LMNA
-
Official Full Name
Lamin A/C -
Overview
Lamin A/C also known as LMNA is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNA gene.[1][2] Lamin A/C belongs to the lamin family of proteins. -
Synonyms
LMNA;lamin A/C;cardiomyopathy, dilated 1A (autosomal dominant) , CMD1A,lamin A/C like 1 , LGMD1B,limb girdle muscular dystrophy 1B (autosomal dominant) , LMN1, LMNL1, PRO1,progeria 1 (Hutchinson Gilford type);prelamin-A/C;HGPS;70 kDa Lamin;Cardiomyopathy dilated 1A (autosomal dominant);CDCD1;CDDC;Charcot Marie Tooth Disease Axonal Type 2B1;CMD1A;CMT2B1;EMD2;FPL;FPLD;HGPS;IDC;Lamin A/C;Lamin A/C Isoform 1 Precursor;Lamin A/C Isoform 2;Lamin A/C Isoform 3;Lamin-A/C;LDP1;LFP;LGMD1B;Limb girdle muscular dystrophy 1B (autosomal dominant);LMN 1;LMN A;LMN C;LMN1;LMNA;LMNA_HUMAN;LMNC;NY REN 32 antigen;PRO1;Progeria 1 (Hutchinson Gilford Type);Renal carcinoma antigen NY REN 32;Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-32;Renal carcinoma antigen NYREN32;lamin-A/C;70 kDa lamin;lamin A/C-like 1;OTTHUMP00000015843;OTTHUMP00000015845;OTTHUMP00000015846;OTTHUMP00000015847;OTTHUMP00000015848;OTTHUMP00000217835;renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-32;FPL;IDC;LFP;CDDC;EMD2;FPLD;LDP1;LMN1;LMNC;PRO1;CDCD1;CMD1A;FPLD2;LMNL1;CMT2B1;LGMD1B
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is LMNA Protein?
LMNA protein, also called lamin A/C, is part of the nuclear lamina found inside cell nuclei. It helps keep the nucleus sturdy and is key in organizing DNA and managing gene expression. When there are changes or mutations in the LMNA gene, this can lead to various health issues like muscular dystrophy and premature aging disorders. Moreover, LMNA proteins assist in DNA repair and play a part in the cell's response to mechanical stress, influencing how cells age and perform.What is the Function of LMNA Protein?
The LMNA protein, known as lamin A/C, mainly supports the nucleus of a cell, ensuring it maintains its shape and integrity. It organizes the DNA and regulates genes, helping cells function properly. During cell division, LMNA breaks down and reassembles, aiding the process. If there's a mutation in the LMNA gene, it can lead to disorders such as muscular dystrophy or premature aging. Additionally, LMNA is involved in how cells respond to physical forces and repair DNA, playing a role in how cells age and adapt to stress.LMNA Related Signaling Pathway
LMNA proteins are involved in various signaling pathways, particularly those affecting cellular structure and stress responses. They play a role in nuclear integrity, impacting pathways associated with cell division and DNA repair. In diseases such as muscular dystrophy and cardiomyopathy, mutations in LMNA affect cellular mechanics and stress signaling pathways. This can lead to issues in how cells handle strain and repair, contributing to disease progression. Overall, LMNA is crucial in maintaining the balance in cellular responses to physical and genetic stressors.LMNA Related Diseases
Mutations in the LMNA gene can lead to numerous conditions, often termed laminopathies. Among these are Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, impacting nerves, and Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, which affects both skeletal and heart muscles. Familial partial lipodystrophy changes how body fat is distributed, while Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome results in accelerated aging. The gene is also linked to congenital muscular dystrophy and mandibuloacral dysplasia, affecting muscles, bones, and fat. Heart-related conditions include arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy and familial dilated cardiomyopathy. These conditions arise from disruptions in nuclear envelope stability, impacting cells, especially in muscles and fat tissues.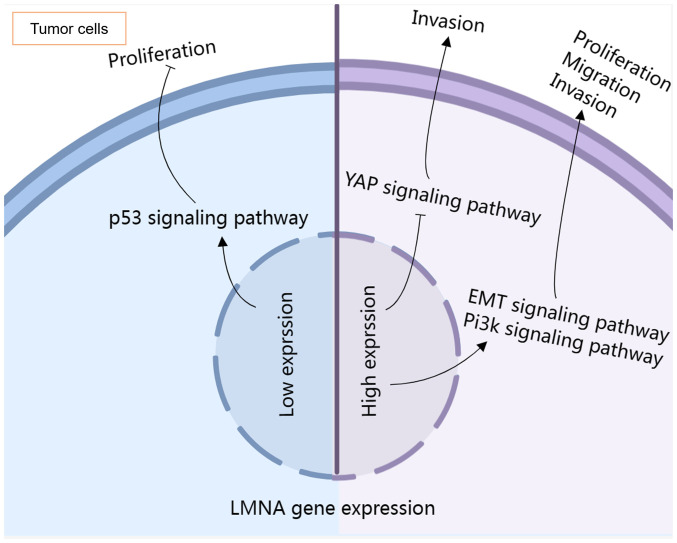
Fig1. Effects of LMNA expression levels on common signaling pathways in tumor cells. (Jiumei Zhao, 2024)
Bioapplications of LMNA
LMNA, encoding lamin A/C, is crucial in various biomedical applications due to its role in nuclear structure and integrity. It's significant in diagnosing and understanding several disorders, known as laminopathies, like muscular dystrophies, cardiomyopathies, and progeria. LMNA's involvement in DNA repair and cell stress responses makes it a target for treatments in aging and muscle-wasting conditions. Research into LMNA aids in developing gene therapies and understanding the pathology of diseases linked to nuclear envelope defects, ultimately helping design drugs that target these pathways.Case Study
Case Study 1: Ghosh S. et al. Nat Commun. 2024
Cancer changes the nucleus of cells, including critical tumor supporters called CAFs. When skin fibroblasts lose the androgen receptor (AR), their nuclear structure alters, sparking CAF traits without aging the cells. Bringing AR back reverses these changes. Normally, AR connects lamin A/C and PPP1 proteins. Without it, lamin A/C shifts and gets more phosphorylation at Ser 301, a CAF feature. This altered lamin A/C hits genes that make fibroblasts become tumor-promoting CAFs.-
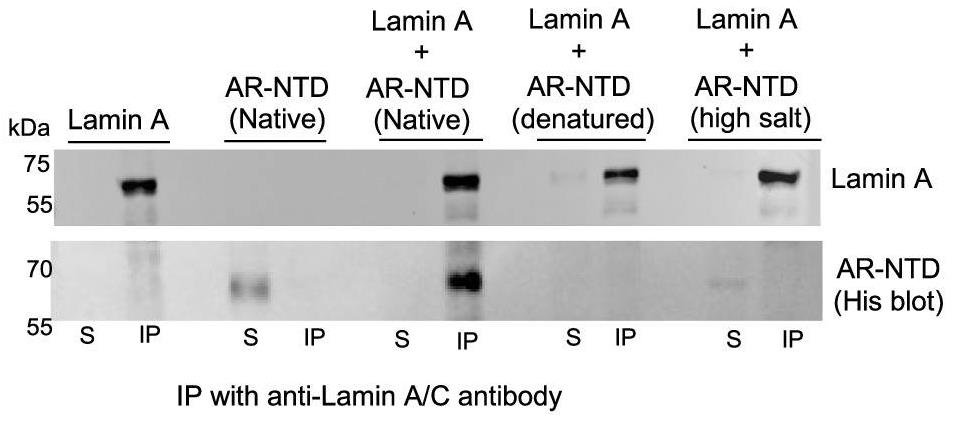 Fig1. In vitro interaction assay of AR and lamin A.
Fig1. In vitro interaction assay of AR and lamin A. -
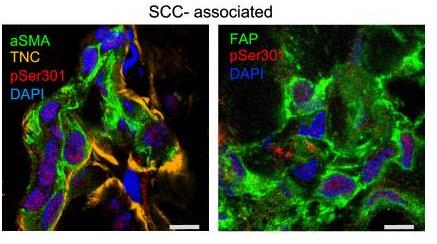 Fig2. IF analysis of skin SCC-associated fibroblasts with antibodies against pSer301 lamin A/C.
Fig2. IF analysis of skin SCC-associated fibroblasts with antibodies against pSer301 lamin A/C.
Case Study 2: Yin Q. et al. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2023
In idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), the lungs become stiff due to excess myofibroblasts and matrix material. Lamins help convey signals to the nucleus. Researchers identified a new lamin A/C variant that's more abundant in IPF. This variant appears when the matrix is stiff and impacts cell growth, aging, and transformation. In IPF lungs, they noticed wrinkled nuclei, linking back to lamin-related effects.-
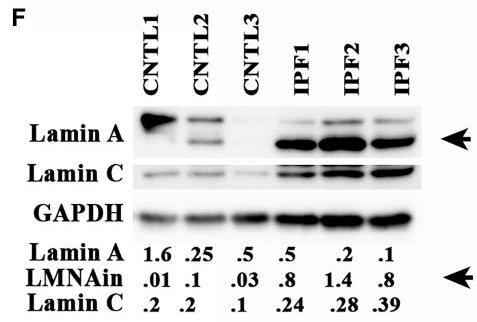 Fig3. The lamin protein isoform was highly expressed in fibroblasts isolated from IPF lung compared with control lung fibroblasts.
Fig3. The lamin protein isoform was highly expressed in fibroblasts isolated from IPF lung compared with control lung fibroblasts. -
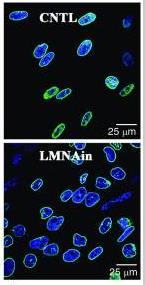 Fig4. Nuclear morphology changes in LMNAin-transduced fibroblasts.
Fig4. Nuclear morphology changes in LMNAin-transduced fibroblasts.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LMNA-267H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LMNA-267H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LMNA-25HFL)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LMNA-25HFL)
Involved Pathway
LMNA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LMNA participated on our site, such as Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM),Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC),Dilated cardiomyopathy, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LMNA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) | ACTN3,ITGB8,DES,SGCB,ATP2A2,DSG2,SGCG,EMD,DSC2,Itga10&Itgb1 |
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) | CACNG6,PRKAA1,ITGB7,SLC8A1,TGFB1,PRKAG2,ITGA6,RYR2,MYBPC3,PRKAB2 |
| Dilated cardiomyopathy | ITGA1,CACNB3,ITGB1,ITGB6,MYL2,Adcy4,CACNB2,CACNA2D1,Itga10&Itgb1,CACNG1 |
-
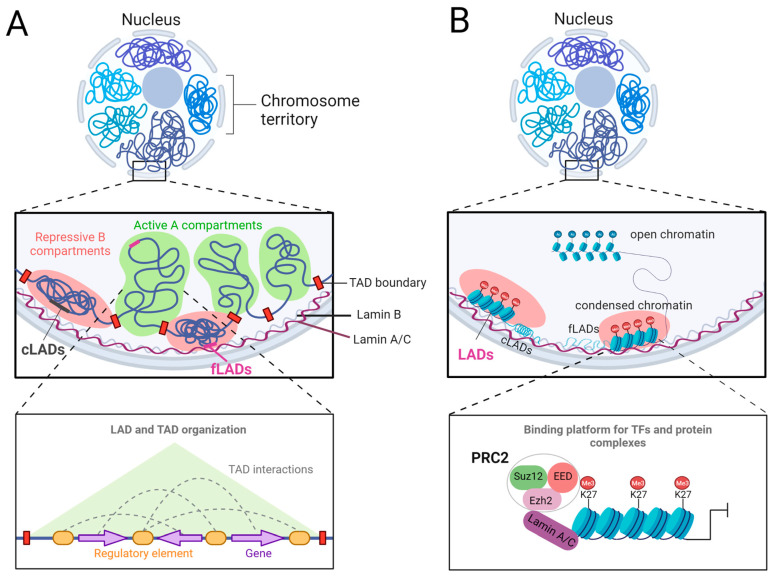 Fig1. Lamin-A/C-mediated chromatin organization. (Yinuo Wang, 2023)
Fig1. Lamin-A/C-mediated chromatin organization. (Yinuo Wang, 2023) -
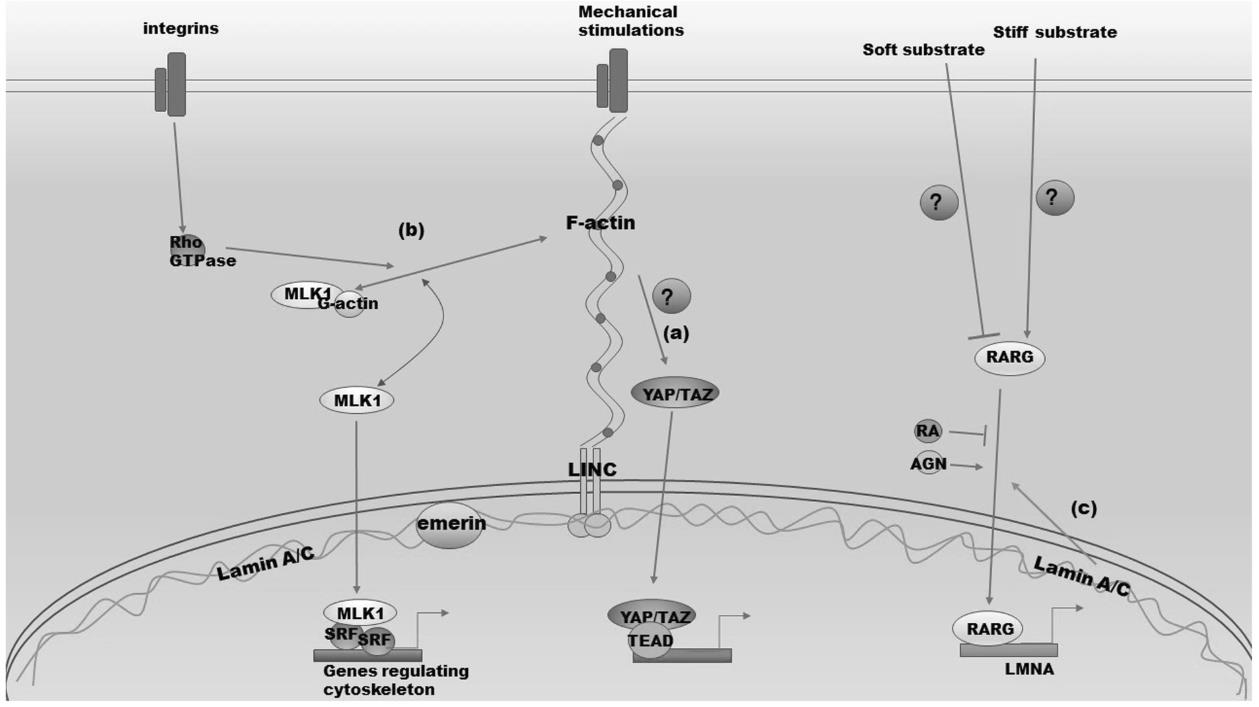 Fig2. Crosstalk between lamin A/C and other mechanosensitive signaling pathways. (Bo Zhang, 2019)
Fig2. Crosstalk between lamin A/C and other mechanosensitive signaling pathways. (Bo Zhang, 2019)
Protein Function
LMNA has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,structural molecule activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LMNA itself. We selected most functions LMNA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LMNA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| structural molecule activity | PGM5,SPRR2H,CLDNK,MAP7D1,MAP7D2A,SEPT4,CLDN18,CLDN20,PNN,KRTAP3-2 |
| protein binding | NACC2,CBFA2T3,SYCE2,FZD8,MAPK8,NXT1,ASS1,CDK4,PEX1,SPAG5 |
Interacting Protein
LMNA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LMNA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LMNA.
H2AFX;SUN2;KRTAP10-7;YWHAZ;DUSP13;MYC
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Quarta, G; Syrris, P; et al. Mutations in the Lamin A/C gene mimic arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. EUROPEAN HEART JOURNAL 33:1128-U49(2012).
- Chen, SC; Kennedy, BK; et al. Phosphorylation of connexin43 on S279/282 may contribute to laminopathy-associated conduction defects. EXPERIMENTAL CELL RESEARCH 319:888-896(2013).


