis to control how long it presents antigens to MAIT cells and how the immune system detects microbial metabolic signatures.-
 Fig3. Expression of mutant MR1 molecules in HeLa cells.
Fig3. Expression of mutant MR1 molecules in HeLa cells. -
 Fig4. C1R cells expressing MR1-WT, the MR1-CD1d-tail, or MR1-T316V were metabolically radiolabeled with 35S-methionine/cysteine.
Fig4. C1R cells expressing MR1-WT, the MR1-CD1d-tail, or MR1-T316V were metabolically radiolabeled with 35S-methionine/cysteine.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MR1-609HFL)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MR1-609HFL) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MR1-5529H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MR1-5529H)
Involved Pathway
MR1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MR1 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MR1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
-
 Fig1. The MR1 trafficking pathway and associated cellular machinery. (Hamish E G McWilliam, 2024)
Fig1. The MR1 trafficking pathway and associated cellular machinery. (Hamish E G McWilliam, 2024) -
 Fig2. Roles of iNKT cells and Th2 cells in the development of AHR and airway inflammation. (Chiaki Iwamura, 2018)
Fig2. Roles of iNKT cells and Th2 cells in the development of AHR and airway inflammation. (Chiaki Iwamura, 2018)
Protein Function
MR1 has several biochemical functions, for example, MHC class I receptor activity,peptide antigen binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MR1 itself. We selected most functions MR1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MR1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | HCK,AP1S2,CNEP1R1,MED23,AMDHD2,PDE9A,BCL2A1A,MTA2,NRBP1,PHB |
| peptide antigen binding | HLA-DPA1,MAML1,MHC1ZE,HLA-DQA1,HLA-B,CD209,MHC1UJA,HLA-DRA,MHC1ZFA,HLA-DRB5 |
| MHC class I receptor activity | CD160,KIR3DS1,KLRF1,LILRB1 |
Interacting Protein
MR1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MR1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MR1.
FATE1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Mariati; Koh, EYC; et al. Toward stable gene expression in CHO cells Preventing promoter silencing with core CpG island elements. BIOENGINEERED 5:340-345(2014).
- Mariati; Yeo, JHM; et al. Insertion of core CpG island element into human CMV promoter for enhancing recombinant protein expression stability in CHO cells. BIOTECHNOLOGY PROGRESS 30:523-534(2014).


