COL17A1
-
Official Full Name
collagen, type XVII, alpha 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes the alpha chain of type XVII collagen. Unlike most collagens, collagen XVII is a transmembrane protein. Collagen XVII is a structural component of hemidesmosomes, multiprotein complexes at the dermal-epidermal basement membrane zone that mediate adhesion of keratinocytes to the underlying membrane. Mutations in this gene are associated with both generalized atrophic benign and junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Two homotrimeric forms of type XVII collagen exist. The full length form is the transmembrane protein. A soluble form, referred to as either ectodomain or LAD-1, is generated by proteolytic processing of the full length form. -
Synonyms
COL17A1;collagen, type XVII, alpha 1;BPAG2;collagen alpha-1(XVII) chain;BP180;alpha 1 type XVII collagen;collagen XVII, alpha-1 polypeptide;180 kDa bullous pemphigoid antigen 2;bullous pemphigoid antigen 2 (180kD);bA16H23.2 (collagen, type XVII,
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293T
- HEK293
- E.coli
- His
- Non
- Fc
- GST
- Avi
Background
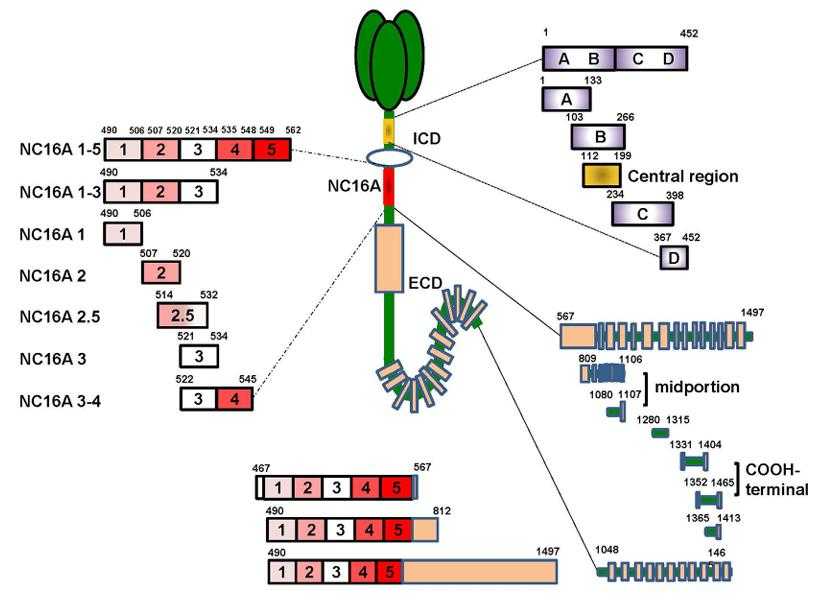
Fig1. The target sites of the BP180 molecule. (Yale Liu, 2017)
What is COL17A1 protein?
COL17A1 gene (collagen type XVII alpha 1 chain) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10q25. This gene encodes the alpha chain of type XVII collagen, also called BP180. Unlike most collagens, collagen XVII is a transmembrane protein. Collagen XVII is a structural component of hemidesmosomes, multiprotein complexes at the dermal-epidermal basement membrane zone that mediate adhesion of keratinocytes to the underlying membrane. Mutations in this gene are associated with both generalized atrophic benign and junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Two homotrimeric forms of type XVII collagen exist. The full length form is the transmembrane protein. The COL17A1 protein is consisted of 1497 amino acids and COL17A1 molecular weight is approximately 150.4 kDa.
What is the function of COL17A1 protein?
COL17A1 protein is a protein used to assemble type XVII collagen. This protein plays a vital role in strengthening and stabilizing the skin. Type XVII collagen is a major component of hemidesmosomes, a microstructure located on the inner side of the outermost layer of skin (epidermis) that helps anchor the epidermis to the lower layer of skin. Type XVII collagen is essential for the stability of the hemidesmosomes and therefore plays an important role in maintaining the binding between layers of skin.
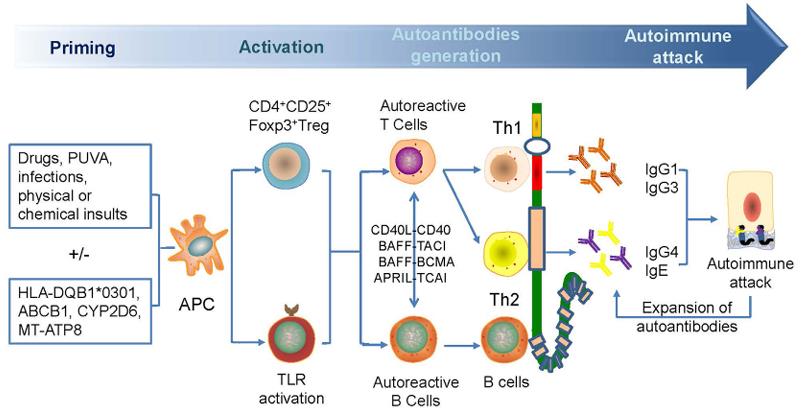
Fig2. A possible mechanism for the generation of anti-BP180 autoantibodies. (Yale Liu, 2017)
COL17A1 Related Signaling Pathway
COL17A1 plays a role in intercellular connections and cell adhesion to the basement membrane, influencing intercellular interactions and cell morphology and movement. The abnormal expression of COL17A1 may be related to the activation of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, which plays a key role in cell proliferation, survival and metabolism. By affecting the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, COL17A1 affects mTOR and its downstream effectors, such as 4EBP1, which may influence cell proliferation and tumor development. The accumulation of COL17A1 may enhance the resistance of cells to ferroptosis, which may be related to the regulation of apoptosis.
COL17A1 Related Diseases
Mutations or dysregulated expression of the COL17A1 gene have been linked to a range of diseases affecting skin and other tissues, particularly those affecting cell adhesion and stability of the extracellular matrix. Mutations in the COL17A1 gene can lead to different types of epidermolysis bullosa (EB), especially borderline EB (JEB), which is a serious inherited skin disease. Abnormal expression of COL17A1 may be associated with linear IgA disease (LAD), a chronic, relapsing skin disease characterized by deposition of IgA antibodies at the dermo-epidermal junction. COL17A1 expression is abnormal in a variety of tumors, including breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, etc. Mutations in the COL17A1 gene are associated with certain corneal diseases, such as epithelial recurrent invasive keratopathy (ERED).
Bioapplications of COL17A1
Specific COL17A1 antibodies are used in Western Blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunocytochemistry (ICC/IF) and flow cytometry (FACS) to help detect and quantify the expression of COL17A1 in different samples, providing a basis for the diagnosis of related diseases. COL17A1 antibodies play a key role in the study of diseases associated with abnormal COL17A1 function, such as epidermolysis bullosa (EB) and linear IgA disease (LAD), helping to shed light on the pathogenesis of these diseases. During the drug screening process, COL17A1 antibodies can be used to identify potential drug molecules that may affect the function of COL17A1, supporting the development of new drugs to treat related diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Daisuke Nanba, 2021
Skin regenerative capacity declines with age, but the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. Here researchers demonstrate a functional link between epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and type XVII collagen (COL17A1) proteolysis on age-associated alteration of keratinocyte stem cell dynamics in skin regeneration. Live-imaging and computer simulation experiments predicted that human keratinocyte stem cell motility is coupled with self-renewal and epidermal regeneration. Receptor tyrosine kinase array identified the age-associated decline of EGFR signaling in mouse skin wound healing. Culture experiments proved that EGFR activation drives human keratinocyte stem cell motility with increase of COL17A1 by inhibiting its proteolysis through the secretion of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP1). In addition, COL17A1 directly regulated keratinocyte stem cell motility and collective cell migration by coordinating actin and keratin filament networks.
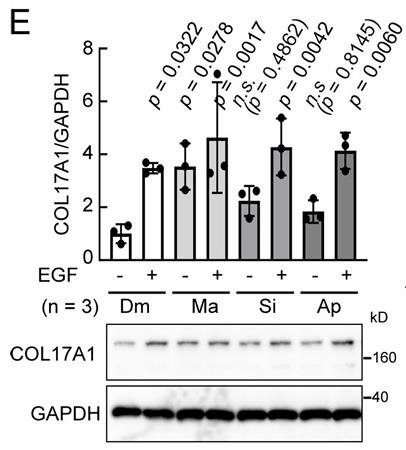
Fig1. Expression of COL17A1 in keratinocytes treated with protease inhibitors.
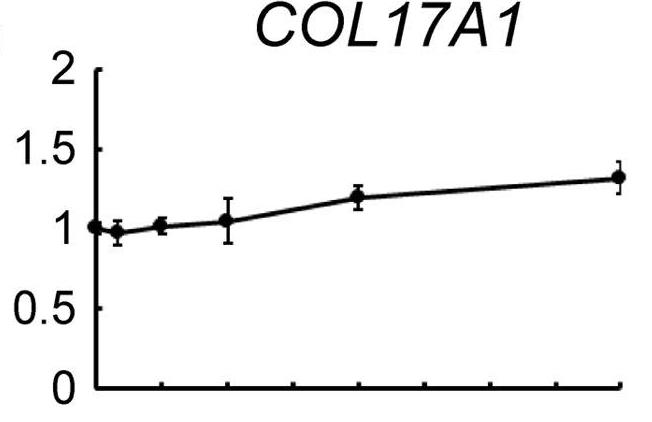
Fig2. Time-course analysis of COL17A1 expression.
Case Study 2: Muttarin Lothong, 2021
Collagen XVII (COL17), a cell-matrix adhesion protein, has been found to be suppressed in breast cancer. The present study used the stable COL17-overexpressing MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells to reveal an anti-proliferative effect of COL17 on breast cancer cell through mTOR deactivation. The correlation was confirmed by decreased expression of the proliferative marker Ki67 in COL17-expressing cells. In addition, overexpression of COL17 reduced the clonogenicity and growth of the cells. Researchers demonstrated that COL17 affects the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by deactivation of AKT, mTOR and downstream effectors, particularly 4EBP1. The high expression of COL17A1 gene encoding COL17 is associated with low-proliferation tumors, extended tumor-free period, and overall survival of breast cancer patients. In conclusion, these results revealed the novel function of COL17 using in vitro and in vivo models and elucidated the related pathway in breast cancer cell growth and proliferation.
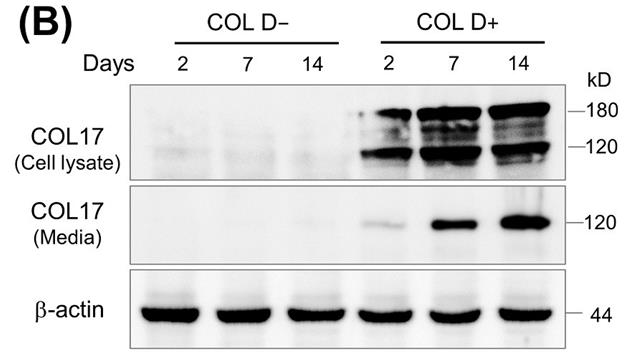
Fig3. Relative COL17 expression in COL cells treated with Dox.
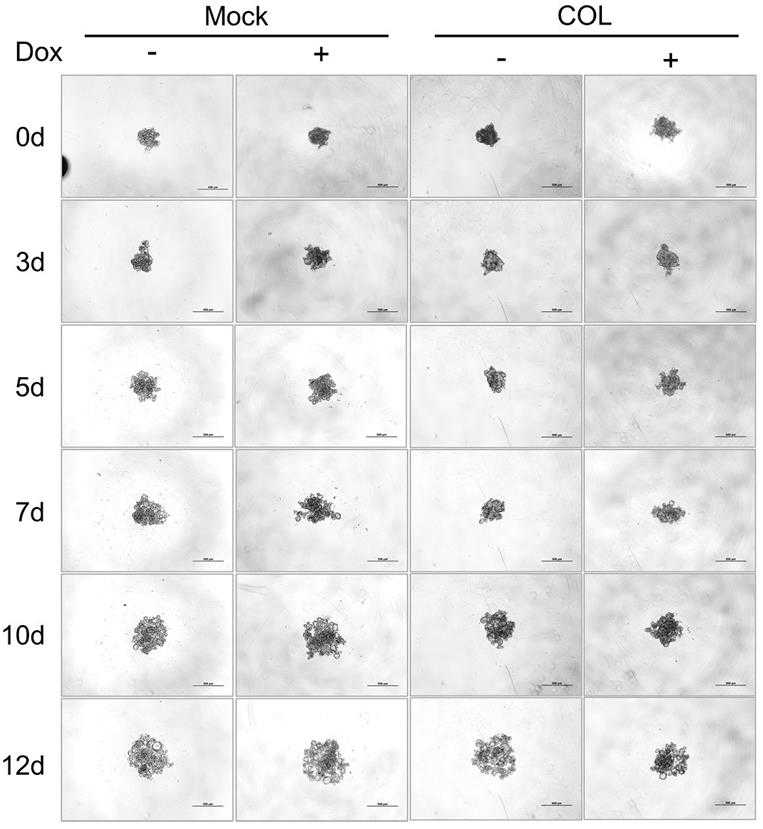
Fig4. COL17 reduces the spheroid size and proliferation in 3D culture.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (COL17A1-329H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (COL17A1-1775H)
Involved Pathway
COL17A1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways COL17A1 participated on our site, such as Alpha6-Beta4 Integrin Signaling Pathway,Cell junction organization,Cell-Cell communication, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with COL17A1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Collagen biosynthesis and modifying enzymes | TLL1,COL5A3A,COL5A2,COL23A1,COL9A1B,COL4A3,PCOLCE,COL2A1,BMP1A,SERPINH1B |
| Extracellular matrix organization | MMP10,COL2A1,TLL2,ADAM8A,MATN3B,DST,ASPN,PCOLCEB,CTS7,ADAM8 |
| Cell-Cell communication | KIRREL3L,TESK1,CLDN20,CDH12,SPTBN1,SKAP2,RSU1,FBLIM1,CADM2A,F11R.2 |
| Collagen formation | COL9A1A,BMP1A,COL4A6,COL6A3,COL5A2,COL15A1B,PRP,TLL2,COL8A2,COL28A1A |
| Alpha6-Beta4 Integrin Signaling Pathway | EIF4E,EGFR,DST,SMAD3B,PLEC,YWHAQ,CDKN1A,MST1R,RTKN,CD151 |
| Collagen degradation | MMP20,MMP11,CTSB,CTSK,COL13A1,COL19A1,MMP13,MGC174152,COL23A1,MGC174857 |
| Cell junction organization | FBLIM1,CDH2,F11R.2,CLDN4,RSU1,CLDN3,CDH10,CADM2,INADL,CTNND1 |
| Degradation of the extracellular matrix | CTSS,MMP8,MMP10,COL13A1,MMP11,COL9A1,BMP1B,MMP17,TLL2,KLK7 |
Protein Function
COL17A1 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by COL17A1 itself. We selected most functions COL17A1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with COL17A1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | TP63,AK3,MAP3K9,CUL3,CST5,WBP2NL,CALCOCO1,GSTM4,PNRC2,ALOX12 |
Interacting Protein
COL17A1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with COL17A1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of COL17A1.
ssdna_dtdc;EGFR
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Krenacs, T; Kiszner, G; et al. Collagen XVII is expressed in malignant but not in benign melanocytic tumors and it can mediate antibody induced melanoma apoptosis. HISTOCHEMISTRY AND CELL BIOLOGY 138:653-667(2012).
- Levell, NJ; Wingfield, CG; et al. Severe lower limb cellulitis is best diagnosed by dermatologists and managed with shared care between primary and secondary care. BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY 164:1326-1328(2011).

