GGPS1
-
Official Full Name
geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase 1 -
Overview
This gene is a member of the prenyltransferase family and encodes a protein with geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) synthase activity. The enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of GGPP from farnesyl diphosphate and isopentenyl diphosphate. GGPP is an important molecule responsible for the C20-prenylation of proteins and for the regulation of a nuclear hormone receptor. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, both protein-coding and non-protein-coding, have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
GGPS1;geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase 1;geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase;GGPPS1;GGPPSase;GGPP synthase;geranyltranstransferase;farnesyltranstransferase;dimethylallyltranstransferase;farnesyl diphosphate synthase;(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosp
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- T7
- Non
- Strep
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- SUMO
Background
What is GGPS1 Protein?
The GGPS1 protein plays a crucial role in synthesizing geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP), which is essential for various cellular functions. GGPP is a building block for producing molecules that help anchor proteins to cell membranes, facilitating processes like cell growth and regulation. These anchored proteins are vital in cellular signaling and function. Disruption of GGPS1 activity can affect muscle function, cellular regulation, and even lead to metabolic or developmental disorders. Understanding GGPS1's role helps in researching conditions where these processes go awry and could guide therapeutic strategies.What is the Function of GGPS1 Protein?
The GGPS1 protein is crucial in creating geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP), which is key for adding lipid groups to proteins, specifically aiding their attachment to cell membranes. This process, known as prenylation, is essential for proteins involved in cell signaling, growth, and other functions. GGPP helps proteins like small GTPases to anchor on the membrane, ensuring they relay signals effectively. Disruption in GGPS1 function might affect cell regulation and lead to certain diseases by impacting this signaling pathway.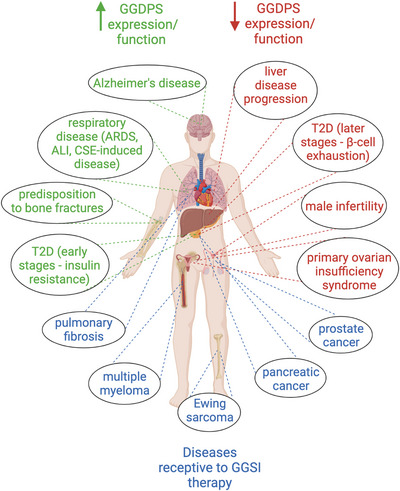
Fig1. Overview of the pathological processes impacted by altered GGDPS expression or activity. (Molly E Muehlebach, 2023)
GGPS1 Related Signaling Pathway
GGPS1 connects to the mevalonate pathway, essential for creating cholesterol and isoprenoids like GGPP. GGPP plays a critical role in prenylation, where it attaches lipids to proteins to help them stick to cell membranes, ensuring they function and signal correctly. Prenylation affects small GTPases, which play significant roles in cell growth, survival, and movement. Disrupting GGPS1 or the mevalonate pathway can impair these processes, leading to metabolic or developmental issues. Understanding this pathway helps in exploring treatments for conditions tied to cellular signaling disruptions.GGPS1 Related Diseases
GGPS1 is associated with several health issues, particularly due to its role in the mevalonate pathway. When GGPS1 does not function properly, it can disrupt cholesterol and isoprenoid synthesis, impacting cellular processes. This malfunction is linked to diseases such as metabolic disorders and certain developmental conditions. Additionally, abnormalities in protein prenylation due to impaired GGPS1 activity can lead to issues in cell signaling, potentially contributing to neurological disorders and some forms of cancer. Understanding GGPS1's involvement in these pathways provides insights into potential therapeutic targets.Bioapplications of GGPS1
GGPS1 plays a significant role in bioapplications, particularly in developing treatments for metabolic disorders and cancers. By influencing the mevalonate pathway, GGPS1 affects cholesterol and isoprenoid production, which are crucial for cell growth and maintenance. Research into GGPS1 can lead to therapies targeting diseases like cardiovascular conditions or cancer, where cell signaling and metabolism are disrupted. Scientists also explore modulating GGPS1 activity to adjust protein prenylation, aiming to restore proper cellular functions and address various metabolic and neurological disorders.Case Study
Case Study 1: Wang Z. et al. Hum Cell. 2022
Mechanical ventilation can cause lung injury, and reducing autophagy might help. This study found that knocking out the GGPPS1 gene in mice reduced lung damage and inflammation related to ventilation. Autophagy markers were lower in these mice. When lung cells were stretched, removing GGPPS1 decreased inflammation. However, using rapamycin reduced these positive effects. The study also discovered Rab37 levels decreased in these knockout mice, indicating Rab37's role in increasing autophagy.-
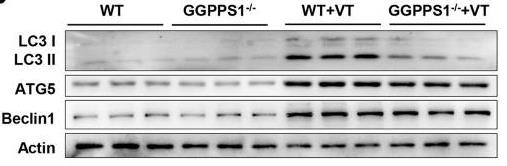 Fig1. Protein expression of autophagy markers, including LC3 I/II, ATG5, and Beclin1, was detected by western blot analysis.
Fig1. Protein expression of autophagy markers, including LC3 I/II, ATG5, and Beclin1, was detected by western blot analysis. -
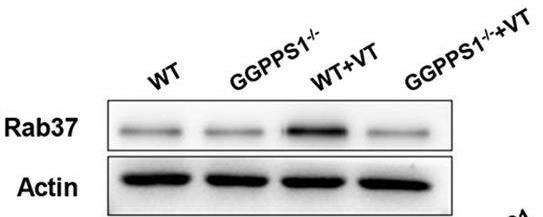 Fig2. GGPPS1−/− mice subjected to mechanical ventilation.
Fig2. GGPPS1−/− mice subjected to mechanical ventilation.
Case Study 2: Sang YJ. et al. J Mol Cell Biol. 2021
Dystocia complicates childbirth and often requires C-sections. Uterine dysfunction, a key factor, results in newborn issues. Current treatments are limited. Statins, reducing preterm birth risk, haven't been fully vetted for pregnant women. In a study, deleting the Ggps1 gene in mice's uterine cells disrupted contractions, leading to dystocia. Ggps1 is vital for uterine contractions, activating the RhoA/Rock2/p-MLC pathway. Disrupting the MVA pathway may cause delivery problems, but adjusting protein prenylation might help.-
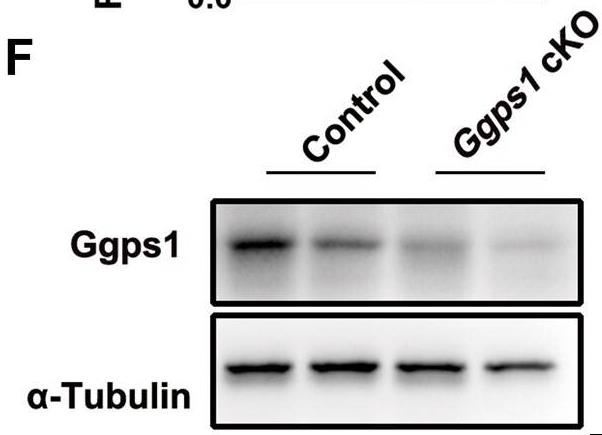 Fig3. Western blot analysis of Ggps1 in the uterus of 3-week-old control and Ggps1 cKO mice.
Fig3. Western blot analysis of Ggps1 in the uterus of 3-week-old control and Ggps1 cKO mice. -
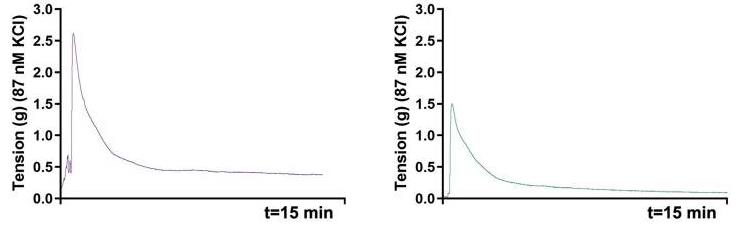 Fig4. The maximal contractile force of Ggps1 cKO strips was largely decreased upon KCl treatment.
Fig4. The maximal contractile force of Ggps1 cKO strips was largely decreased upon KCl treatment.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GGPS1-1260H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GGPS1-1260H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GGPS1-4873H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GGPS1-4873H)
Involved Pathway
GGPS1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GGPS1 participated on our site, such as Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GGPS1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolic pathways | GATM,FDFT1,POLE2,ATP6AP1B,CYP51A1,ASNS,HEXB,AMY2A3,POLR3GLB,GCDHA |
| Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis | ZMPSTE24,FNTA,PMVK,MVDA,PDSS2,FDPS,DHDDS,HMGCS2,HMGCS1,PCYOX1 |
-
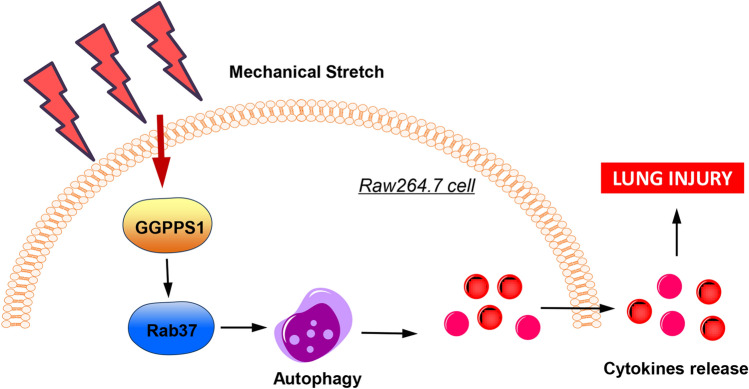 Fig1. Schematic diagram of the effects of GGPPS1 on mechanical stretch-induced lung injury. (Zexu Wang, 2022)
Fig1. Schematic diagram of the effects of GGPPS1 on mechanical stretch-induced lung injury. (Zexu Wang, 2022) -
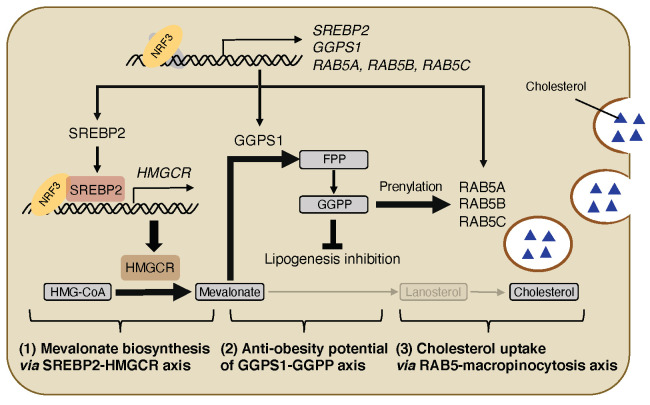 Fig2. NRF3-regulated lipid metabolism through three axes. (Tsuyoshi Waku, 2021)
Fig2. NRF3-regulated lipid metabolism through three axes. (Tsuyoshi Waku, 2021)
Protein Function
GGPS1 has several biochemical functions, for example, dimethylallyltranstransferase activity,farnesyltranstransferase activity,geranyltranstransferase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GGPS1 itself. We selected most functions GGPS1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GGPS1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| dimethylallyltranstransferase activity | FDPS |
| geranyltranstransferase activity | FDPS |
| metal ion binding | CHSY3,CHORDC1,ZSCAN5A,ADH8A,MDP1,ADAP2,TRIM26,PPP5C,PPARAB,POGZA |
| protein binding | UBE2D2A,DTX1,ASB9,SUGP1,ZNF10,CENPP,CAMK2D,GTF3C6,ABLIM1,FANCF |
| farnesyltranstransferase activity | FNTB,COX10 |
Interacting Protein
GGPS1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GGPS1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GGPS1.
ATOX1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


