DEK
-
Official Full Name
DEK oncogene -
Overview
This gene encodes a protein with one SAP domain. This protein binds to cruciform and superhelical DNA and induces positive supercoils into closed circular DNA, and is also involved in splice site selection during mRNA processing. Chromosomal aberrations involving this region, increased expression of this gene, and the presence of antibodies against this protein are all associated with various diseases. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
DEK;DEK oncogene;DEK oncogene (DNA binding);protein DEK;D6S231E;DEK gene;DEK oncogene DNA binding;DEK_HUMAN;DNA binding;OTTHUMP00000039357;OTTHUMP00000016078;OTTHUMP00000221544;OTTHUMP00000221545
Recombinant Proteins
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is DEK Protein?
DEK gene (DEK proto-oncogene) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6p22. This gene encodes a protein with one SAP domain. This protein binds to cruciform and superhelical DNA and induces positive supercoils into closed circular DNA, and is also involved in splice site selection during mRNA processing. Chromosomal aberrations involving this region, increased expression of this gene, and the presence of antibodies against this protein are all associated with various diseases. The DEK protein is consisted of 375 amino acids and DEK molecular weight is approximately 42.7 kDa.
What is the Function of DEK Protein?
DEK can bind to highly open chromatin and prefer to bind to hypomethylated DNA regions that are rich in activating histone markers such as H3K4me2/3, H3K27ac, and H3K9ac. In particular, DEK protein is mainly located near the transcription start site of highly transcribed genes, and its binding pattern is similar to that of RNA polymerase II, suggesting that it plays an important role in gene expression regulation. The study found that the knockout of DEK can lead to significant up-regulation or down-regulation of the genes to which it binds, suggesting that DEK plays a dual role in activating and suppressing both highly expressed and widely expressed genes. In addition, DEK are associated with a variety of cellular processes, including self-renewal, proliferation, differentiation, senescence, and apoptosis, and have important effects on cell transformation.
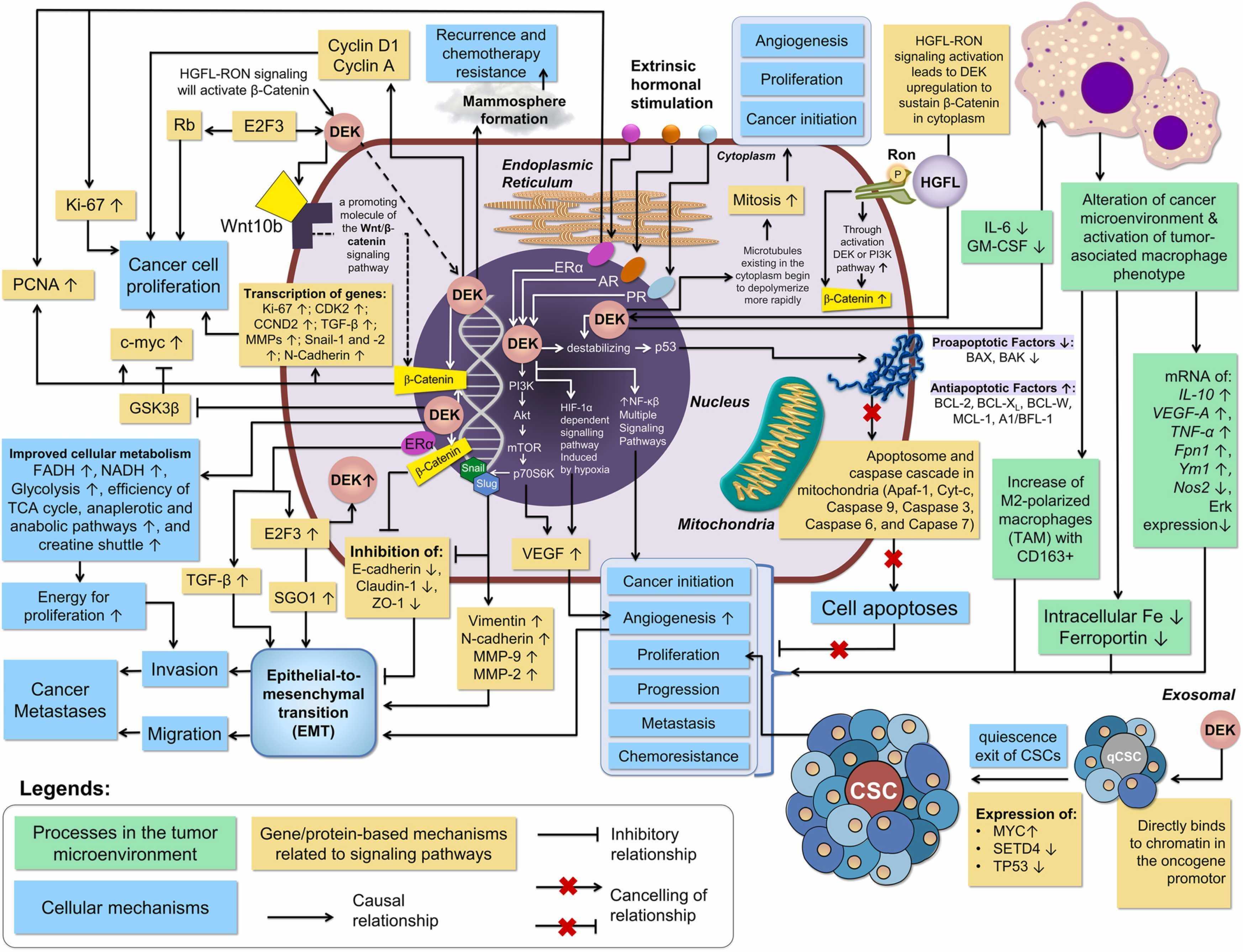
Fig1. The summary of multiple roles and pathways related to DEK in breast cancer carcinogenesis. (Muhammad Habiburrahman, 2023)
DEK Related Signaling Pathway
Multiple signaling pathways involved in DEK are related to the occurrence and development of the disease. In triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), DEK promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) and angiogenesis by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, thereby promoting tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. In cholangiocarcinoma, DEK promotes tumor cell proliferation, migration, and EMT by activating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. In asthma studies, DEK-targeted oligonucleotides (DTA-64) alleviated EMT in bronchial epithelial cells by inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad, MAPK, and PI3K signaling pathways, thereby improving airway remodeling. In acute myeloid leukemia (AML), EBs of DEK/CAN may be involved in the activation of signaling pathways including AKT/mTOR, SFK, ABL1, and c-MYC, which are regulated through a phosphorylation cascade and are involved in the development of cancer, maintenance of cancer stem cells, and determination of therapeutic response.
DEK Related Diseases
DEK is associated with a variety of diseases, particularly the development of cancer, including but not limited to acute myeloid leukemia (AML), breast, ovarian, bladder, colon, skin, and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). In these cancers, abnormal expression of DEK can promote the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells, and may play a role by affecting signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR, TGF-β1/Smad, and MAPK. In addition, DEK is also involved in the airway remodeling process in non-neoplastic diseases such as asthma.
Bioapplications of DEK
DEK protein has become a potential target for drug development due to its abnormal expression and role in a variety of cancers. Although there are currently no approved drugs directly targeting DEK on the market, in preclinical studies, small molecule inhibitors, siRNA, shRNA, etc., targeting DEK are being developed for the treatment of certain types of cancer. For example, by inhibiting DEK, it interferes with the metabolic pathways of tumor cells, thereby inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis. In addition, the expression level of DEK has also been studied as a biomarker for certain cancers for disease surveillance and prognostic assessment.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Emrah Özçelik, 2022
DEK has a short isoform (DEK isoform-2; DEK2) that lacks amino acid residues between 49-82. The full-length DEK (DEK isoform-1; DEK1) is ubiquitously expressed and plays a role in different cellular processes but whether DEK2 is involved in these processes remains elusive. Researchers stably overexpressed DEK2 in human bone marrow stromal cell line HS-27A, in which endogenous DEKs were intact or suppressed via short hairpin RNA (sh-RNA). Contrary to ectopic DEK1, DEK2 locates in the nucleus and nucleolus, causes persistent γH2AX signal upon doxorubicin treatment, and couldn't functionally compensate for the loss of DEK1. In addition, DEK2 overexpressing cells were more sensitive to doxorubicin than DEK1-cells. Expressions of DEK1 and DEK2 in cell lines and primary tumors exhibit tissue specificity. DEK1 is upregulated in cancers of the colon, liver, and lung compared to normal tissues while both DEK1 and DEK2 are downregulated in subsets of kidney, prostate, and thyroid carcinomas. Interestingly, only DEK2 was downregulated in a subset of breast tumors suggesting that DEK2 can be modulated differently than DEK1 in specific cancers.
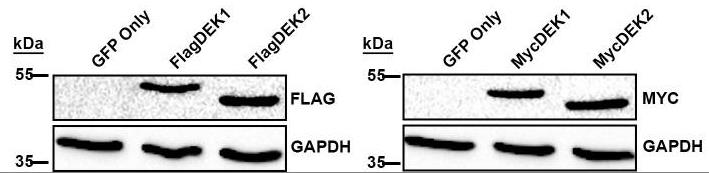
Fig1. Western blot analyses show ectopic expression of Flag (left panel) or Myc (right panel) epitope-tagged DEK1 and DEK2.
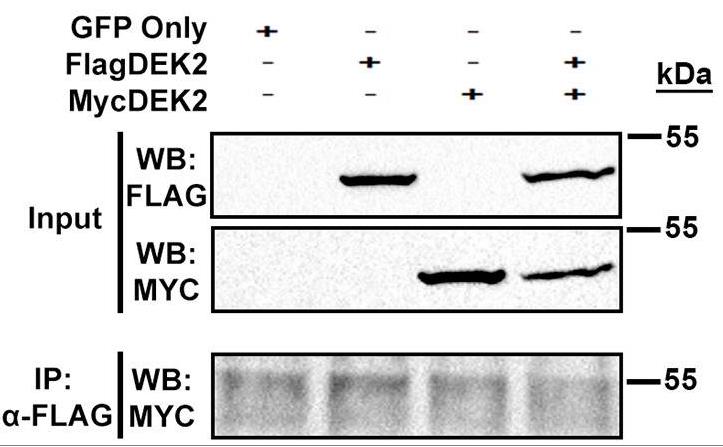
Fig2. Co-IP assay in the cells that transiently co-expressed FlagDEK2 and MycDEK2 indicated that DEK2 doesn't form homodimers.
Case Study 2: Kari E Hacker, 2018
DNA damage repair alterations play a critical role in ovarian cancer tumorigenesis. Mechanistic drivers of the DNA damage response consequently present opportunities for therapeutic targeting. The chromatin-binding DEK oncoprotein functions in DNA double-strand break repair. Researchers therefore sought to determine the role of DEK in epithelial ovarian cancer. DEK is overexpressed in both primary epithelial ovarian cancers and ovarian cancer cell lines. To assess the impact of DEK expression levels on cell growth, small interfering RNA and short hairpin RNA approaches were utilized. Decreasing DEK expression in ovarian cancer cell lines slows cell growth and induces apoptosis and DNA damage. The biologic effects of DEK depletion are enhanced with concurrent chemotherapy treatment. The in vitro effects of DEK knockdown are reproduced in vivo, as DEK depletion in a mouse xenograft model results in slower tumor growth and smaller tumors compared to tumors expressing DEK.
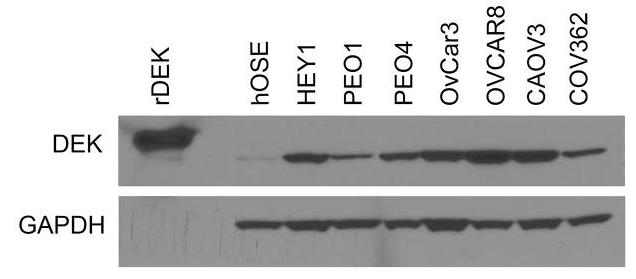
Fig3. DEK is overexpressed in epithelial ovarian cancer cell lines and primary tumor specimens.
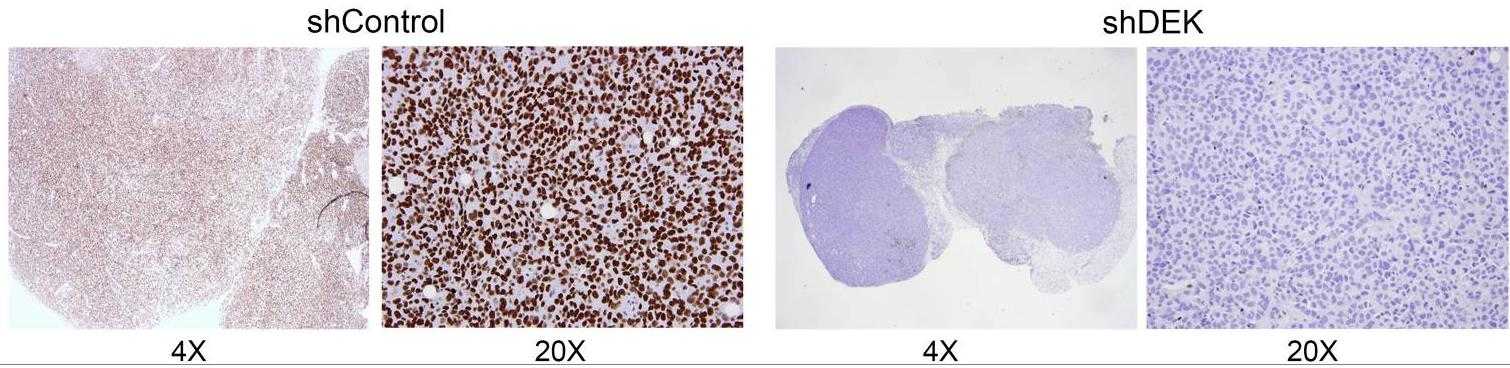
Fig4. DEK immunohistochemistry was performed on tumors to demonstrate DEK knockdown.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DEK-1385H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DEK-5902H)
Involved Pathway
DEK involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DEK participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DEK were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
DEK has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,histone binding,poly(A) RNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DEK itself. We selected most functions DEK had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DEK. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| histone binding | CHD8,BRDT,SMARCA4A,ASF1A,TONSL,HIST1H3E,HIST1H4D,RNF168,MYSM1,HIST1H3F |
| DNA binding | SCML2,MGAA,TCF4,DHARMA,MUS81,ZNF444,POU5F3,NPAS2,TIGD5,PA2G4 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | EIF4G3,CPEB4,MKRN1,POLDIP3,DHX36,S100A16,MTERF,SNRPA,RPL17,SAMD4A |
Interacting Protein
DEK has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DEK here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DEK.
DAXX;CSNK2A1;UPF1;q7cit1_yerpe;NOP56;ESR1;DBP;CSNK2A2;RPL10;HIST2H4B;HIST1H3D;NR5A1;Rpl35;MMGT1;HDAC2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Patel, RM; Walters, LL; et al. DEK expression in Merkel cell carcinoma and small cell carcinoma. JOURNAL OF CUTANEOUS PATHOLOGY 39:753-757(2012).
- Kostianets, O; Shyian, M; et al. Serological Analysis of SEREX-Defined Medullary Breast Carcinoma-Associated Antigens. CANCER INVESTIGATION 30:519-527(2012).


