FDXR
-
Official Full Name
Ferredoxin Reductase -
Overview
Ferredoxin reductase is a ubiquitous flavoenzyme, containing noncovalently bound FAD as a prosthetic group. It plays a role in delivering NADPH or low potential one-electron donors such as ferredoxin and flavodoxin to redox-based metabolisms in plastids, mitochondria and bacteria. In mammals, ferredoxin reductase is loosely associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane and receives electrons from NADPH. These electrons are transferred to ferredoxin which shuttles electrons to cytochrome P450 in the adrenal cortex mitochondrial steroid hydroxylation systems. -
Synonyms
FDXR;ferredoxin reductase;ADXR;NADPH: adrenodoxin oxidoreductase, mitochondrial;AR;adrenodoxin reductase;ferredoxin--NADP(+) reductase;NP_004101.2;EC 1.18.1.2;NP_077728.2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Bovine
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
Background
What is FDXR protein?
FDXR gene (ferredoxin reductase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q25. The FDXR protein is an enzyme that plays an important role in human cells. It is mainly involved in the biosynthesis of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) protein and is a key factor in maintaining mitochondrial function in cells. FDXR facilitates the assembly of Fe-S proteins by using NADPH as an electron donor to help transfer electrons to other proteins, such as FDX1 and FDX2. Abnormal functioning of FDXR is associated with a variety of diseases, including mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration. The FDXR protein is consisted of 491 amino acids and FDXR molecular weight is approximately 53.8 kDa.
What is the function of FDXR protein?
The FDXR protein is a ferredoxin reductase that plays a role primarily in the mitochondria of organisms. Its main function is to participate in cellular REDOX reactions as part of the electron transport chain, transferring electrons from NADPH to ferredoxin, and then participating in a variety of metabolic pathways, such as heme synthesis and fatty acid lengthening. In addition, FDXR protein is also associated with the occurrence and development of certain diseases, such as hereditary ferredoxin deficiency.
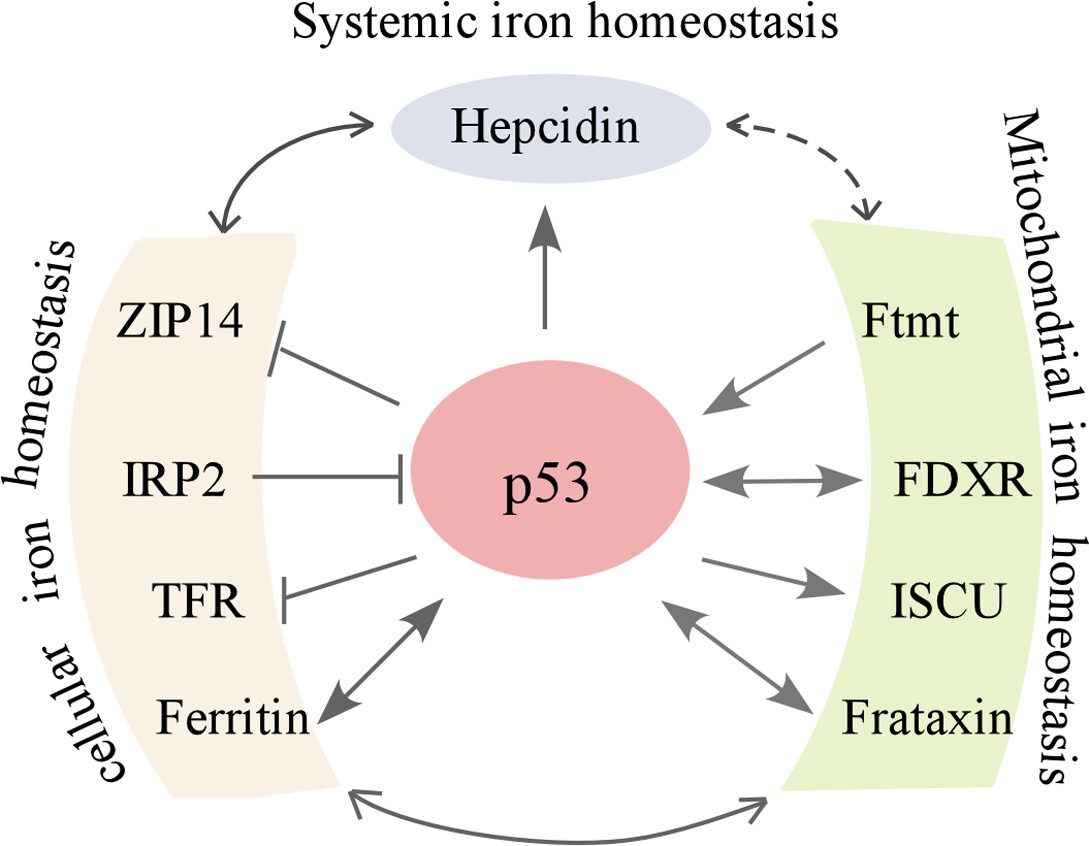
Fig1. Crosstalk between p53 and iron regulators. (Jin Zhang, 2019)
FDXR related signaling pathway
Fdxr-related signaling pathways mainly involve nitrite reductase (NRF) and mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC). Under normal physiological conditions, FDXR, as a member of NRF, participates in intracellular REDOX reaction and maintains the REDOX balance in the cell. At the same time, FDXR also interacts with other proteins in mitochondrial ETC, such as ferrithionein (FXN) and ferredoxin 2 (FDX2), which together regulate mitochondrial energy metabolism and oxidative stress response. In pathological states, such as hereditary ferredoxin deficiency caused by mutations in the FDXR gene, these signaling pathways may be disrupted, which in turn affects intracellular energy metabolism, oxidative stress response, and the occurrence and progression of disease.
FDXR related diseases
The FDXR protein plays an important role in human cells, especially in the assembly of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters. FDXR facilitates the assembly of Fe-S proteins by using NADPH as an electron donor to help transfer electrons to other proteins, such as FDX1 and FDX2. Abnormal functioning of FDXR is associated with a variety of diseases, including mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration. For example, biallelic mutations in the FDXR gene can cause optic nerve atrophy and ataxia, symptoms associated with iron metabolism disorders and neuroinflammation. These effects of FDXR highlight its importance in cell metabolism and disease development.
Bioapplications of FDXR
RhFDXR, or recombinant human ferredoxin reductase, has a variety of applications in the biomedical field. First of all, rhFDXR can be used to study mitochondrial related diseases, such as hereditary ferredoxin deficiency. Through expression and purification of rhFDXR protein in vitro, its structure and function can be deeply studied, providing a theoretical basis for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Second, rhFDXR can act as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative stress damage, and may have anti-aging and neuroprotective effects. In addition, rhFDXR can also be used for drug screening and development, such as drug research for mitochondria-related diseases. Finally, rhFDXR also has certain applications in the field of biotechnology, such as participating in biocatalytic reactions as biocatalysts.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jesse D Slone, 2020
The FDXR protein is essential for the synthesis of iron-sulfur clusters and steroidogenesis. Iron and sulfur clusters are essential cofactors in cellular processes, and their synthesis has been associated with many diseases. Previous studies have found that deactivating mutations in FDXR cause mitochondrial disease and optic nerve atrophy in humans and mice, which are associated with reduced function of the electron transport chain and increased reactive oxygen species. Inflammation and peripheral neuropathy are also typical features of the disease. This paper shows that FDXR mutations lead to significant optic nerve transmission defects, which may underlie the major clinical manifestations of optic atrophy in FDXR patients, as well as neurodegenerative loss of central nervous system cells. Molecular analysis showed that FDXR mutation also caused mitochondrial iron overload and mitochondrial membrane potential changes, further supporting the hypothesis that FDXR mutation caused neurodegeneration by affecting iron metabolism.
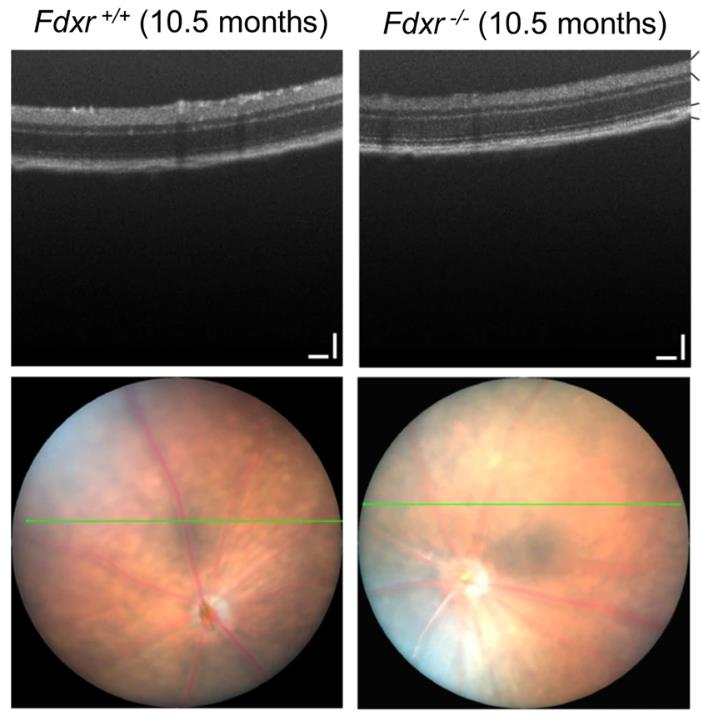
Fig1. Optic disc and OCT scanning of P120 mice.
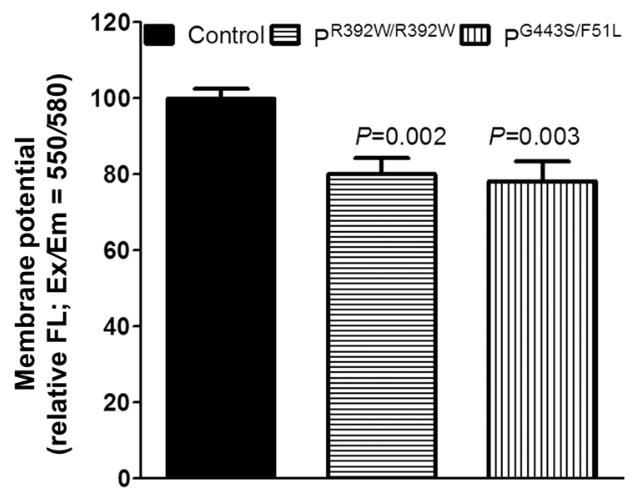
Fig2. The mitochondrial membrane potential was measured in patient fibroblasts.
Case Study 2: Yanbo Shi, 2012
Ferredoxins are iron-containing thioneins that have been studied for many years for their role in catalyzing the monooxygenase reaction of P450 enzymes. Recent studies have shown that they also play an important role in the assembly of iron-sulfur clusters. The human genome contains two homologous ferredoxins: FDX1 and FDX2. Studies have shown that FDX1 mainly interacts with P450 enzymes to synthesize mitochondrial steroid precursors, while FDX2 is used for the synthesis of iron-sulfur clusters and does not participate in steroid production. To further evaluate the role of FDX-FDXR systems in mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis, we conducted siRNA studies on multiple human cell lines. The results show that both FDX1 and FDX2 are important for the biosynthesis of iron-sulfur clusters. Loss of FDX1 activity disrupts iron-sulfur cluster enzyme activity and cellular iron homeostasis, leading to mitochondrial iron overload and cytoplasmic iron depletion. In addition, knockdown of FDXR reduces assembly of iron-sulfur clusters and, together with cytoplasmic iron depletion, causes mitochondrial iron overload.
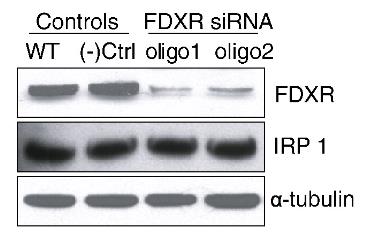
Fig3. siRNA treatments of the FDXR cause decreased iron–sulfur protein activities and activation of IRPs.
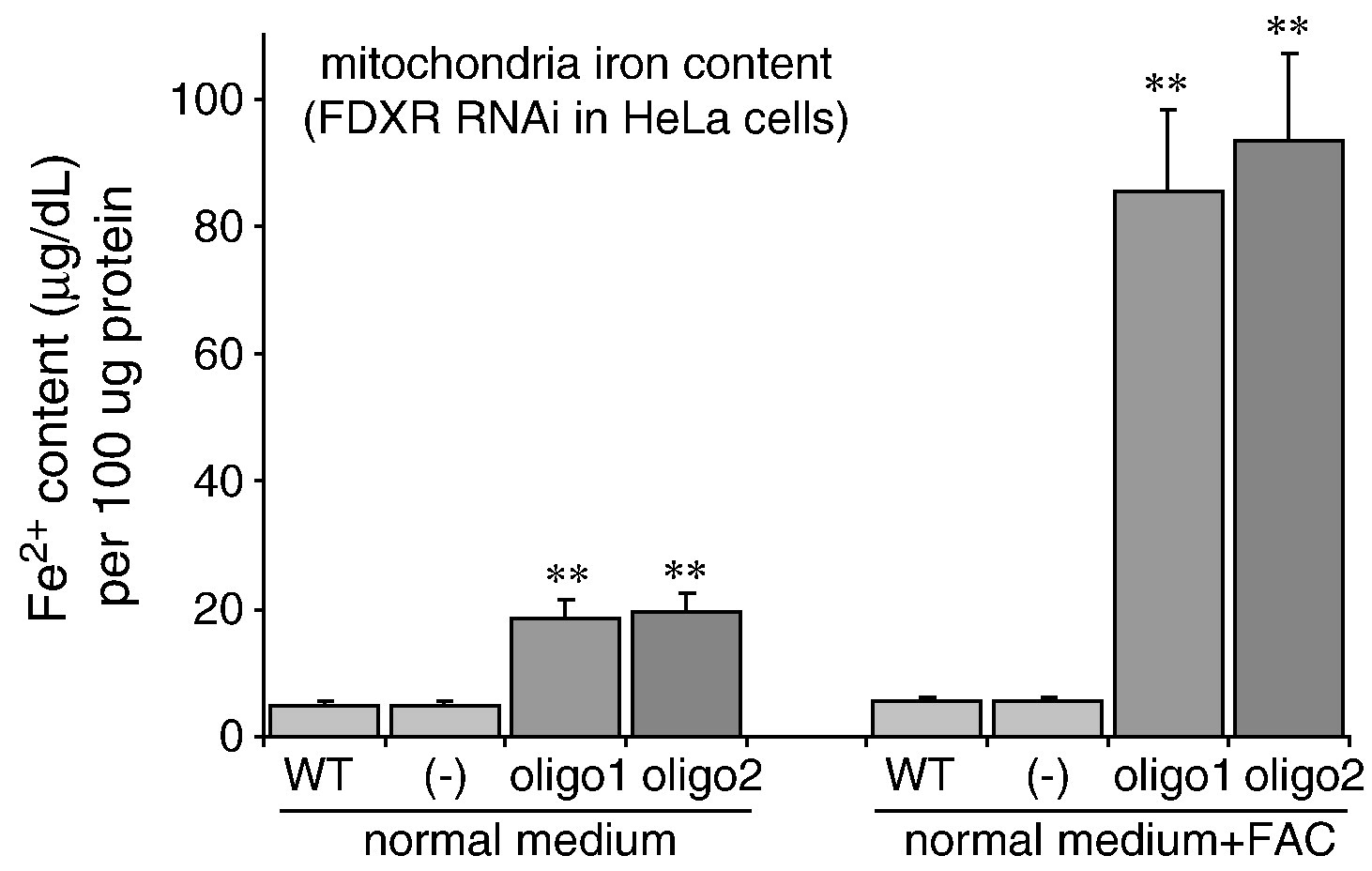
Fig4. Knockdown of FDXR results in mitochondrial iron overload in HeLa cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FDXR-15H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FDXR-1648H)
Involved Pathway
FDXR involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FDXR participated on our site, such as Biological oxidations,Cytochrome P450 - arranged by substrate type,Defective CYP11A1 causes Adrenal insufficiency, congenital, with 46,XY sex reversal (AICSR), which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FDXR were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Biological oxidations | CYP2A13,ADH4,SULT1C2,CES1,SULT1C4,SULT1B1,CYP7A1,CYP2K19,Sult2a2,UGT1B7 |
| Endogenous sterols | FDX1,CYP11B2,CYP7A1,CYP19A1,CYP11A1,CYP8B2,FDX1L,CYP46A1,CYP27A1,CYP21A2 |
| Disease | NA,CHMP4B,CUX1,VPS37A,CFTR,SFTPB,TICAM1,TNKS,HEY2,CCDC167 |
| Defective CYP11A1 causes Adrenal insufficiency, congenital, with 46,XY sex reversal (AICSR) | FDX1L,FDX1,CYP11A1 |
| Diseases of metabolism | EPM2A,MMAA,AMN,GYG1,CYP11A1,SFTPB,SFTPC,CCDC59,MMADHC,GYG2 |
| Direct p53 effectors | NDRG1,CCNK,CD82,DGCR8,EPHA2,AIFM2,BNIP3L,SCN3B,HIC1,CEBPZ |
| Electron transport from NADPH to Ferredoxin | FDX1,FDX1L |
| Cytochrome P450 - arranged by substrate type | CYP2N13,CYP2AD2,CYP2E1,CYP3C1,CYP2K22,CYP1A1,CYP2R1,CYP1B1,CYP4T8,CYP2C8 |
Protein Function
FDXR has several biochemical functions, for example, NADPH-adrenodoxin reductase activity,ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FDXR itself. We selected most functions FDXR had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FDXR. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | RB1CC1,MIEN1,TIMM10,PIK3CG,BCL2L13,HMGB4,SERPINF1,SV2B,SYTL1,MAPK10 |
Interacting Protein
FDXR has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FDXR here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FDXR.
FHIT;HSPD1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wang, JL; Guise, CP; et al. Identification of one-electron reductases that activate both the hypoxia prodrug SN30000 and diagnostic probe EF5. BIOCHEMICAL PHARMACOLOGY 91:436-446(2014).
- Imamichi, Y; Mizutani, T; et al. Transcriptional regulation of human ferredoxin reductase through an intronic enhancer in steroidogenic cells. BIOCHIMICA ET BIOPHYSICA ACTA-GENE REGULATORY MECHANISMS 1839:33-42(2014).


