ITGB3
-
Official Full Name
integrin, beta 3 (platelet glycoprotein IIIa, antigen CD61) -
Overview
The ITGB3 protein product is the integrin beta chain beta 3. Integrins are integral cell-surface proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. A given chain may combine with multiple partners resulting in different integrins. Integrin beta 3 is found along with the alpha IIb chain in platelets. Integrins are known to participate in cell adhesion as well as cell-surface mediated signalling. -
Synonyms
GT;CD61;GP3A;BDPLT2;GPIIIa;integrin beta-3;platelet glycoprotein IIIa;platelet membrane glycoprotein IIIa;CD41;CD41b;GP 2B;GP IIb;GTA;HPA3;Integrin alpha 2b;ITGA2B;ITGB3;Tadocizumab;339086-80-5
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Mus musculus
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Plasma
- Human Cells
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- S
- Non
- Flag
- Strep
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is ITGB3 protein?
ITGB3 gene (integrin subunit beta 3) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q21. The ITGB3 protein product is the integrin beta chain beta 3. Integrins are integral cell-surface proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. A given chain may combine with multiple partners resulting in different integrins. Integrin beta 3 is found along with the alpha IIb chain in platelets. Integrins are known to participate in cell adhesion as well as cell-surface mediated signalling. The ITGB3 protein is consisted of 788 amino acids and ITGB3 molecular weight is approximately 87.1 kDa.
What is the function of ITGB3 protein?
ITGB3 protein is a glycoprotein on the cell surface and is a member of the integrin family. It plays an important role in a variety of biological processes, including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and signaling. In disease states, ITGB3 plays a key role in tumor development, including promoting tumor angiogenesis, influencing metabolic reprogramming of tumor cells, regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT), maintaining tumor stem cell properties, and participating in the formation of drug resistance. In addition, ITGB3 is also involved in intercellular communication in the tumor microenvironment, affecting the interaction between tumors and stromal cells and immune cells.
ITGB3 related signaling pathway
ITGB3 proteins play a role in a variety of signaling pathways, especially in the tumor microenvironment. It is involved in the regulation of tumor metabolic reprogramming, epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT), maintenance of stem cell properties, acquisition of drug resistance, promotion of angiogenesis, remodeling of tumor matrix and immune microenvironment. ITGB3 interacts with extracellular matrix (ECM) to activate a variety of downstream signaling pathways, including FAK/PI3K/AKT, MEK/ERK, YAP/TAZ, KRAS/RalB/NF-κB, etc., affecting the behavior and microenvironment of tumor cells. In addition, ITGB3 is also involved in interactions with the innate and adaptive immune systems in the tumor immune microenvironment, which may function differently on immune regulation in different situations.
ITGB3 related diseases
ITGB3 (integrin β3 subunit) is associated with a variety of diseases, especially in the development of tumors. ITGB3 is associated with poor prognosis and reduced survival in a variety of cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and glioma. In addition, ITGB3 has been implicated in platelet-related disorders such as Glanzmann thrombopenia, a hemorrhagic disorder caused by deficiency or dysfunction of platelet integrin αIIbβ3. In the tumor immune microenvironment, the role of ITGB3 may vary by tumor type and may promote the formation of an immunosuppressive environment in solid tumors, while it may promote the activation of natural killer cells and Th1 cells in hematologic tumors, thereby enhancing anti-tumor effects.
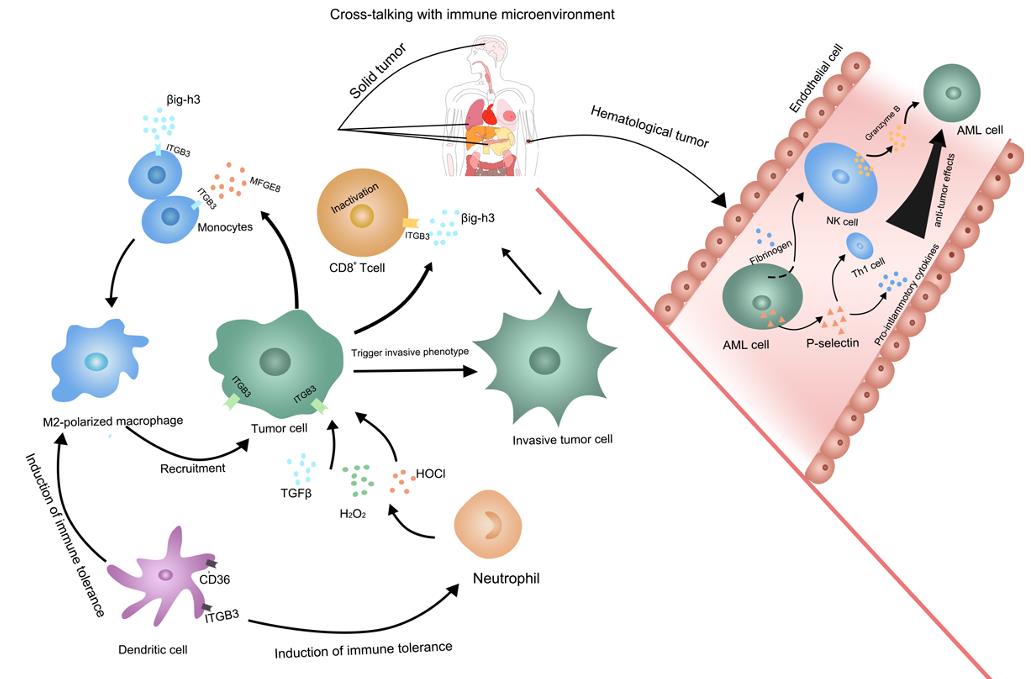
Fig1. The multiple functions of ITGB3 in tumor immune microenvironment. (Chen Zhu, 2019)
Bioapplications of ITGB3
ITGB3 has a wide range of applications in the biomedical field, especially in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. It plays a key role in the development of many cancers, such as breast, lung, colorectal, etc., and is often used as a drug target or biomarker. For example, by inhibiting the activity of ITGB3 or using it as a drug target, the effect of anti-tumor drugs can be enhanced. Other studies have shown that miRNA-30b can regulate the expression of ITGB3 and promote the apoptosis of breast cancer cells. In diseases such as thrombocytopathenia, mutations in the ITGB3 gene are also associated with the occurrence of the disease. Therefore, ITGB3 is an attractive target in treatment strategies for the disease, and therapeutic strategies targeting ITGB3 may provide new avenues for cancer treatment and other related diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Pedro Fuentes, 2020
Metastasis, responsible for most cancer-related fatalities, involves the dispersion of cancer cells to remote body sites. While ITGB3's contribution to breast cancer metastasis is recognized, the specific mechanisms were unclear. Recent findings reveal ITGB3's critical role in vesicle uptake, facilitated by its engagement with heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) and integrin endocytosis, which promote the internalization of extracellular vesicles. Additionally, ITGB3's function is pivotally linked to the activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK), essential for vesicle endocytosis.
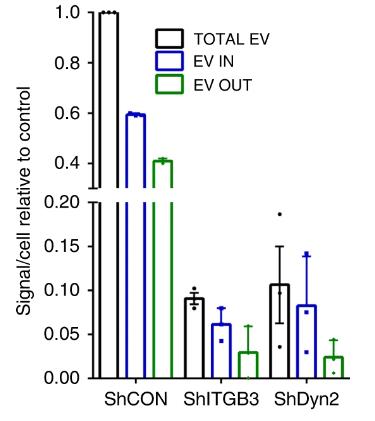
Fig1. Analysis of EV internalization in MDA.MB.231 shCON, shITGB3 and shDyn2 cells after 3D reconstruction.
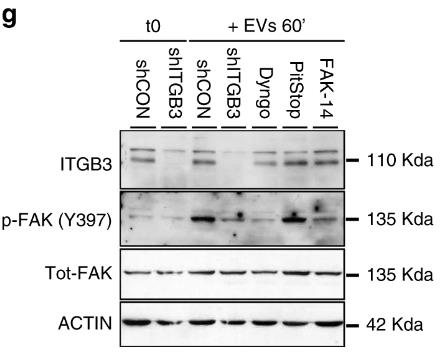
Fig2. Representative immunoblot analysis of the autophosphorylation of FAK at Y397 as readout for its kinase activity.
Case Study 2: Yunlong Lei, 2011
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a leading global cancer, with many patients presenting with metastatic disease and a grim prognosis. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are key drivers of CRC metastasis, with higher ROS levels in metastatic CRC cells (SW620) than in primary tumor cells (SW480). The study used proteomics to identify 63 proteins with altered expression in SW620 versus SW480 cells, highlighting the role of redox-regulatory and ROS-responsive proteins in CRC metastasis. Notably, increased ROS led to upregulation of ITGB3 in SW480 cells, enhancing their aggressiveness, while ITGB3 knockdown reduced the invasiveness of SW620 cells. This effect was mediated by the integrin αvβ3 heterodimer and involved the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway, implicating ITGB3 and STMN1 in ROS-induced CRC cell migration and invasion.
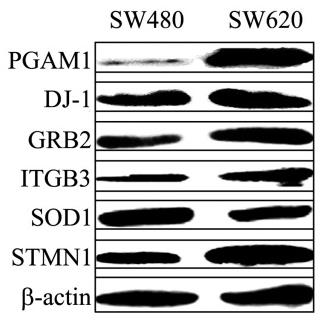
Fig3. The relative expression of PGAM1, GRB2, DJ-1, ITGB3, SOD1, and STMN1 in SW480 and SW620 cells.
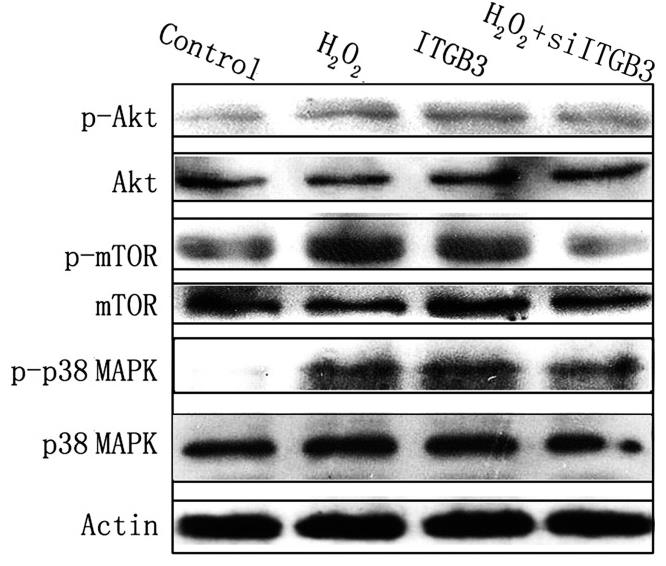
Fig4. Akt-mTOR and p38 MAPK signaling pathways are involved in ROS-ITGB3-induced migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ITGB3-16H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ITGB3-3269H)
Involved Pathway
ITGB3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ITGB3 participated on our site, such as Rap signaling pathway,Phagosome,PIK-Akt signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ITGB3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) | TNF,ITGB8,TGFB2,MYBPC3,PRKAA2,ITGAV,MYL2,TGFB1,CACNG6,IGF1 |
| Phagosome | ABCB3L1,Cd209g,CD209C,ATP6V1H,NOX3,MHC1UXA2,MHC1UEA,C3A.3,BLA,TUBB |
| Osteoclast differentiation | MAPK11,NFKBIA,cgr2b,GRB2,PIK3CG,TNFRSF11B,LILRB1,PIK3CA,PIK3CD,TNFRSF11A |
| Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) | CACNA2D4,AASS,ITGB4,CTNNA3,ITGA4,PKP2,ITGA1,CTNNA1,LAMA2,SGCA |
| Dilated cardiomyopathy | MYL2,ATP2A2,CACNG2,PRKACB,CACNG1,ITGA2,Adcy4,MYL3,CACNA2D4,TTN |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | GNG12A,RASSF7,RAF1A,ABI2B,TMSB4Y,PTK2AA,FGF18,FGF3,RRAS,FGF10 |
| Focal adhesion | CAPN2A,FYNA,PDGFRB,RAC1B,ITGA1,COL6A1,ZYX,EGFRA,COL6A5,PPP1CC |
| Platelet activation | STIM1,PIK3CA,FERMT3,MYL12B,PPP1R12A,PIK3R3,ARHGEF1,PLCB4,TLN1,PRKACA |
| MicroRNAs in cancer | PLCG2,PRKCG,SOX4,KIF23,PIK3R2,TNC,RHOA,RAF1,BMI1,HDAC1 |
Protein Function
ITGB3 has several biochemical functions, for example, cell adhesion molecule binding,enzyme binding,extracellular matrix binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ITGB3 itself. We selected most functions ITGB3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ITGB3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 binding | ITGA5,PDCL3,GREM1,VEGFA |
| extracellular matrix binding | CD248,CYR61,BGN,DMP1,TGFBI,SPOCK2,VTN,SPP1,GPR56,VEGFA |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding | PDGFAA,PDGFB,VEGFA,TYMP,PDGFD,PDGFRB,ITGA5,FIGF,IL1R1,PTEN |
| protease binding | ADAMTS4,FLOT1,SERPINE1,RYR1,SEMG2,THAP5,CCBE1,NDUFS7,COMP,ADAM8A |
| enzyme binding | NOTCH3,ZNF346,TSPAN5,CD4,BIRC7,PARK7,MSH3,TSPAN14,YWHAE,PIAS3 |
| virus receptor activity | GPR172B,PVRL1,SCARB2,XPR1,ICAM1,DAG1,ITGB7,TFRC,ITGB1,EFNB3 |
| fibronectin binding | LRRC15,ITGA4,MFAP2,PLEKHA2,FBLN1,CTSS,MYOC,LPA,ITGA3,HSD17B12 |
| protein disulfide isomerase activity | ERP44,ERO1L,GLRX2,TMX3,TXNDC5,ZNF169,PDIA6,TMX1,PIGK,PDIA2 |
| protein binding | RAB3A,PTCH1,KCNJ9,SUMO3,TTC3,TTC30B,SMPDL3A,PAPOLA,SUSD2,UCHL1 |
Interacting Protein
ITGB3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ITGB3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ITGB3.
ITGAV;ITGA2B
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Regassa, A; Kim, WK; et al. Transcriptome analysis of hen preadipocytes treated with an adipogenic cocktail (DMIOA) with or without 20(S)-hydroxylcholesterol. BMC GENOMICS 16:-(2015).
- Jin, Y; Wang, LM; et al. Differential expression of 5-HT-related genes in symptomatic pulmonary embolism patients. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL MEDICINE 8:512-518(2015).


