DMP1
-
Official Full Name
dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein 1 -
Overview
Dentin matrix protein 1, also known as DMP-1, is an extracellular matrix protein and a member of the small integrin binding ligand N-linked glycoprotein family. This protein, which is critical for proper mineralization of bone and dentin, is present in diverse cells of bone and tooth tissues. In undifferentiated osteoblasts it is primarily a nuclear protein that regulates the expression of osteoblast-specific genes. During osteoblast maturation the protein becomes phosphorylated and is exported to the extracellular matrix, where it orchestrates mineralized matrix formation. Mutations in DMP-1 are known to cause autosomal recessive hypophosphatemia, a disease that manifests as rickets and osteomalacia. -
Synonyms
DMP1;dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein 1;dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein;dentin matrix protein 1;ARHP;ARHR;DMP-1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Dog
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- E.coli
- Yeast
- His
- GST
- Non
- SUMO
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
 transcription factor.jpg)
Fig1. The structure of the Dmp1 (Dmtf1) transcription factor. (K Inoue, 2007)
What is DMP1 protein?
DMP1 (DEAD-box helicase 6) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4q22. Dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein is an extracellular matrix protein and a member of the small integrin binding ligand N-linked glycoprotein family. This protein, which is critical for proper mineralization of bone and dentin, is present in diverse cells of bone and tooth tissues. The protein contains a large number of acidic domains, multiple phosphorylation sites, a functional arg-gly-asp cell attachment sequence, and a DNA binding domain. In undifferentiated osteoblasts it is primarily a nuclear protein that regulates the expression of osteoblast-specific genes. During osteoblast maturation the protein becomes phosphorylated and is exported to the extracellular matrix, where it orchestrates mineralized matrix formation. The DMP1 protein is consisted of 513 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 55.8 kDa.
What is the function of DMP1 protein?
DMP1 is essential for the biomineralization of calcium phosphate in bone and dentin. It nucleates the formation of hydroxyapatite, which increases mineralization. DMP1 is crucial for the maturation of odontoblasts and osteoblasts, which are important for bone formation and repair. DMP1 is a major local suppressor of the hormone FGF23 (Fibroblast Growth Factor 23). Inactivating mutations of DMP1 can lead to an overproduction of FGF23, which in turn causes renal phosphate wasting and contributes to conditions like rickets and osteomalacia. DMP1 has a protective role against osteocyte apoptosis, which is particularly important in the context of high circulating phosphate levels. DMP1 is a member of the small integrin-binding ligand N-linked glycoprotein (SIBLING) family, which includes other proteins that play roles in bone mineralization and are involved in various diseases.
DMP1 Related Signaling Pathway
Dmp1-mediated calcium signaling can activate p38 MAPK and promote osteoblast differentiation. DMP1 interacts with the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway to prevent tumor formation by affecting the Arf/Mdm2/p53 signaling pathway. Lipopolysaccharide affects the proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of human dental pulp stem cells by regulating Notch signaling pathway, and the expression of DMP1 is related to the activation of this pathway. In rat dental pulp stem cells, DMP1 expression is regulated by the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. DMP1 is involved in the regulation of phosphorus and vitamin D metabolism by influencing the expression and activity of FGF23. DMP1 may interact with the Hedgehog signaling pathway to influence bone development and homeostasis. DMP1 may affect cell proliferation and survival through the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.
DMP1 Related Diseases
The disease is caused by an inactivated mutation in the DMP1 gene and is characterized by increased kidney phosphorus excretion, resulting in hypophosphatemia and bone mineralization disorders. DMP1 is involved in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis by influencing FGF23 expression and WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway. DMP1 plays a role in the process of fracture healing, and the change of its expression level is related to the rate of fracture healing. Mutations in the DMP1 gene may be associated with certain types of osteosclerosis, a disease in which bones harden and thicken. DMP1 may be associated with osteoporosis associated with thalassemia, manifested by a high rate of bone renewal and increased serum Dkk-1 concentration. DMP1 may play a role in the occurrence and development of bone tumors, and its specific role in tumor bone metastasis needs to be further studied.
Bioapplications of DMP1
DMP1 plays a role in the fracture healing process and may help promote fracture healing by regulating DMP1 activity or expression levels. DMP1 plays a key role in the tooth mineralization process and can be used to develop materials that promote tooth repair and regeneration. DMP1 can be used to develop biologically active bone repair materials that promote bone formation in bone tissue engineering. As a drug target, DMP1 can be used to screen small molecule drugs that can modulate their activity for the treatment of related diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Aleksandra Porębska, 2020
Dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1) is an acidic, extracellular matrix protein essential for biomineralization of calcium phosphate, in bone and dentin. It is proteolytically processed into two fragments, 44K and 56K. Recently, the presence of DMP1 was noticed in inner ear, specifically in otoconia, which are calcium carbonate biominerals involved in sensing of balance. In this study, the solution structure and biomineralization activity of otoconial 44K and 56K fragments toward calcium carbonate were investigated. The results of analytical ultracentrifugation, circular dichroism, and gel filtration indicated that DMP1 fragments are disordered in solution. Notably, 56K formed oligomers in the presence of calcium ions. It was also observed that both fragments influenced the crystal growth by in vitro biomineralization assay and scanning electron microscopy. In addition, they sequester the calcium ions during the calcite formation. Calcium carbonate crystals precipitated in vitro changed their size and shape in the presence of DMP1 fragments. Oligomerization propensity of 56K may significantly enhance this function.
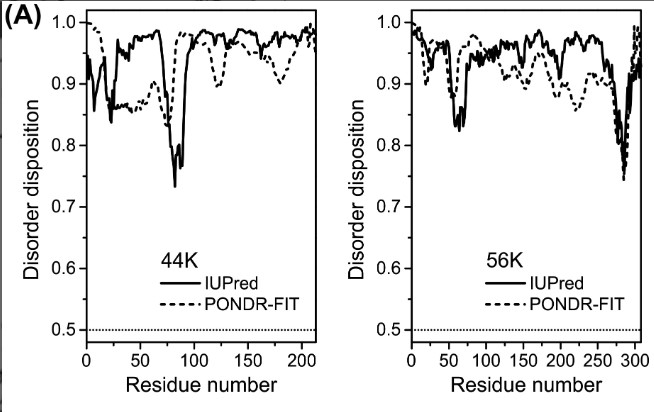
Fig1. The prediction of the disordered regions from an amino acid sequence.
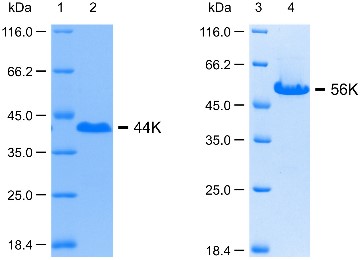
Fig2. SDS-PAGE analysis of purified human DMP1 fragments 44K (lane 2) and 56K (lane 4).
Case Study 2: Chang-Yun Yoon, 2016
Recent reports demonstrated that dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1) acts as an inhibitor of vascular calcification and might be a potential biomarker for chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder; however, no clinical investigations regarding DMP1 have been performed in dialysis patients. The researchers investigated the prognostic value of DMP1 on cardiovascular outcomes in prevalent peritoneal dialysis patients. They recruited 223 prevalent peritoneal dialysis patients and divided them into high and low DMP1 groups according to log-transformed plasma DMP1 levels. A Cox proportional hazards analysis determined DMP1 was independently associated with cardiovascular outcomes. In vitro mouse osteocytes were cultured in media containing indoxyl sulfate (IS), and the expressions of DMP1 were examined. The multiple logistic regression analysis indicated that DMP1 levels were independently associated with the presence of vascular calcification after adjustment for multiple confounding factors. A Kaplan-Meier plot showed that the low DMP1 group had a significantly higher rate of incident cardiovascular events compared with the high DMP1 group. In addition, multiple Cox analysis showed that low DMP1 was significantly associated with incident cardiovascular events. In IS-stimulated osteocytes, mRNA and protein expression levels of DMP1 were significantly decreased compared with control osteocytes.

Fig3. Comparison of the log-transformed median value of DMP1 levels between the PD group and controls by using box plots.
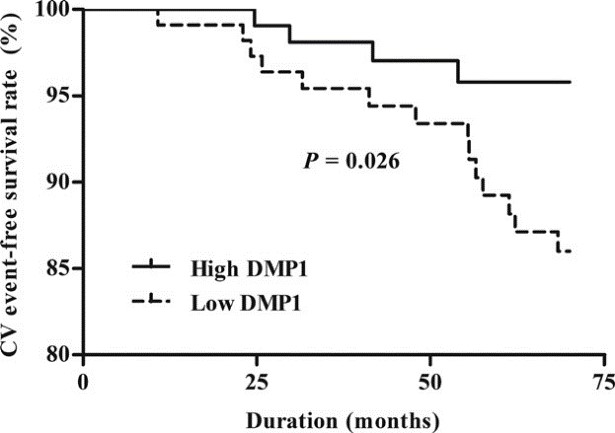
Fig4. Kaplan-Meier plots for CV outcome-free survival between the lower and higher DMP1 groups.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DMP1-2706H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DMP1-1973H)
Involved Pathway
DMP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DMP1 participated on our site, such as ECM proteoglycans,Extracellular matrix organization, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DMP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Extracellular matrix organization | PRP,LTBP4,CRTAP,MMP24,COL17A1A,FURINB,FN1B,MFAP1,COL3A1,DDR2 |
| ECM proteoglycans | PTPRS,DAG1,BGNB,MATN3B,VCANB,MATN4,ITGB3A,HAPLN1,MATN1,COMP |
Protein Function
DMP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,extracellular matrix binding,integrin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DMP1 itself. We selected most functions DMP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DMP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| extracellular matrix binding | SPARC,ITGAV,DCN,ITGA2B,FBLN2,VTN,SID4,TGFBI,GPR56,ITGB3 |
| integrin binding | WISP3,JAM3,ADAMTS8,KDR,FAP,CTGFA,S1PR3,COL4A3,THBS4,IGF1 |
| calcium ion binding | DSG3,CDH2,PCDH2G8,CRELD1,PCDH2G12,SYT15,CRB1,CRELD2,ITGB1BP2,S100A1 |
Interacting Protein
DMP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DMP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DMP1.
Resources
Research Area
Osteoclast MarkersOsteoblast and Osteoclast Markers
Osteogenesis Markers
Extracellular Matrix Molecules
Osteocyte Markers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Sapir-Koren, R; Livshits, G; et al. Osteocyte control of bone remodeling: is sclerostin a key molecular coordinator of the balanced bone resorption-formation cycles?. OSTEOPOROSIS INTERNATIONAL 25:2685-2700(2014).
- Sato, S; Hashimoto, J; et al. Novel sandwich ELISAs for rat DMP1: Age-related decrease of circulatory DMP1 levels in male rats. BONE 57:429-436(2013).


