GYS1
-
Official Full Name
glycogen synthase 1 (muscle) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the addition of glucose monomers to the growing glycogen molecule through the formation of alpha-1,4-glycoside linkages. Mutations in this gene are associated with muscle glycogen storage disease. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
GYS1;glycogen synthase 1 (muscle);GYS;glycogen [starch] synthase, muscle;GSY
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- E.coli
- HeLa
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- Flag
Background
What is GYS1 Protein?
The GYS1 protein, or muscle glycogen synthase, is key for making glycogen in muscles, especially in the heart and skeletal muscles. Glycogen works as a major energy reserve, built when we eat and broken down during intense muscle activity to provide energy. When GYS1 has mutations, it can lead to glycogen storage disease type 0, causing muscle cramps or weakness, especially after exercise, as the body lacks stored energy. This condition can also raise the risk of heart troubles due to the absence of glycogen in heart muscles.What is the Function of GYS1 Protein?
The GYS1 protein plays a major role in storing energy in the form of glycogen within muscle cells. It's mainly found in heart and skeletal muscles, where it helps transform glucose from food into glycogen, the energy reserve of our body. When muscles need energy, they tap into this stored glycogen, breaking it down for use during activities like exercise. Any issues with GYS1 can lead to problems with energy storage, resulting in conditions where muscles get easily tired or weak, such as glycogen storage disease type 0.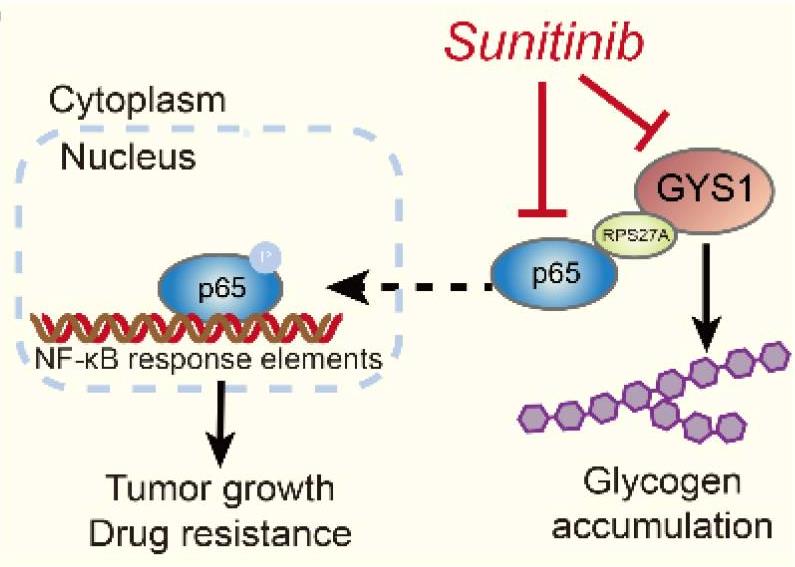
Fig1. An oncogenic role for GYS1 in cell proliferation and glycogen metabolism in ccRCC. (Shi-Lu Chen, 2020)
GYS1 Related Signaling Pathway
GYS1 is primarily involved in the glycogen synthesis pathway. This pathway transforms glucose into glycogen for energy storage in muscles. Insulin plays a central role by activating the protein kinase B (Akt) signaling, which in turn promotes glycogen synthase activity, the enzyme produced by GYS1. This cascade ensures glucose is stored as glycogen after meals. Interruption in this signaling can lead to insufficient glycogen storage, affecting energy supply during physical activities. If GYS1 is not properly regulated, it might result in disorders related to improper glycogen utilization in muscles.GYS1 Related Diseases
GYS1 is linked to glycogen storage disease type 0, a condition where the body can't properly store glycogen in muscles. This can lead to a lack of energy, causing muscle weakness, pain, and potential cramps, especially after exercising. Since glycogen is missing in the heart muscle too, those affected might face higher risks of heart issues like arrhythmias or cardiac arrest after physical activity. It's a genetic condition, meaning it often runs in families and is due to mutations affecting how glycogen synthase, the enzyme from GYS1, works in storing energy.Bioapplications of GYS1
GYS1 bioapplications mainly revolve around understanding energy metabolism and developing therapies for metabolic disorders. By studying GYS1, scientists can delve into how muscles store energy and how this impacts overall metabolism. This knowledge is useful in tackling metabolic diseases like diabetes, where glycogen storage and utilization are key issues. Additionally, GYS1 is explored in athletic performance research, aiming to optimize energy storage for better physical output. Drug development targeting GYS1 pathways might also emerge, focusing on enhancing or correcting metabolic imbalances related to glycogen storage.Case Study
Case Study 1: Cid E. et al. FEBS J. 2005
Muscle glycogen synthase (MGS) appears in the nucleus when muscle cells lack glucose and glycogen. This correlates with low glycogen levels. Although blocked exit by leptomycin B suggests CRM1 involvement, no traditional signal is identified. Amino acids 555-633, rich in Arg, are essential for nuclear presence, which Glc6P affects. Mutations here disrupt accumulation, while usual activation sites don't affect cell location. MGS coexists with certain nuclear proteins and changes location if transcription is blocked, suggesting a nuclear role beyond metabolism.-
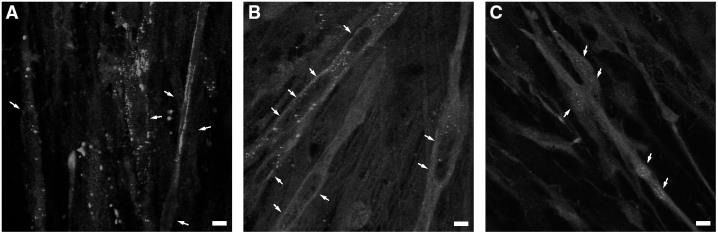 Fig1. MGS immunolocalization in primary cultured human muscle cells.
Fig1. MGS immunolocalization in primary cultured human muscle cells. -
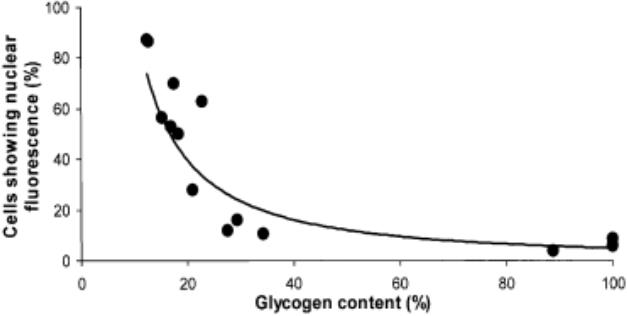 Fig2. Correlation between nuclear concentration of MGS and cellular glycogen content.
Fig2. Correlation between nuclear concentration of MGS and cellular glycogen content.
Case Study 2: Biensø RS. et al. Diabetes. 2012
To see how inactivity leads to muscle insulin resistance, 12 young men stayed in bed for 7 days. Muscle and blood tests showed a drop in glucose uptake and key proteins like GLUT4 after bed rest. Insulin was less effective, but exercise boosted glucose uptake, even post-rest. Inactivity reduced proteins crucial for glucose management, causing resistance.-
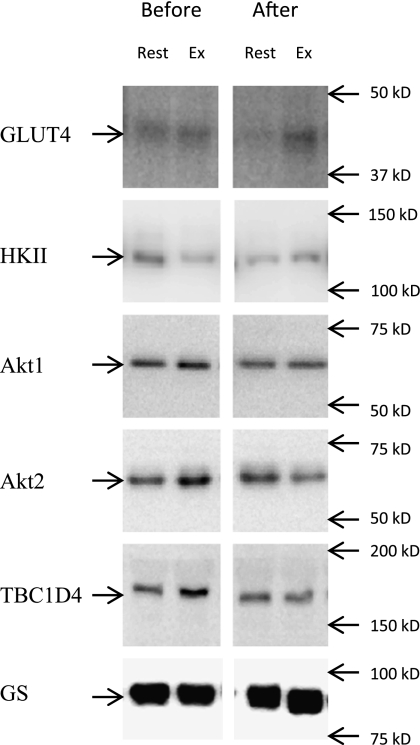 Fig3. Representative blots showing GLUT4, HKII, Akt1, Akt2, TBC1D4, and GS protein.
Fig3. Representative blots showing GLUT4, HKII, Akt1, Akt2, TBC1D4, and GS protein. -
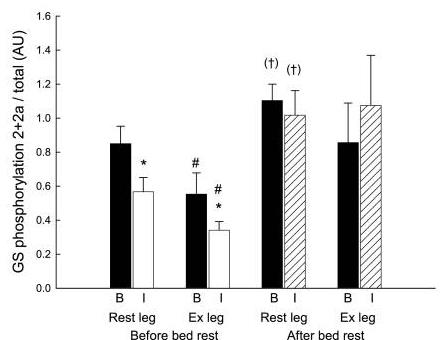 Fig4. GS site 2+2a phosphorylation.
Fig4. GS site 2+2a phosphorylation.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GYS1-910H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GYS1-910H)
Involved Pathway
GYS1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GYS1 participated on our site, such as Starch and sucrose metabolism,PIK-Akt signaling pathway,AMPK signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GYS1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Starch and sucrose metabolism | UGT1A7,GAA,AMY2B,G6PCA.2,AGLA,UGT1A6B,UGT1A7C,HK1,PGM2L1,UGT1A3 |
| Insulin signaling pathway | PDPK1B,RAF1B,PIK3R5,PPP1R3D,AKT2L,PPP1R3B,PRKACBB,PRKAB1A,SLC2A4,PIK3R3B |
| Insulin resistance | PPP2R4,SLC2A1,SLC27A1A,PRKAG2,PRKCBB,PPP1CBL,IRS1,SOCS3,FOXO1B,NOS3 |
| AMPK signaling pathway | AKT1,CCNA1,FOXO1,PRKAG1,PPP2R3C,SLC2A4,CRTC2,CPT1A,HNF4A,STRADA |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | IFNA8,COL6A6,FGF20,ANGPT2,LAMA3,IL7,PPP2R5C,Reln,IBSP,IL6 |
-
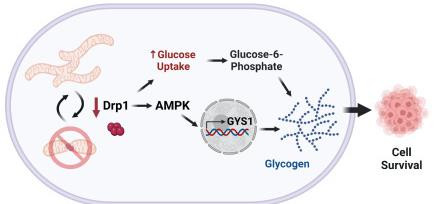 Fig1. Disruption of mitochondrial dynamics as a consequence of silencing Drp1 increases glucose uptake and AMPK-dependent transcriptional activation of GYS1. (Sumati Hasani, 2023)
Fig1. Disruption of mitochondrial dynamics as a consequence of silencing Drp1 increases glucose uptake and AMPK-dependent transcriptional activation of GYS1. (Sumati Hasani, 2023) -
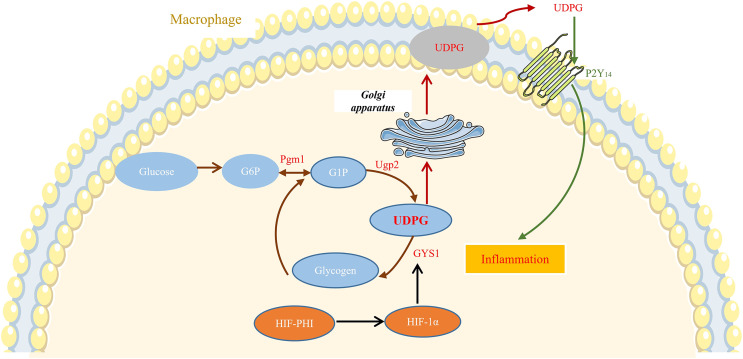 Fig2. MK8617 inhibits M1 macrophage inflammation via the HIF-1α/GYS1/UDPG/P2Y14 pathway. (Lingling Qian, 2023)
Fig2. MK8617 inhibits M1 macrophage inflammation via the HIF-1α/GYS1/UDPG/P2Y14 pathway. (Lingling Qian, 2023)
Protein Function
GYS1 has several biochemical functions, for example, glucose binding,glycogen (starch) synthase activity,glycogen synthase activity, transferring glucose-1-phosphate. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GYS1 itself. We selected most functions GYS1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GYS1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein kinase binding | CHRNA7,CDC25A,Fert2,TEX14,TSACC,ZBTB4,EEF1A2,CSPG4,SMAD1,FBXO7 |
| protein binding | HIST1H4I,HPRT1,RUSC1-AS1,KLHL22,ACTR10,NCOA5,GPR50,SMAD3A,GPATCH8,JAK2 |
| glycogen (starch) synthase activity | GYS2 |
| glycogen synthase activity, transferring glucose-1-phosphate | GYS2 |
| glucose binding | SLC2A8,PYGL,G6PD,HK2,UGP2,HK1,HK3,HKDC1,G6PDX,SLC2A3 |
Interacting Protein
GYS1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GYS1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GYS1.
GYG1;GSK3B;AIMP2;CCDC36;GABARAPL1;PASK;PRKAB2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



