FMO3
-
Official Full Name
flavin containing monooxygenase 3 -
Overview
Flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMO) are an important class of drug-metabolizing enzymes that catalyze the NADPH-dependent oxygenation of various nitrogen-,sulfur-, and phosphorous-containing xenobiotics such as therapeutic drugs, dietary compounds, pesticides, and other foreign compounds. The human FMO gene family is composed of 5 genes and multiple pseudogenes. FMO members have distinct developmental- and tissue-specific expression patterns. The expression of this FMO3 gene, the major FMO expressed in adult liver, can vary up to 20-fold between individuals. This inter-individual variation in FMO3 expression levels is likely to have significant effects on the rate at which xenobiotics are metabolised and, therefore, is of considerable interest to the pharmaceutical industry. This transmembrane protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum of many tissues. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. Mutations in this gene cause the disorder trimethylaminuria (TMAu) which is characterized by the accumulation and excretion of unmetabolized trimethylamine and a distinctive body odor. In healthy individuals, trimethylamine is primarily converted to the non odorous trimethylamine N-oxide. -
Synonyms
FMO3;flavin containing monooxygenase 3;dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 3;Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N oxide forming] 3;Dimethylaniline monooxygenase 3;Dimethylaniline oxidase 3;dJ127D3.1;FMO 3;FMO form 2;FMO II;FMO3_HUMAN;FMOII;Hepatic flavin containing monooxygenase 3;Hepatic flavin-containing monooxygenase 3;MGC34400;hepatic flavin-containing monooxygenase-3;TMAU
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is FMO3 protein?
FMO3 gene (flavin containing dimethylaniline monoxygenase 3) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q24. FMO members have distinct developmental- and tissue-specific expression patterns. The expression of this FMO3 gene, the major FMO expressed in adult liver, can vary up to 20-fold between individuals. This inter-individual variation in FMO3 expression levels is likely to have significant effects on the rate at which xenobiotics are metabolised and, therefore, is of considerable interest to the pharmaceutical industry. This transmembrane protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum of many tissues. The FMO3 protein is consisted of 532 amino acids and FMO3 molecular weight is approximately 60.0 kDa.
What is the function of FMO3 protein?
FMO3 is particularly important for the metabolism of nitrogen- and sulfur-containing compounds. It functions by catalyzing the insertion of an oxygen atom into these compounds, which is often a critical step in their detoxification or activation. FMO3 also has a significant role in the metabolism of trimethylamine (TMA) to trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a process that impacts platelet responsiveness and the rate of thrombus formation. FMO3 gene expression varies significantly among individuals, which can affect the metabolism of certain drugs and xenobiotics.
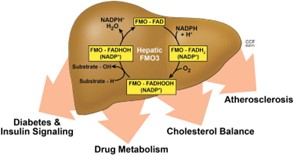
Fig1. Roles of FMO3 enzyme in cholesterol metabolism and atherosclerosis. (Rebecca C Schugar, 2015)
FMO3 Related Signaling Pathway
In the TMA/FMO3/TMAO signaling pathway, FMO3 oxidizes trimethylamine (TMA) to trimethylamino-n-oxide (TMAO) in the liver. TMA is produced by gut microbes using dietary precursors such as choline, while FMO3 directly affects platelet reactivity and the rate of thrombosis by regulating TMAO concentrations. FMO3 inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells by negatively regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. FMO3 is an important drug metabolizing enzyme involved in NADPH-dependent oxidation of a variety of nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus containing allobiotics, such as therapeutic drugs, dietary compounds, insecticides, and other exotic compounds.
FMO3 Related Diseases
FMO3 is associated with several diseases, most notably trimethylaminuria, a condition characterized by the inability to properly metabolize trimethylamine (TMA) due to FMO3 deficiency. This leads to a buildup of TMA and its excretion in the urine, which has a characteristic fishy odor. Elevated levels of TMAO, a product of TMA metabolism, have also been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, potentially through pro-inflammatory effects and contributing to vascular inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Furthermore, research indicates that FMO3 and TMAO are involved in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, with TMAO being implicated in the dysfunction of pancreatic β-cells.
Bioapplications of FMO3
The production of trimethylamino-n-oxide (TMAO) catalyzed by FMO3 is thought to be associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease, and its plasma concentration can be used as a predictor of disease risk. The polymorphism of FMO3 gene is associated with a variety of diseases, and its effects on enzyme activity, drug metabolism and disease are potential targets for drug development. Individual differences in FMO3 activity have important effects on drug response and disease susceptibility, and contribute to the implementation of personalized medicine.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Chongliang Gao, 2018
Human flavin-containing monooxygenase isoform 3 (hFMO3) is an important hepatic drug-metabolizing enzyme, catalyzing the monooxygenation of nucleophilic heteroatom-containing xenobiotics. Based on the structure of bacterial FMO, it is proposed that a conserved asparagine is involved in both NADP(H) and substrate binding. In order to explore the role of this amino acid in hFMO3, two mutants were constructed. To better understand the substrate-enzyme interaction, in vitro as well as in silico experiments were carried out with methimazole as substrate. Methimazole is a high-affinity substrate of hFMO3 and can competitively suppress the metabolism of other compounds. The results demonstrate that methimazole Pi-stacks above the isoalloxazine ring of FAD in hFMO3, in a similar way to indole binding to the bacterial FMO. However, for hFMO3 indole is found to act as a non-substrate competitive inhibitor.
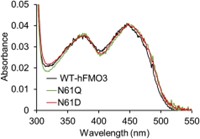
Fig1. UV–vis spectra (300–550 nm) of WT-hFMO3, N61Q and N61D.
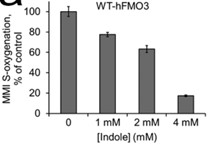
Fig2. Inhibition of the methimazole (MMI) S-oxygenation catalyzed by WT-hFMO3.
Case Study 2: Phuong Thi Thu Nguyen, 2019
The widely used second-line antituberculosis drug ethionamide shows wide interindividual variability in its disposition; however, the relevant factors affecting this phenomenon have not been characterized. In this study, ethionamide metabolism was potentially inhibited by methimazole in vitro. The drug-drug interaction leading to methimazole affecting the disposition of ethionamide mediated by FMO3 was then quantitated using a bottom-up approach with a physiologically based pharmacokinetic framework. Subsequently, researchers explored the effect of FMO3 genetic polymorphism on metabolic capacity, by constructing 2 common functional variants, Lys158 -FMO3 and Gly308 -FMO3. Compared to the wild type, recombinant Lys158 -FMO3 and Gly308 -FMO3 variants significantly decreased the intrinsic clearance of ethionamide by 2% and 24%, respectively. Two prevalent functional variants of FMO3 were predicted to affect ethionamide disposition, with mean ratios of Cmax and AUC of up to 1.5 and 1.7, respectively, in comparison with the wild type. In comparing single ethionamide administration with the wild type, simulations of the combined effects of comedications and FMO3 genetic polymorphism estimated that the Cmax and AUC ratios of ethionamide increased up to 1.7 and 2.0, respectively.
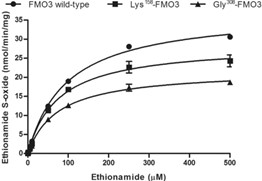
Fig3. Metabolism of ethionamide by human recombinant FMO3 enzymes and its variants including Lys158-FMO3 and Gly308-FMO3.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FMO3-856H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FMO3-1633H)
Involved Pathway
FMO3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FMO3 participated on our site, such as Drug metabolism - cytochrome P, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FMO3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Drug metabolism - cytochrome P | GSTAL,FMO4,UGT5G1,MAOA,UGT2A2,GSTT1,MGST1.1,UGT1A4,UGT1A6B,GSTP2 |
Protein Function
FMO3 has several biochemical functions, for example, N,N-dimethylaniline monooxygenase activity,NADP binding,flavin adenine dinucleotide binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FMO3 itself. We selected most functions FMO3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FMO3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| N,N-dimethylaniline monooxygenase activity | FMO2,FMO5,FMO1 |
| flavin adenine dinucleotide binding | ETFDH,MTRR,ACADVL,AIFM2,ACOX3,ACAD11,MAOB,MTO1,NOS2,ACADSB |
| NADP binding | NOX1,PGD,NOX5,CRYM,POR,MIOX,SPR,DHFRL1,GAPDHS,G6PD |
Interacting Protein
FMO3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FMO3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FMO3.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Warrier, M; Shih, DM; et al. The TMAO-Generating Enzyme Flavin Monooxygenase 3 Is a Central Regulator of Cholesterol Balance. CELL REPORTS 10:326-338(2015).
- Dkhil, MA; Al-Quraishy, S; et al. Epigenetic modifications of gene promoter DNA in the liver of adult female mice masculinized by testosterone. JOURNAL OF STEROID BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 145:121-130(2015).



