CLDN5
-
Official Full Name
claudin 5 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the claudin family. Claudins are integral membrane proteins and components of tight junction strands. Tight junction strands serve as a physical barrier to prevent solutes and water from passing freely through the paracellular space between epithelial or endothelial cell sheets. Mutations in this gene have been found in patients with velocardiofacial syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
CLDN5;claudin 5;AWAL, TMVCF, transmembrane protein deleted in velocardiofacial syndrome;claudin-5;BEC1;CPETRL1;TMDVCF;transmembrane protein deleted in VCFS;transmembrane protein deleted in velocardiofacial syndrome;AWAL;TMVCF
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Bovine
- Mus musculus
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- Protein Conjugation
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- E.coli
- Non
- His
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
Background
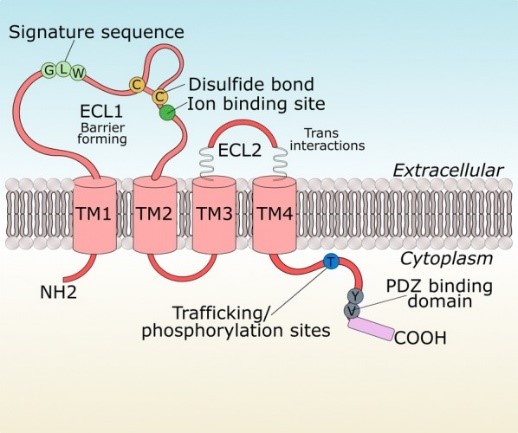
Fig1. Structure of claudin-5. (Chris Greene, 2019)
What is CLDN5 protein?
CLDN5 (claudin 5) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 22 at locus 22q11. This gene encodes a member of the claudin family. Claudins are integral membrane proteins and components of tight junction strands. Tight junction strands serve as a physical barrier to prevent solutes and water from passing freely through the paracellular space between epithelial or endothelial cell sheets. Mutations in this gene have been found in patients with velocardiofacial syndrome. The CLDN5 protein is consisted of 218 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 23.1 kDa.
What is the function of CLDN5 protein?
CLDN5 contributes to the selective barrier in endothelial and epithelial cells, regulating the passage of ions and molecules between cells. It helps regulate the permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from non-selectively crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system. CLDN5 is involved in cell adhesion, which is important for tissue integrity and the organization of multicellular organisms. It has been implicated in the process of angiogenesis, which is the formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature. CLDN5 plays a role in embryonic development, particularly in the formation of the vascular system.
CLDN5 Related Signaling Pathway
CLDN5 is a critical component of tight junctions, which are complexes that seal the paracellular space between cells. CLDN5 is involved in cell adhesion and migration signaling pathways. It helps regulate the interactions between cells and the extracellular matrix, which is important for tissue repair and development. There is evidence that CLDN5 may interact with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in cell fate decisions, tissue regeneration, and cancer. CLDN5 may be associated with integrin signaling pathways, which are involved in cell adhesion, migration, and the transmission of mechanical and chemical signals across the cell membrane. CLDN5 may also be involved in various intracellular signal transduction pathways that affect gene expression and cellular responses to external stimuli.
CLDN5 Related Diseases
Mutations or dysregulation of CLDN5 have been associated with Cerebral Cavernous Malformations (CCM), a disease characterized by abnormally dilated capillaries in the brain and spinal cord, which can lead to bleeding and neurological symptoms. CLDN5's involvement in the blood-brain barrier makes it a potential factor in autoimmune diseases like Multiple Sclerosis (MS), where the barrier's integrity is compromised. Altered expression of CLDN5 has been reported in various cancers. It may contribute to tumor progression, angiogenesis, and the formation of the blood-tumor barrier. It could also be involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is a process that cancer cells undergo to become more invasive. CLDN5 may play a role in the development of diabetic kidney disease, where alterations in tight junction proteins can affect the permeability and function of the glomerular filtration barrier. CLDN5 is expressed in certain stem cells and may be involved in their differentiation into specific cell types, with dysregulation potentially leading to developmental disorders.
Bioapplications of CLDN5
CLDN5 serves as a potential biomarker for certain diseases, and its recombinant protein can be used to develop diagnostic kits to help clinicians detect and monitor disease states. In tissue engineering, recombinant CLDN5 protein may be used to improve the properties of cell culture media, promote cell growth and differentiation, and build artificial tissues with better barrier function. In some cases, recombinant CLDN5 or its simulated peptides may be used in cosmetics and skin care products to enhance skin barrier function. In the field of food safety, recombinant CLDN5 protein may be used to develop detection systems for contaminants in food that may affect the expression or function of CLDN5 proteins.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Rina Hashimoto, 2022
In the initial process of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infects respiratory epithelial cells and then transfers to other organs the blood vessels. It is believed that SARS-CoV-2 can pass the vascular wall by altering the endothelial barrier using an unknown mechanism. In this study, the researchers investigated the effect of SARS-CoV-2 on the endothelial barrier using an airway-on-a-chip that mimics respiratory organs and found that SARS-CoV-2 produced from infected epithelial cells disrupts the barrier by decreasing Claudin-5 (CLDN5), a tight junction protein, and disrupting vascular endothelial cadherin-mediated adherens junctions. Consistently, the gene and protein expression levels of CLDN5 in the lungs of a patient with COVID-19 were decreased. CLDN5 overexpression or Fluvastatin treatment rescued the SARS-CoV-2-induced respiratory endothelial barrier disruption.
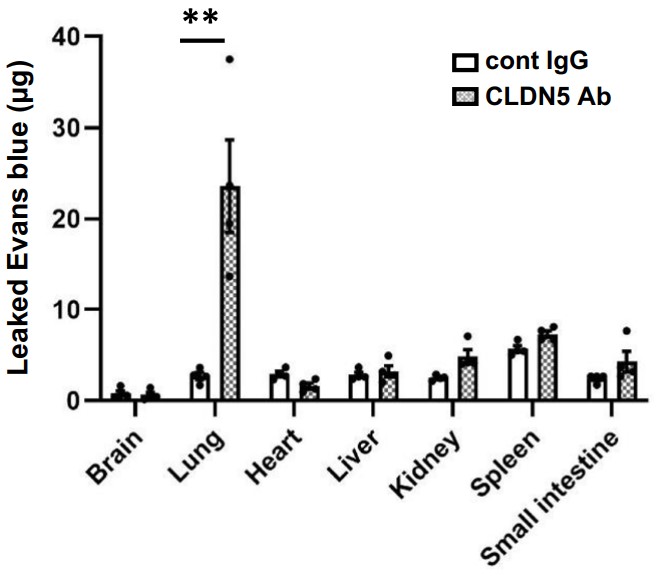
Fig1. The Miles assay using hCLDN5-KI mice.
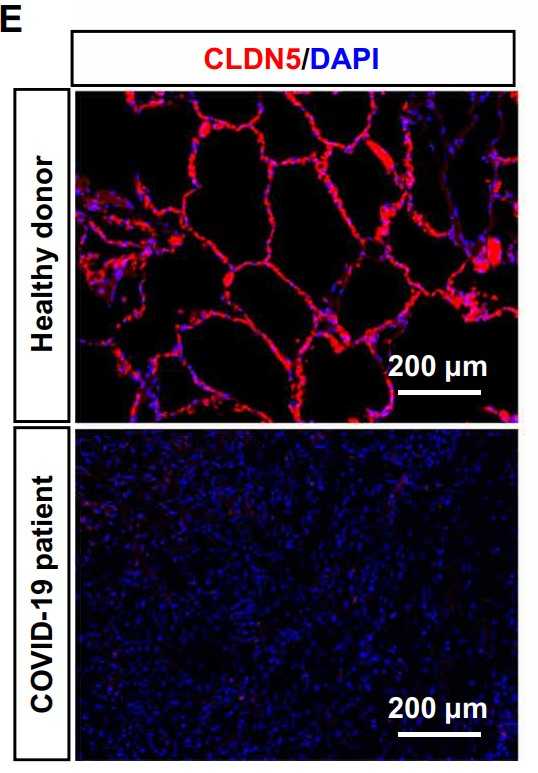
Fig2. Immunofluorescent staining for CLDN5 in the lungs of patients with or without COVID-19.
Case Study 2: Yang Zhao, 2017
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) regulates molecular and cellular entry from the cerebrovasculature into the surrounding brain parenchyma. Many diseases of the brain are associated with dysfunction of the BBB, where hypoxia is a common stressor. However, the contribution of hypoxia to BBB dysfunction is challenging to study due to the complexity of the brain microenvironment. In this study, the researchers used a BBB model with brain microvascular endothelial cells and pericytes differentiated from iPSCs to investigate the effect of hypoxia on barrier function. They found that hypoxia-induced barrier dysfunction is dependent upon increased actomyosin contractility and is associated with increased fibronectin fibrillogenesis. They propose a role for actomyosin contractility in mediating hypoxia-induced barrier dysfunction through modulation of junctional claudin-5.
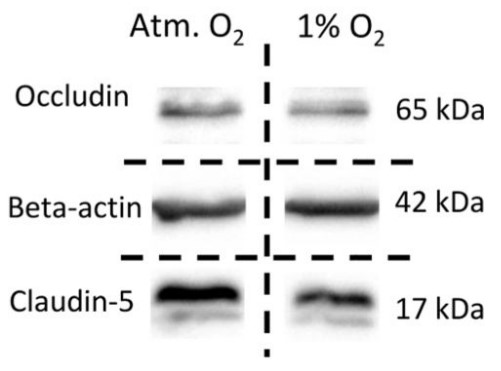
Fig3. Representative western blot for claudin-5.
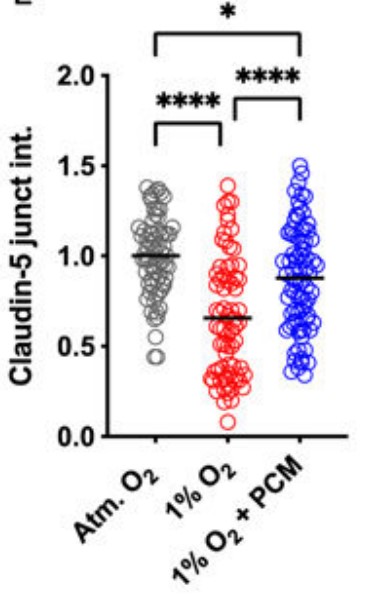
Fig4. Junctional intensity of claudin-5.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CLDN5-193H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CLDN5-194H)
Involved Pathway
CLDN5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CLDN5 participated on our site, such as Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs),Tight junction,Leukocyte transendothelial migration, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CLDN5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | CLDNE,JAM2,BMA2,NEGR1,NRXN3A,SELP,CLDN17,BF1,CLDNC,VCAN |
| Hepatitis C | IFNA7,IKBKG,PDPK1,OSTN,BRAF,IFIT1,GSK3B,CLDN9,Ifna11,OAS1A |
| Tight junction | YES1,JAM3,CTNNA3,MYH7B,OCLNB,PRKCH,ACTB,PPP2R2BB,CLDN3,JAM2A |
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | CLDN9,PIK3CD,CYBB,CLDN6,ITGB2L,MMP9,MAPK12,RHOH,CXCL12,ITGA4 |
Protein Function
CLDN5 has several biochemical functions, for example, molecular_function. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CLDN5 itself. We selected most functions CLDN5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CLDN5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| molecular_function | FIBINB,OARD1,INPP4AA,ZNF688,GM12695,PRR15LA,SLC45A4,LMF2B,NMBB,OSGIN2 |
Interacting Protein
CLDN5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CLDN5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CLDN5.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


