IRAK4
-
Official Full Name
interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 -
Overview
IRAK-4 is a member of the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family. The IRAK family is implicated in the Toll-like receptor (TLR) and Il-1R signaling pathway (1). Upon phosphorylation, IRAK-4 interacts with IRAK-1, MYD88 and TRAF6 to form a complex, and activate NF-kB and MAPK pathways (2-3). IRAK-4 phosphorylates and activates IRAK-1 at thr387 and is also known to interact with IRAK-1 but not with the other IRAK members. Additionally, like IRAK-1, IRAK-4 possesses an auto and crossphosphorylation kinase activity (4). -
Synonyms
IRAK4;interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4;NY REN 64;renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-64;IPD1;REN64;IRAK-4;NY-REN-64
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Sf21 Cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is IRAK4 protein?
IRAK4 gene (interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase 4) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12q12. IRAK4 is a protein that plays a key role in the human body, especially in the innate immune response. It is an important component of Toll-like receptor (TLRs) and interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) signaling pathways that promote immune cell survival, activation, and expansion by activating nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and Janus kinase/signal transducers and transcriptional activator 3 (JAK-STAT3) pathways. The function of IRAK4 is not limited to its role in immune signaling pathways, it is also involved in a variety of biological processes, including cell differentiation, inflammatory response, and tumor development. The IRAK4 protein is consisted of 460 amino acids and IRAK4 molecular weight is approximately 51.5 kDa.
What is the function of IRAK4 protein?
IRAK4 is crucial for initiating the innate immune response against foreign pathogens. It is involved in the signaling pathways of both Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and the interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R). The activation of NF-κB and other downstream pathways by IRAK4 leads to the expression of genes involved in inflammation, helping the body to fight off infections. IRAK4 phosphorylates and activates IRAK1, which is an essential step in the continuation of the TLR/IL-1R signaling cascade. IRAK4 interacts with other proteins such as MYD88 and IRAK2 to form a complex known as the Myddosome, which is important for signal transduction.
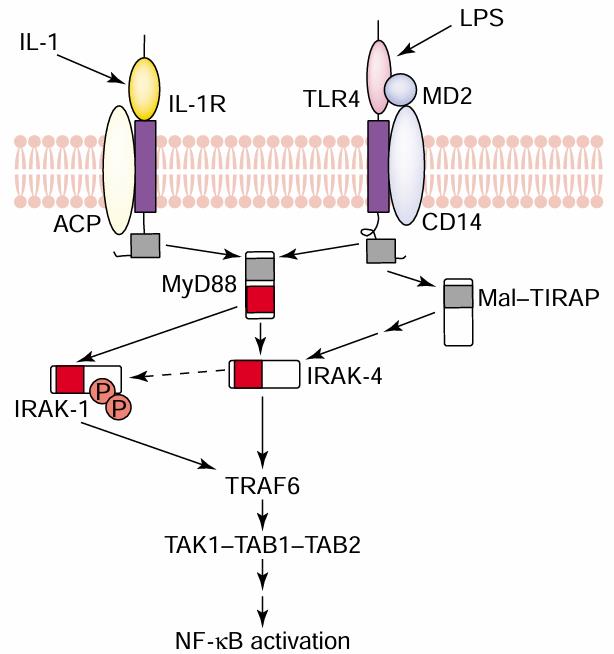
Fig1. A simplified scheme of signaling pathways induced by ligand stimulation of the representative TIR receptors, IL-1R and TLR4. (Nobutaka Suzuki, 2002)
IRAK4 Related Signaling Pathway
In the TLR signaling pathway, TLRs recognizes pathogen-related molecular patterns, recruits the adaptor protein MyD88 after activation, and then activates IRAK4. IRAK4 activates IRAK1, which promotes the activation of TRAF6, which activates the IKK complex, leading to the activation of NF-κB. In the IL-1R signaling pathway, after IL-1R binds to ligand, IRAK4 is recruited through MyD88, and IRAK4 activates IRAK1, which then activates NF-κB and MAP kinases (such as JNK, p38 MAPK) to promote the expression of inflammatory factors. The role of IRAK4 in the NF-κB pathway is through activation of the IKK complex, resulting in phosphorylation and degradation of IκB, the release of NF-κB, which promotes its incorporation into the nucleus and activates the expression of inflammation-related genes. IRAK4 is also involved in activating the JAK-STAT3 pathway.
IRAK4 Related Diseases
Abnormal activity or expression of IRAK4 has been associated with a variety of diseases, especially pathological states involving inflammation and immune responses. For example, in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), overactivation of IRAK4 can lead to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. IRAK4 dysfunction has also been associated with certain cancers, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and other B-cell malignancies, where abnormal TLR signaling may promote tumor development and immune escape. In addition, mutations in the IRAK4 gene can lead to IRAK4 deficiency, an immune deficiency in which patients are prone to repeated aggressive bacterial infections. Inhibitors of IRAK4 are being evaluated in clinical studies as potential treatments aimed at modulating an overactive immune response or blocking signaling pathways that promote tumor growth.
Bioapplications of IRAK4
IRAK4 is an important target for drug development for the treatment of inflammatory and immune-related diseases. Small molecule inhibitors and protein degraders targeting IRAK4 are being investigated for the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease. IRAK4 plays a role in the development of certain cancers, particularly in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other B-cell malignancies. IRAK4 inhibitors may help block tumor cell survival and proliferation signals, and their potential in cancer treatment is currently being evaluated in clinical studies. The expression level and activity of IRAK4 may serve as biomarkers of disease activity and contribute to disease surveillance and therapeutic response evaluation.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jesse Peterson, 2023
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in mammalian systems are well known for their role in innate immunity. In addition, TLRs also fulfil crucial functions outside immunity, including the dorsoventral patterning function of the original Toll receptor in Drosophila and neurogenesis in mice. Recent discoveries in flies suggested key roles for TLRs in epithelial cells in patterning of junctional cytoskeletal activity. Here, researchers address the function of TLRs and the downstream key signal transduction component IRAK4 in human epithelial cells. Using differentiated human Caco-2 cells as a model for the intestinal epithelium, this study shows that these cells exhibit baseline TLR signalling, as revealed by p-IRAK4, and that blocking IRAK4 function leads to a loss of epithelial tightness involving key changes at tight and adherens junctions, such as a loss of epithelial tension and changes in junctional actomyosin. Changes upon IRAK-4 inhibition are conserved in human bronchial epithelial cells.
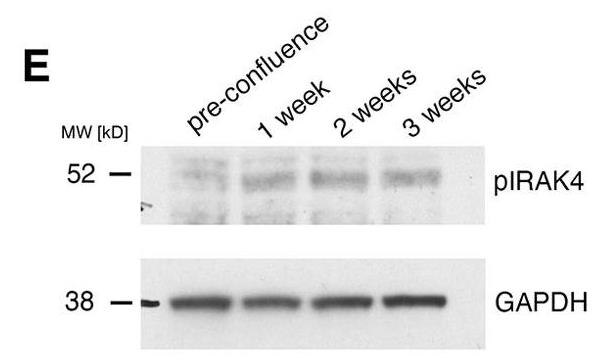
Fig1. Levels of phospho-IRAK4 (pIRAK4) increase with maturation of Caco-2 cells.
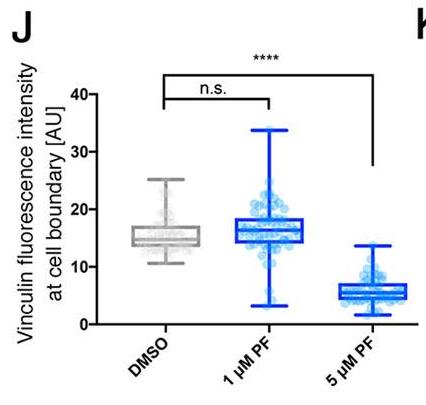
Fig2. Quantification of changes to junctional vinculin fluorescence intensity in control and IRAK4 inhibitor (PF)-treated differentiated Caco-2 cells.
Case Study 2: Milton Pereira, 2022
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases (IRAKs) -4, -2, and -1 are involved in transducing signals from Toll-like receptors (TLRs) via the adaptor myeloid differentiation primary-response protein 88 (MYD88). How MYD88/IRAK4/2/1 complexes are formed, their redundancies, and potential non-enzymatic roles are subjects of debate. Here, researchers examine the hierarchical requirements for IRAK proteins in the context of TLR4 activation and confirmed that the kinase activity of IRAK4 is essential for MYD88 signaling. Surprisingly, the IRAK4 scaffold is required for activation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) by both MYD88 and TIR domain-containing adaptor protein inducing IFN-β (TRIF), a unique adaptation in the TLR4 response. IRAK4 scaffold is, therefore, essential in integrating MYD88 and TRIF in TLR4 signaling.
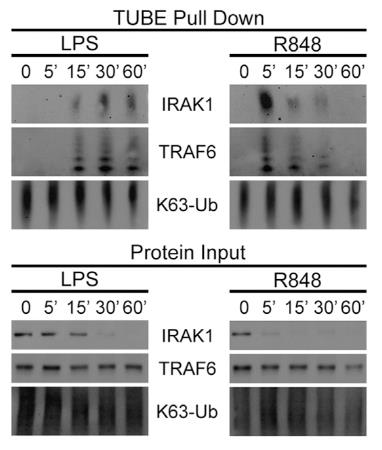
Fig3. IRAK4 scaffold is required for TRAF6 activation.
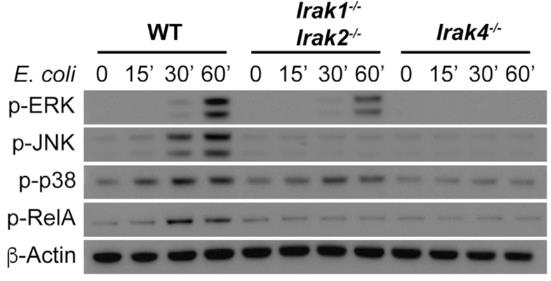
Fig4. Immunoblot of p-ERK, p-JNK, p-p38, p-RelA, and β-actin from WT, Irak1−/−Irak2−/−, and Irak4−/− BMDMs.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
IRAK4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways IRAK4 participated on our site, such as NF-kappa B signaling pathway,Apoptosis,Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with IRAK4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Measles | TNFAIP3,IRF7,CCND1,IRAK1,SH2D1A,DOK1,TP73,CD3D,IFNA21,Cd209g |
| Apoptosis | NTRK1,BMX,IKBKG,TNFRSF10C,IRF4A,HIST1H1C,NFKB1,PPP3R1,BCL2L11,PRKACA |
| Tuberculosis | LSP1,IL6,PPP3R1,IFNA14,IFNA7,NFKB1,BCL2,BID,HLA-DQB1,HLA-DMB |
| Leishmaniasis | NFKBIA,ITGB2L,TGFB2,HLA-DQB1,HLA-DMA,HLA-DRA,MAPK3,STAT1,MAPK1,HLA-DPB1 |
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | ERC1,SYK,TNFRSF13C,DDX58,CCL4L1,PIDD1,IL-8,CCL19,MAP3K7,PTGS2 |
| Pertussis | CXCL6,Casp3,GNAI2,IL6,C1RA,MAPK3,TNF,C1QA,MAPK11,AMCF-II |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | NFKBIA,CAMK2G,HRAS,CALM2,BRAF,CDC42,NTF3,SHC4,RAF1,MAP3K3 |
| Toxoplasmosis | LAMA4,Toxoplasma Gondii Microneme Protein MIC3,LAMB4,PIK3CG,CASP9,RELA,MYD88,IL10RB,HLA-DQB1,IRAK1 |
| Influenza A | IFNA21,NFKBIB,NFKBIA,PIK3R1,PRSS1,Fasl,ICAM1,HLA-DRB3,IFNA10,SLC25A6 |
Protein Function
IRAK4 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,interleukin-1 receptor binding,magnesium ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by IRAK4 itself. We selected most functions IRAK4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with IRAK4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | ACSM5,MYO5B,CASK,TPK1,GMPS,CKM,ATP6V1BA,ITK,ERBB4A,GRK5 |
| interleukin-1 receptor binding | TLR9,IL1F10,IL1B,IL36B,IL36G,IL37,IL36A,IL1RN,TRIP6,IL36RN |
| magnesium ion binding | MAP3K6,MTHFD2,PTENA,TSSK3,DYRK3,EYA2,FOXK2,NUDT5,ABL2,NIM1 |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | HIPK2,STK19,RAF1,PLK2B,GRK5,VPRBP,SIK2,ULK4,CAMKK1B,TESK2 |
| protein binding | FAM98A,GOPC,DCAF12L1,GORAB,SOS1,LRRC4B,CEP164,TMEM43,HIST1H3A,ING5 |
| protein kinase activity | MAP3K4,NEK10,PDK4,HIPK3,PRKAG1,PRKAB1,PLK1,AKT3A,MAPKAPK2,GC2 |
Interacting Protein
IRAK4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with IRAK4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of IRAK4.
PELI2;IRAK1;TIRAP;PELI1;TNFRSF13B;IL1RL1;Irak3;ARNT;TBPL1;MYD88;IRAK2;KIF11
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Cushing, L; Stochaj, W; et al. Interleukin 1/Toll-like Receptor-induced Autophosphorylation Activates Interleukin 1 Receptor-associated Kinase 4 and Controls Cytokine Induction in a Cell Type-specific Manner. JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 289:10865-10875(2014).
- Jang, SE; Hyam, SR; et al. Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose ameliorates inflammation by inhibiting MyD88/NF-kappa B and MyD88/MAPK signalling pathways. BRITISH JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY 170:1078-1091(2013).


.jpg)
.jpg)

