MDH2
-
Official Full Name
malate dehydrogenase 2, NAD (mitochondrial) -
Overview
Malate dehydrogenase (MDH) is a key enzyme in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and malate/aspartate shuttle. MDH is widely expressed in organisms from most bacteria to all eukaryotes. The cytoplasmic MDH isoenzyme (cMDH or MDH1) primarily reduces oxaloacetate -
Synonyms
MDH2;malate dehydrogenase 2, NAD (mitochondrial);malate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial;MDH;MOR1;M-MDH;MGC:3559
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Human
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
- GST
Background
What is MDH2 Protein?
MDH2, or Malate dehydrogenase 2, is an enzyme that's all about converting malate into oxaloacetate in your mitochondria, using NAD+ to NADH in the process. This reaction is a key player in the citric acid (TCA) cycle, vital for producing energy in cells. There are actually two main forms of this enzyme in eukaryotic cells: one in the mitochondria and another in the cytoplasm. These different forms help shuffle things around in cells, keeping processes running smoothly. The enzyme also ties into pathways like gluconeogenesis. In the grand scheme, MDH2 showcases a lot about how cells handle energy and metabolism.
What is the Function of MDH2 Protein?
MDH2, short for malate dehydrogenase 2, is crucial in our cells' energy production. It plays a vital role in the Krebs cycle by transforming malate into oxaloacetate and participates in the malate-aspartate shuttle, a kind of metabolic chain reaction. Beyond energy, this protein is connected to diseases like diabetes, where certain gene mutations can disrupt insulin action and release, leading to a type of familial high blood sugar. Additionally, MDH2 is linked to cancer, particularly in how cancer cells dodge cell death known as ferroptosis. So, MDH2 is not just about energy; it's deeply tied to our cells' core activities and can be at the heart of significant health problems when things go awry.
MDH2 Related Signaling Pathway
MDH2, short for malate dehydrogenase 2, plays a big role in the Krebs cycle, helping to shift malate into oxaloacetate, which is crucial for making cellular energy. But it's not just about metabolism; MDH2 also dives into signaling related to cell death and survival. Recent studies highlight its interaction with FSP1, a protein key in managing ferroptosis—cell death from too much lipid oxidation. By nudging the ubiquitination and breakdown of FSP1, MDH2 can tweak how sensitive a cell is to ferroptosis, which could be a game-changer for cancer therapy, especially in conditions like clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). This non-traditional role in cellular death suggests MDH2 is more than just an energy enzyme; it's involved in signaling that decides cell fate, making it a hot topic in medical research.
MDH2 Related Diseases
MDH2, short for malate dehydrogenase 2, isn't just about how our cells make energy; it's been tied to various health conditions too. In cancer, especially kidney cancer, MDH2 influences how cancer cells deal with ferroptosis, which is a type of cell death. Some mutations in MDH2 are linked to neurological issues, leading to early-onset severe brain diseases with symptoms like muscle weakness and epilepsy. When it comes to metabolic diseases, problems with MDH2 are connected to pediatric epileptic encephalopathy, marked by a unique biochemical profile. Plus, MDH2 might be a biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer, as studies show higher levels in patients' urine compared to healthy folks, hinting at its potential for early cancer detection. So, MDH2 is much more than an enzyme for energy; it's involved in diverse diseases, opening doors for new diagnostic and treatment methods.
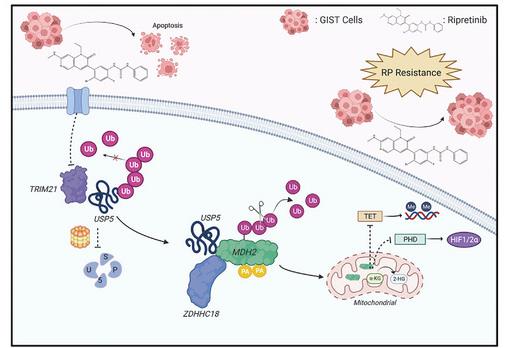
Fig1. Correlation between TRIM21, MDH2, and USP5 expression and relationship with progression-free survival of GISTs. (Haoyu Sun, 2024)
Bioapplications of MDH2
Recombinant MDH2 protein finds its way into various research and industrial applications. In scientific research, it's often used to explore metabolic pathways, particularly the Krebs cycle, since MDH2 is key in converting malate to oxaloacetate. This kind of work helps researchers understand energy metabolism in cells under different conditions, which is crucial for studying diseases related to metabolism. In biotechnology and industrial sectors, recombinant MDH2 can be part of processes that require tightly regulated energy cycles, and it's sometimes used to produce certain chemicals through engineered metabolic pathways. Additionally, it's a tool in drug development, particularly for targeting diseases where MDH2's role is disrupted. Through these applications, recombinant MDH2 is a valuable asset in advancing both basic and applied scientific knowledge.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Baijie Feng, 2024
Malate dehydrogenase 2 (MDH2) is pretty important in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Lately, studies are showing it's tied to different kinds of tumors, though we're still figuring out exactly how it all works. In kidney cancer, a notable drop in MDH2 levels was seen. Interestingly, while losing MDH2 slows down the growth of normal kidney cells, it boosts growth in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). It seems MDH2 helps curb ccRCC growth by promoting ferroptosis and making these cancer cells more responsive to ferroptosis inducers, which leads to more lipid peroxidation. We found that MDH2 affects FSP1 protein levels by influencing its ubiquitination, keeping ccRCC highly sensitive to ferroptosis. Overall, lower MDH2 in ccRCC increases FSP1 expression, reducing ferroptosis sensitivity, highlighting a non-metabolic role of MDH2 in the cancer's progression.
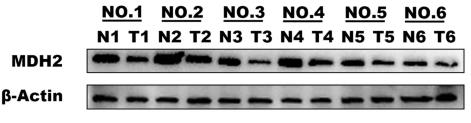
Fig1. The protein level of MDH2 and β-Actin in ccRCC and adjacent normal tissues.
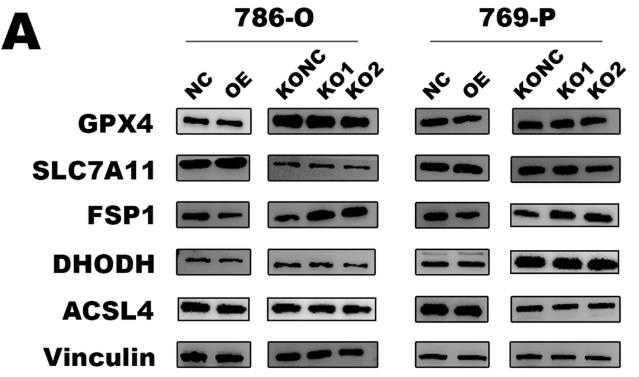
Fig2. Protein expression levels of in ferroptosis key factor in MDH2 overexpressing and knockout ccRCC cells.
Case Study 2: Wei-Tao Shi, 2024
Fusarium mycotoxins are a big worry since they pop up all over the world in food and the environment. We're talking about stuff like fusaric acid (FA), deoxynivalenol (DON), zearalenone (ZEA), T-2 toxin, and fumonisin B1 (FB1) that can mess with our health big time. FA can team up with other toxins to amplify the harm, though we don't fully get how it works. In our research, using CRISPR, we found that genes like MDH2 and PDHB are crucial for the cell death caused by FA. The TCA cycle and other pathways tied to mitochondria play a major role in how toxic FA can be. By knocking out MDH2, we saw a drop in cell death, ROS build-up, and specific protein expressions linked to toxicity. Plus, using an MDH2 inhibitor, LW6, lessened the harm from other toxins like DON and ZEA.
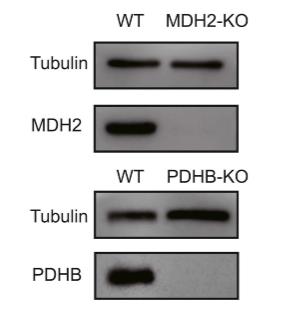
Fig3. Western blotting verification of sgRNA-mediated depletion of MDH2 and PDHB in WT cells.

Fig4. WT, MDH2-KO, and PDHB-KO cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of FA for 24 h, and intracellular ROS levels were detected by flow cytometry.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MDH2-2010H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MDH2-4499H)
Involved Pathway
MDH2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MDH2 participated on our site, such as Citrate cycle (TCA cycle),Cysteine and methionine metabolism,Pyruvate metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MDH2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | BCAT1,CBSB,CTH,BHMT,GOT2B,TST,IL4I1,DNMT1,APIP,MAT2AL |
| Pyruvate metabolism | GRHPR,PDHA1A,LDHA,GRHPRB,ACSS2,ACACA,ACSS2L,LDHB,ACOT12,MDH1 |
| Carbon metabolism | ESD,FBP2,ACO2,HADHA,GAPDH,PGK2,IDH3A,PSPH,GLUD1A,GPT2 |
| Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | GRHPRA,ACAT1,GLDC,AGXTA,GLULB,GLULA,GLULC,ACO1,GRHPR,GCSHA |
| Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) | SDHA,IDH3G,ACO1,DLDH,PDHA2,SDHDA,CS,SDHC,ACLYA,DLAT |
| Metabolic pathways | PGM1,ADH2-2,PDHA1A,GCSHB,HMGCLL1,TKT,AMY2A2,ATP6V0A1B,COX6B2,GK2 |
Protein Function
MDH2 has several biochemical functions, for example, L-malate dehydrogenase activity,malate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity,poly(A) RNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MDH2 itself. We selected most functions MDH2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MDH2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein self-association | CTSB,ADAM8,ACVR2A,TNFAIP3,PTH1R,NKX3-1,CCL5,PROSAPIP1,TRP53,RSAD2 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | PELP1,RPS5,HIST2H4A,GTF2F1,PSPC1,COX4I2,SAMD4,FUBP1,RPS3A,DDX6 |
| L-malate dehydrogenase activity | MDH1AA,MDH1 |
Interacting Protein
MDH2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MDH2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MDH2.
VCAM1;PCNA;FHIT;WARS;ere_dna;MAPK13;GABARAP;FN1;NS;ATF2;GABARAPL2;GABARAPL1;MAP1LC3A
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


