ELAVL1
-
Official Full Name
ELAV like RNA binding protein 1 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the ELAVL family of RNA-binding proteins that contain several RNA recognition motifs, and selectively bind AU-rich elements (AREs) found in the 3 untranslated regions of mRNAs. AREs signal degradation of mRNAs as a means to regulate gene expression, thus by binding AREs, the ELAVL family of proteins play a role in stabilizing ARE-containing mRNAs. This gene has been implicated in a variety of biological processes and has been linked to a number of diseases, including cancer. It is highly expressed in many cancers, and could be potentially useful in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2012] -
Synonyms
ELAVL1;ELAV like RNA binding protein 1;HUR;Hua;MelG;ELAV1;ELAV-like protein 1;Hu antigen R;hu-antigen R;embryonic lethal, abnormal vision, drosophila, homolog-like 1;ELAV (embryonic lethal, abnormal vision, Drosophila)-like 1 (Hu antigen R)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HeLa
- E.coli
- GST
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
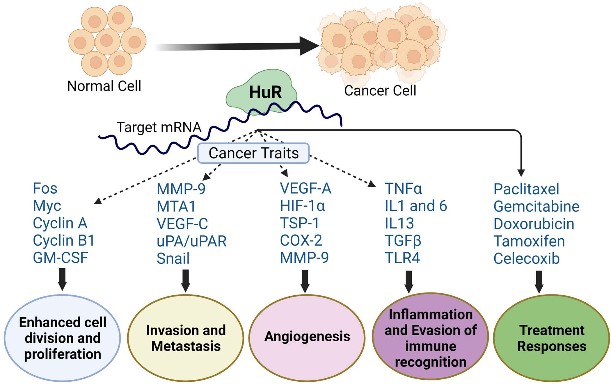
Fig1. Posttranslational modification of HuR by signaling kinases. (Mrinmoyee Majumder, 2022)
What is ELAVL1 protein?
ELAVL1 gene (ELAV like RNA binding protein 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the ELAVL family of RNA-binding proteins that contain several RNA recognition motifs, and selectively bind AU-rich elements (AREs) found in the 3' untranslated regions of mRNAs. AREs signal degradation of mRNAs as a means to regulate gene expression, thus by binding AREs, the ELAVL family of proteins play a role in stabilizing ARE-containing mRNAs. It is highly expressed in many cancers, and could be potentially useful in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. The ELAVL1 protein is consisted of 326 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 36.1 kDa.
What is the function of ELAVL1 protein?
It binds to the 3'-UTR region of mRNAs to increase their stability, which can promote the differentiation of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) by stabilizing specific mRNAs that are not methylated by N6-methyladenosine (m6A). And it's capable of binding to m6A-containing mRNAs, including those of MYC, and contributing to their stability. Also it participates in the regulation of p53/TP53 expression by binding to its mRNA along with ZNF385A, controlling its nuclear export induced by CDKN2A, which may mediate part of the CDKN2A anti-proliferative activity. And it can increase the stability of leptin mRNA that contains an AU-rich element in its 3' UTR. ELAVL1's role in mRNA stability and translational efficiency is also linked to its subcellular localization, with its nucleo-cytoplasmic translocation being controlled by phosphorylation events. Furthermore, ELAVL1 has been implicated in the regulation of inflammatory responses, as it stabilizes pro-inflammatory mRNAs and is involved in LPS-induced inflammatory gene expression.
ELAVL1 Related Signaling Pathway
In glioblastoma, the p38 MAPK pathway affects the nucleoplasmic shuttle of ELAVL1 protein by activating MK2. After ELAVL1 binds to the ARE of IL-6 mRNA, it forms a complex with activated MK2 to trigger nuclear shuttle. AMPK affects mammalian protein expression in a variety of ways, including transcriptional activation, protein synthesis, and post-transcriptional mRNA regulation, in which the ELAVL1 protein shuttles from the cytoplasm into the nucleus. Matrine regulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through the ELAVL1/RBM3 axis and affects the growth of tumor cells. In prostate cancer PC-3 cells, ELAVL1 protein may promote the growth of cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
ELAVL1 Related Diseases
ELAVL1 has been implicated in a variety of diseases, especially in the development of tumors. It is overexpressed in a variety of tumors, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, etc., and may promote tumor cell proliferation, metastasis, and drug resistance through different signaling pathways. For example, in prostate cancer, ELAVL1 may promote cancer cell growth through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. In addition, ELAVL1 is also involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) RNA, affecting HBV replication. In endometriosis, expression of ELAVL1 is also associated with disease development.
Bioapplications of ELAVL1
Due to its overexpression in a variety of cancers, ELAVL1 is considered a potential therapeutic target. Drug development targeting ELAVL1 may help inhibit tumor growth and metastasis. In some cancers, expression levels of ELAVL1 can be used as a biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis, helping to assess disease progression and treatment response. As an RNA-binding protein, ELAVL1 is involved in mRNA stability and translation regulation, and its functional studies are helpful to discover new drug mechanisms of action.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Zunzhe Wang, 2022
The pathological proliferation of cells in vascular smooth muscle underlies neointimal hyperplasia (NIH) development during atherosclerosis. Circular RNAs (circRNAs), which represent novel functional biomarkers and RNA-binding proteins, contribute to multiple cardiovascular diseases; however, their roles in regulating the vascular smooth muscle cell cycle remain unknown. Thus, researchers aimed to identify the roles of circRNAs in vascular smooth muscle during coronary heart disease (CHD). Through circRNA sequencing of CHD samples and human antigen R (ELAVL1) immunoprecipitation, they identified circRNAs that are associated with CHD and interact with ELAVL1. The results suggested that the hsa_circ_0000280 associated with CHD inhibits cell proliferation and induces ELAVL1-dependent cell cycle arrest. Gain/loss-of-function experiments and assays in vivo indicated that hsa_circ_0000280 facilitates interactions between ELAVL1 and cyclin-dependent kinase suppressor 1 (CDKN1A) mRNA and stabilization of this complex and leads to cell cycle arrest at the G1/S checkpoint, inhibiting cell proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and NIH in vivo. Importantly, hsa_circ_0000280 reduced neointimal thickness and smooth muscle cell proliferation in vivo.
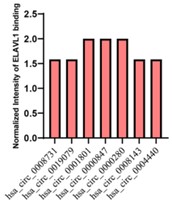
Fig1. ELAVL1 RIP-sequencing revealed top seven circRNAs.
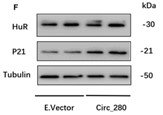
Fig2. Western blots of ELAVL1 and CDKN1A.
Case Study 2: Soumasree De, 2019
Starvation is a cellular stress that induces autophagy, a conserved cellular self-digestion mechanism that allows cells to degrade and recycle damaged proteins and organelles. The present study illustrated that during serum deprivation, Beclin1, a crucial gene that is essential for autophagosome formation in autophagy, gets controlled post-transcriptionally in breast cancer cell-line MCF-7. RNA affinity chromatography and co-immunoprecipitation confirmed the association of HuR with 3'-UTR of beclin1 mRNA. After cytosolic translocation, HuR enhances beclin1 protein synthesis in response to serum starvation by enhancing the association of beclin1 mRNA to the polysomes. Partial silencing of HuR resulted in reduction of beclin1 expression both at mRNA and protein levels, which in turn decreased starvation-induced autophagic flux.

Fig3. Western blot of eluted column fractions.
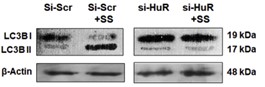
Fig4. Detection of autophagic flux by LC3B immunoblot in MCF-7 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ELAVL1-75HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ELAVL1-6668H)
Involved Pathway
ELAVL1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ELAVL1 participated on our site, such as AMPK signaling,AMPK signaling pathway,Gene Expression, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ELAVL1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| AMPK signaling pathway | INS,PPP2R3C,TSC2,PRKAG1,CREB3L4,PRKAA1,LIPE,CFTR,CCND1,RHEB |
| Regulation of mRNA stability by proteins that bind AU-rich elements | KHSRP,HNRNPD,SETA,SETB,TNPO1,ANP32A,ZFP36L1B,SET,ZFP36L1,HUG |
| HuR (ELAVL1) binds and stabilizes mRNA | HUG,SETB,ANP32A,SETA,SET |
| AMPK signaling | CPT1A,CPT1C,EEF2,SLC2A4RG,LOC729991,CPT1B,PPARGC1B,EIF4EBP1,CAMKK2,CDKN1A |
| Gene Expression | POLR3C,NKX2,ADAT3,ZNF785,IGF2BP2,ZNF529,NR2F6B,ZNF257,ZIM3,ESRRG |
Protein Function
ELAVL1 has several biochemical functions, for example, AU-rich element binding,RNA binding,double-stranded RNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ELAVL1 itself. We selected most functions ELAVL1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ELAVL1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| AU-rich element binding | ZFP36L3,ELAVL3,EXOSC7,ZFP36,CPSF5,HNRNPA0,APOBEC1,ELAVL4,ZFP36L1,EXOSC8 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | RPS15,NOLC1,MSI2,GFM1,CIRH1A,CCBL2,UBE2L3,POLRMT,UBA1,HEATR6 |
| mRNA 3-UTR AU-rich region binding | CPEB3,CPEB2,ZFP36,CPSF1,CPEB1B,CPEB1 |
| nucleotide binding | NUBP1,NLRP4E,PPIP5K2,SR140,PRKACBB,SF3B14,ABCG2A,SRSF7,RBM18,CMPK |
| double-stranded RNA binding | STRBP,LRRFIP1,EIF4A1,TUBA1B,DROSHA,BARHL1,AGO3,STAU1,DHX30,SLC3A2 |
| mRNA 3-UTR binding | KHSRP,TARDBP,TUT1,LARP1,RNF40,PUM1,ELAVL4,CRYZ,IGF2BP2,CIRBP |
| mRNA binding | ESRP1,RBM25,EIF4A3,EDC3,RBFOX3,SRRM4,KHSRP,RBM8A,SOSTDC1B,G3BP1 |
| protein kinase binding | CAMK2N2,TRPV4,DNAJC3,MSN,CACNB3,THY1,PPP1CB,CCNL1B,CAV2,RACGAP1 |
| RNA binding | RPL38,MSI1,RBFOX1,NHP2L1A,TARDBP,PUF60B,GTF3A,PAPOLA,CNOT4B,MIF4GD |
Interacting Protein
ELAVL1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ELAVL1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ELAVL1.
SDCBP;q99ib8-pro_0000045602;TOP1;Smurf2;UBC;SF3A2;RBFOX2;GJB3;PTBP1;NOS3
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



