MAPK1
-
Official Full Name
mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. The activation of this kinase requires its phosphorylation by upstream kinases. Upon activation, this kinase translocates to the nucleus of the stimulated cells, where it phosphorylates nuclear targets. One study also suggests that this protein acts as a transcriptional repressor independent of its kinase activity. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein, but differing in the UTRs, have been reported for this gene. -
Synonyms
ERK;p38;p40;p41;ERK2;ERT1;ERK-2;MAPK2;PRKM1;PRKM2;P42MAPK;p41mapk;p42-MAPK;MAPK1;mitogen-activated protein kinase 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is MAPK1 protein?
MAPK1 gene (mitogen-activated protein kinase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 22 at locus 22q11. This gene encodes a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. The activation of this kinase requires its phosphorylation by upstream kinases. Upon activation, this kinase translocates to the nucleus of the stimulated cells, where it phosphorylates nuclear targets. The MAPK1 protein is consisted of 360 amino acids and MAPK1 molecular weight is approximately 41.4 kDa.
What is the function of MAPK1 protein?
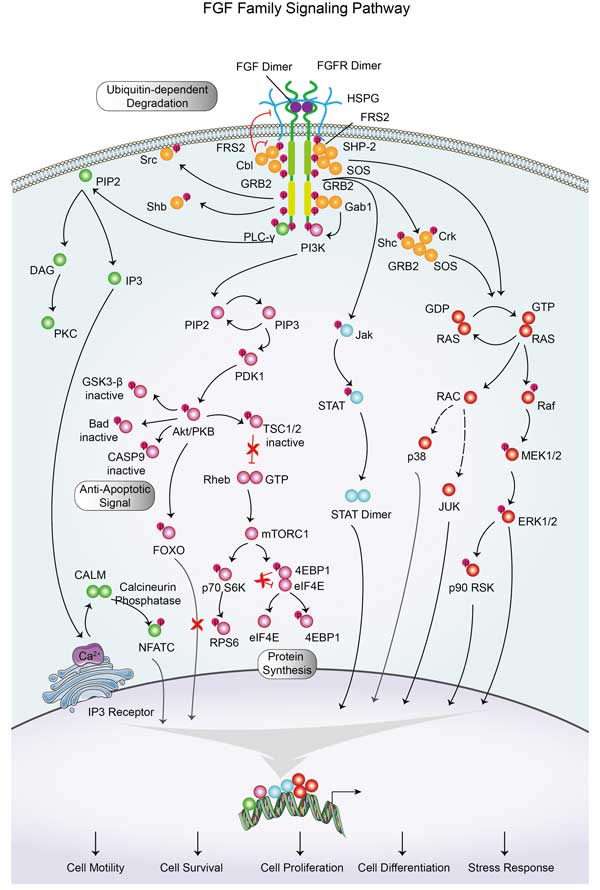
MAPK1, also known as ERK2, is a serine/threonine kinase that is a crucial component of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal transduction pathway. This pathway is involved in transmitting extracellular signals to cellular responses. MAPK1, along with MAPK3/ERK1, plays a significant role in the MAPK/ERK cascade, which is important for various biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival, and differentiation. These processes are mediated through the regulation of transcription, translation, and cytoskeletal rearrangements. The MAPK/ERK cascade also participates in the initiation and regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells by phosphorylating numerous transcription factors, leading to about 160 substrates being discovered for ERKs, including transcription factors, cytoskeletal elements, regulators of apoptosis, and other signaling-related molecules.
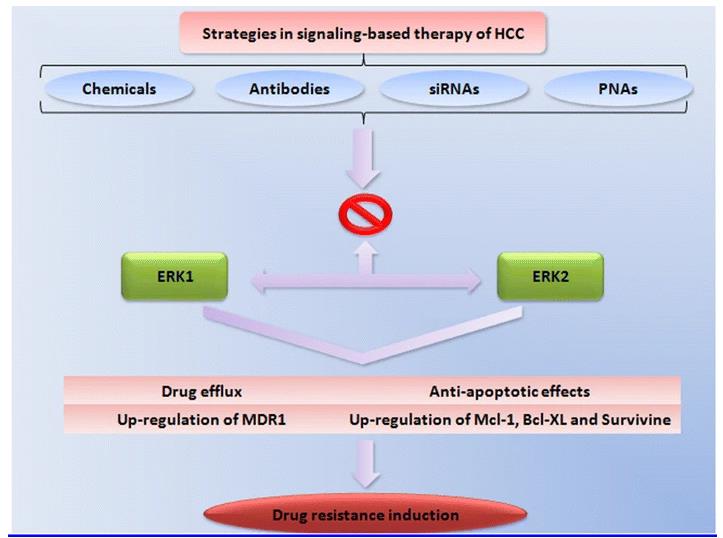
Fig1. There are nearly 200 substrates for ERK1/2 which mediate drug resistance through several mechanisms including drug efflux, drug inactivation, cell death inhibition and drug targeted alteration. (Amir Mehdizadeh, 2016)
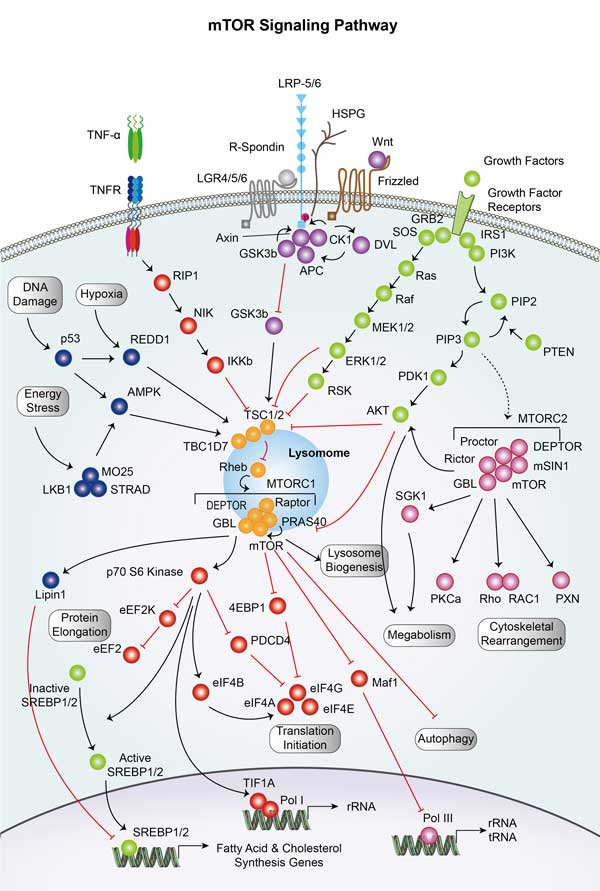
MAPK1 related signaling pathway
MAPK1 is a crucial component of the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. This pathway plays a significant role in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Upon activation by extracellular stimuli such as growth factors, hormones, or cytokines, MAPK1 becomes phosphorylated and activated through a series of kinase phosphorylation events. Once activated, MAPK1 translocates to the nucleus where it phosphorylates various transcription factors, leading to changes in gene expression that drive cellular responses. Dysregulation of the MAPK1 signaling pathway is implicated in numerous diseases, including cancer, where it often promotes uncontrolled cell growth and survival.
MAPK1 related diseases
MAPK1 is a critical component of the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Dysregulation of this pathway is implicated in various diseases, particularly cancers such as melanoma, colorectal cancer, and pancreatic cancer, where it promotes cell proliferation and survival. Additionally, mutations or overexpression of MAPK1 can lead to other disorders, including neurological conditions like certain types of epilepsy and cardiovascular diseases such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. These associations underscore the importance of tightly regulating MAPK1 activity for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing disease progression.
Bioapplications of MAPK1
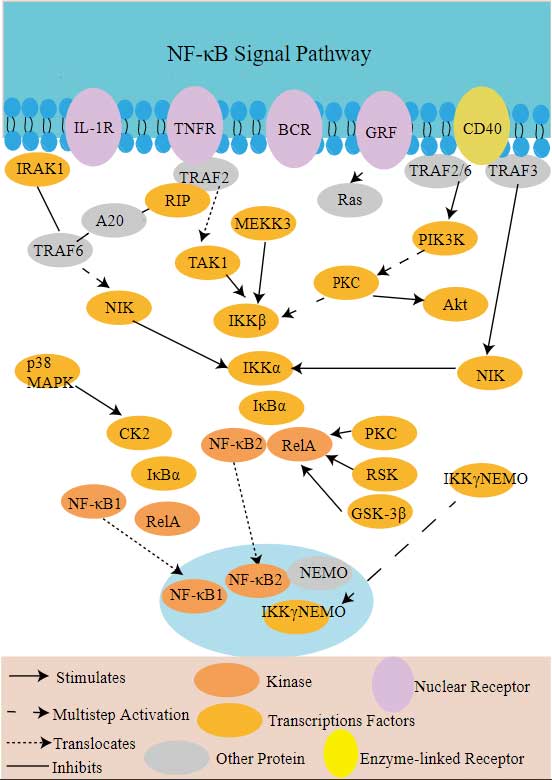
The bioapplications of MAPK1, also known as ERK2, are primarily in the field of cancer research and therapy. MAPK1 is a key enzyme in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which is involved in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and migration. This pathway is often dysregulated in cancer, making it a significant target for cancer treatments. Inhibitors of the MAPK pathway, including those that target MAPK1, have been developed to treat various types of cancer. Moreover, the MAPK pathway plays a crucial role in innate immunity, and MAPK1 is involved in the regulation of immune responses. It has been implicated in the activation of immune cells and the production of inflammatory cytokines.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jan Rasl, 2022
The ERK signaling pathway, comprising Raf, MEK, and ERK1/2 kinases, regulates key cellular functions such as proliferation and migration. This study examined the effects of low-level ERK2 overexpression in MDCK epithelial cells, revealing that it diminished cell-cell adhesion and prevented the formation of a cuboidal shape, resulting in flatter, more spread-out cells with adhesion only on their basal side. While ERK2 overexpression did not significantly alter the phosphorylation of downstream targets or increase the expression of the pro-migratory factor Fra1, it did enhance cell scattering in response to HGF/SF. These findings suggest that increased ERK2 expression weakens intercellular cohesion, facilitating the transition from multicellular structures to individual migrating cells. Clinically, higher ERK2 levels in pancreatic adenocarcinoma are associated with poorer outcomes, highlighting its potential role in cancer progression.
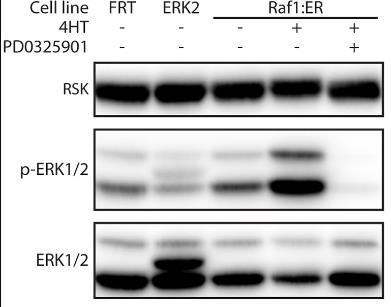
Fig1. Western blot analysis of the phospho-ERK level in FRT-, ERK2- and Raf1:ER MDCK.
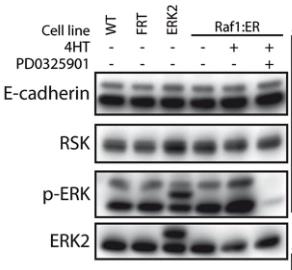
Fig2. E-cadherin expression in WT-, FRT-, ERK2- and Raf1:ER MDCK cells.
Case Study 2: Xin Yang, 2022
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), such as GK intronic transcript 1 (GK-IT1), play a role in cancer development and spread, particularly in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Our analysis of ESCC data from The Cancer Genome Atlas and quantitative PCR on clinical samples revealed that GK-IT1 is overexpressed in ESCC and linked to later clinical stages, indicating it as a prognostic marker. Functional assays showed that GK-IT1 boosts ESCC cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and inhibits apoptosis and autophagy. In vivo tumorigenesis experiments in nude mice confirmed GK-IT1's role in promoting tumor growth and metastasis. Mechanism-wise, GK-IT1 binds to MAPK1, hindering its interaction with DUSP6 and regulating MAPK1 phosphorylation, which in turn fuels ESCC progression.
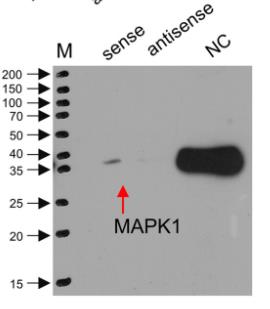
Fig3. Western blotting of MAPK1 following pulldown of GK-IT1 or negative RNA control.
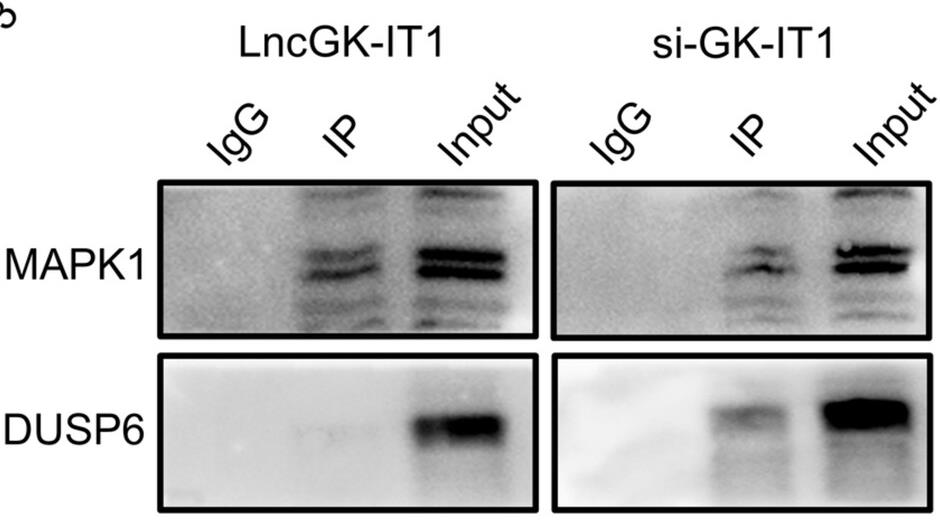
Fig4. Co-IP assay showed that DUSP6 could not be pulled down by anti-MAPK1 in TE-10 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MAPK1-101HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MAPK1-048H)
Involved Pathway
MAPK1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MAPK1 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,ErbB signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MAPK1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | PIK3CD,WNT2B,PIK3CG,FGFR4,SMAD2,ID2,WNT2,SOX2,ESRRB,SMAD4 |
| Type II diabetes mellitus | PIK3CB,IRS1,IKBKB,INS-IGF2,PDX1,HK3,SLC2A2,INS2,ADIPOQ,MAPK10 |
| Thyroid cancer | TP53,LEF1,MAP2K1,MAP2K2,TFG,PAX8,NRAS,TRP53,CCND1,CCDC6 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | STAT5A,EIF4EBP1,HRAS,IKBKB,CEBPA,BRAF,STAT5B,PIK3R2,MYC,CCND1 |
| Prolactin signaling pathway | SOCS6,PIK3R3,INS1,NEK3,FOS,SOCS5,LHB,MAPK12,MAPK8,CSN2 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | NR4A1,PPM1B,MKNK1,MAP3K14,NFKB2,NTRK2,JIP1,FGF5,FGF6A,TAOK3 |
| Hepatitis B | PIK3CB,FOS,CASP8,NFKB1,TRP53,IFNA7,MAP3K1,BAX,PIK3R5,CXCL8 |
| Pancreatic cancer | TGFB3,MAPK9,TRP53,SMAD2,PLD1,PIK3R3,AKT2,RALBP1,RALGDS,TGFB2 |
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | GNAS,CACNA2D2,GNAO1,NFATC4,NFATC1,PLCB2,FOS,NPR1,CACNG7,PPP3CB |
Protein Function
MAPK1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,DNA binding,MAP kinase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MAPK1 itself. We selected most functions MAPK1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MAPK1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | HSPE1,MYHC4,NLRC5,RUNX3,NLRC4,ACSL3,ILF2,UBA2,TBK1,CDC34 |
| phosphatase binding | CTSC,PPP1R21,TSC2,PPP1R26,DZIP3,PPARA,SYTL2,SPRED1,CRY1,PPP1R36 |
| RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain kinase activity | CDK12,CDK7,CDK9,CDK13,CDK1,CDK8,CCNK |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | HIPK4,PRKD2,BSK146,CSNK1DA,NEK8,PLK3,IRAK1,MAP3K8,TAOK1,MAP3K10 |
| transcription factor binding | TRIM6,MAPK9,PPP1R13L,FHL2,SMARCD3,PIAS1,EPAS1,NBN,HDAC3,MED25 |
| mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding | MAP4K2,CDC42,MAP2K1,TRAF6,TRAF2,MAP3K11,PPEF2,MARVELD3,CDC37,STK38 |
| DNA binding | KDM5B,TRIM16,ZFP184,HIST2H3C,C17orf49,TLX3B,JUNBB,TAF1D,PQBP1,PTF1A |
| phosphotyrosine binding | SHC1,MAPK3,GRB2,LDLRAP1,ACP2,CBLB,CBLC,PTPN3,ZAP70,FGR |
| protein binding | RAB5C,SIK2,LGALS9C,ACTR6,EVI5L,HSPD1,RAD51L3,ANO2,PRH2,IPO13 |
Interacting Protein
MAPK1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MAPK1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MAPK1.
PTPN7;RPS6KA3;DUSP1;MAPK14
MAPK1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Liszka, L; et al. DUCTAL ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE PANCREAS USUALLY RETAINED SMAD4 AND p53 PROTEIN STATUS AS WELL AS EXPRESSION OF EPITHELIAL-TO-MESENCHYMAL TRANSITION MARKERS AND CELL CYCLE REGULATORS AT THE STAGE OF LIVER METASTASIS. POLISH JOURNAL OF PATHOLOGY 65:100-112(2014).
- Reverchon, M; Bertoldo, MJ; et al. CHEMERIN (RARRES2) Decreases In Vitro Granulosa Cell Steroidogenesis and Blocks Oocyte Meiotic Progression in Bovine Species. BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 90:-(2014).