CHST11
-
Official Full Name
carbohydrate (chondroitin 4) sulfotransferase 11 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the sulfotransferase 2 family. It is localized to the golgi membrane, and catalyzes the transfer of sulfate to position 4 of the N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) residue of chondroitin. Chondroitin sulfate constitutes the predominant proteoglycan present in cartilage, and is distributed on the surfaces of many cells and extracellular matrices. A chromosomal translocation involving this gene and IgH, t(12;14)(q23;q32), has been reported in a patient with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
CHST11;carbohydrate (chondroitin 4) sulfotransferase 11;carbohydrate sulfotransferase 11;C4ST;C4St 1;C4ST1;HSA269537;C4S-1;C4ST-1;Chondroitin 4 O sulfotransferase 1;Chondroitin 4 sulfotransferase;Chondroitin 4-O-sulfotransferase 1;Chondroitin 4-sulfotransferase 1;CHST 11;CHSTB_HUMAN;IgH/CHST11 fusion;OTTHUMP00000242139;OTTHUMP00000242140
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is CHST11 Protein?
CHST11 (Carbohydrate Sulfotransferase 11) is a vital enzyme that catalyzes the sulfation of chondroitin, a process critical for synthesizing chondroitin sulfate—a major component of cartilage and the extracellular matrix. This sulfation directly impacts tissue structure, cellular signaling, and joint health. Research highlights CHST11's role in musculoskeletal development, as its dysfunction is linked to osteoarthritis, cartilage degradation, and skeletal abnormalities. Beyond structural support, CHST11 influences cell adhesion and growth factor interactions, making it a focus in regenerative medicine and biotech therapies. Targeting CHST11 pathways could advance treatments for joint disorders, tissue engineering, and biomarker-driven diagnostics, emphasizing its potential in precision medicine and connective tissue disease management.What is the Function of CHST11 Protein?
The CHST11 protein, formally known as carbohydrate sulfotransferase 11, serves a critical role in catalyzing the sulfation of chondroitin, a process essential for synthesizing chondroitin sulfate—a key component of cartilage and the extracellular matrix. This enzymatic activity ensures proper structural support, joint flexibility, and cellular communication in connective tissues. CHST11’s function is pivotal in musculoskeletal health, with dysregulation linked to osteoarthritis, cartilage degradation, and skeletal abnormalities. Additionally, it influences cell adhesion and growth factor interactions, making it a focus in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Targeting CHST11 pathways offers therapeutic potential for treating joint disorders, enhancing biomarker-driven diagnostics, and advancing precision medicine strategies for connective tissue diseases. Its role in maintaining tissue integrity underscores its importance in biotech research and innovative therapies.CHST11 Related Signaling Pathway
The CHST11 protein is central to signaling pathways governing chondroitin sulfate synthesis, a process vital for extracellular matrix formation and cartilage integrity. It interacts with key pathways like TGF-beta, FGF, and Wnt, which regulate cell differentiation, tissue repair, and skeletal development. By sulfating chondroitin, CHST11 modulates cell-matrix interactions and growth factor signaling, influencing cartilage homeostasis and joint function. Dysregulation in CHST11-linked pathways is implicated in osteoarthritis, skeletal dysplasia, and connective tissue disorders. Targeting these pathways offers therapeutic potential for cartilage regeneration, tissue engineering, and precision treatments. Research into CHST11 signaling also enhances biomarker discovery for musculoskeletal diseases, driving innovations in regenerative medicine and biotech-driven therapies.CHST11 Related Diseases
The CHST11 protein governs critical signaling pathways essential for chondroitin sulfate synthesis, a cornerstone of extracellular matrix stability and cartilage integrity. Central to pathways like TGF-beta, FGF, and Wnt signaling, CHST11 regulates cellular differentiation, tissue repair, and skeletal development through its sulfation activity. This enzymatic function ensures proper cell-matrix adhesion, growth factor communication, and cartilage homeostasis, directly influencing joint flexibility and structural resilience. Dysregulated CHST11 signaling is implicated in osteoarthritis, skeletal dysplasia, and connective tissue degradation, underscoring its role in musculoskeletal health. Targeting these pathways offers therapeutic potential for cartilage regeneration, tissue engineering, and precision medicine. Advances in CHST11 research also drive biomarker discovery for early disease detection and innovative biotech applications in regenerative therapies. By elucidating its pathway interactions, scientists aim to develop targeted treatments for joint disorders and enhance strategies for managing connective tissue diseases, positioning CHST11 as a pivotal focus in musculoskeletal and biotechnological research.Bioapplications of CHST11
The CHST11 protein holds transformative bioapplications, particularly in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. By enabling precise chondroitin sulfate synthesis, CHST11 supports the development of biomimetic scaffolds for cartilage repair, addressing conditions like osteoarthritis and spinal disc degeneration. Its role in modulating extracellular matrix composition enhances 3D-printed tissue constructs for joint and bone regeneration. In diagnostics, CHST11 serves as a biomarker for early detection of musculoskeletal disorders and cancer progression, where altered sulfation patterns influence tumor behavior. Biotech therapies targeting CHST11 pathways aim to restore cartilage integrity and combat connective tissue diseases. Additionally, its application in drug delivery systems leverages sulfated glycosaminoglycans for improved therapeutic efficacy. These advancements position CHST11 at the forefront of precision medicine, biotech innovation, and next-generation therapies for degenerative and oncological conditions.Case Study
Case Study 1: Chen X. et al. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023
KIAA1429, or VIRMA, is a key player in m6A modification and impacts diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). High levels of KIAA1429 are linked to worse outcomes in DLBCL patients. Studies show that removing KIAA1429 slows cancer cell growth, stops the cell cycle, and reduces tumor size. It works by altering the stability of CHST11 mRNA through m6A, which then affects MOB1B and the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway. This makes KIAA1429 a promising target for treating DLBCL.-
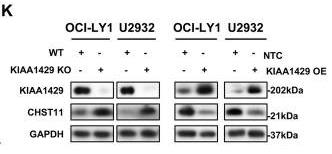 Fig1. The protein expression of KIAA1429 and CHST11 was negatively correlated as confirmed by western blotting.
Fig1. The protein expression of KIAA1429 and CHST11 was negatively correlated as confirmed by western blotting. -
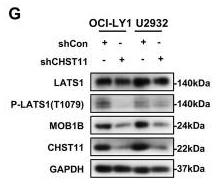 Fig2. Knockdown of CHST11 suppressed MOB1B protein expression and LATS1 phosphorylation.
Fig2. Knockdown of CHST11 suppressed MOB1B protein expression and LATS1 phosphorylation.
Case Study 2: Zhou H. et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2016
Carbohydrate sulfotransferases 11-13 (CHST11-13) are enzymes that modify chondroitin and are linked to various diseases. This study found that CHST11 and CHST13 levels are lower in highly invasive hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells (MHCC97H) compared to less invasive cells (MHCC97L). Manipulating these enzymes changed the cells' metastatic potential and drug sensitivity. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of the MAPK pathway in these cells reduced invasiveness and restored drug sensitivity, highlighting CHST11-13's role in HCC progression.-
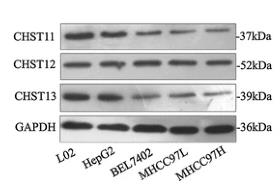 Fig3. Western blotting analysis revealed significant reduced protein levels of CHST11, CHST13 in MHCC97H cells.
Fig3. Western blotting analysis revealed significant reduced protein levels of CHST11, CHST13 in MHCC97H cells. -
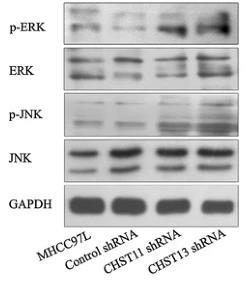 Fig4. Detected by real-time PCR, expression of MAPK signaling molecules is raised at phosphorylation levels in MHCC97L cells with CHST11 or CHST13 shRNA transfection.
Fig4. Detected by real-time PCR, expression of MAPK signaling molecules is raised at phosphorylation levels in MHCC97L cells with CHST11 or CHST13 shRNA transfection.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CHST11-1295H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CHST11-1295H)
Involved Pathway
CHST11 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CHST11 participated on our site, such as Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis - chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CHST11 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis - chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate | CSGALNACT1,XYLT1,CHST3,B3GAT3,B3GALT6,CHST7,CHST3B,CHST3A,CSGALNACT2,CHST14 |
-
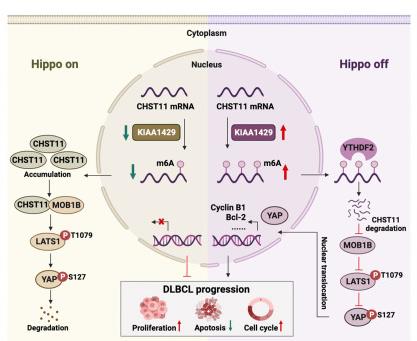 Fig1. Model of KIAA1429-mediated m6A modification regulating DLBCL progression through the Hippo–YAP pathway. (Xiaomin Chen, 2023)
Fig1. Model of KIAA1429-mediated m6A modification regulating DLBCL progression through the Hippo–YAP pathway. (Xiaomin Chen, 2023) -
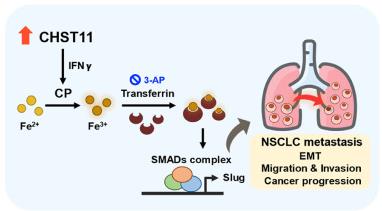 Fig2. Hypothetical model showed the CHST11-CP-iron axis maintains persistent NSCLC metastasis potential. (Wei-Min Chang, 2022)
Fig2. Hypothetical model showed the CHST11-CP-iron axis maintains persistent NSCLC metastasis potential. (Wei-Min Chang, 2022)
Protein Function
CHST11 has several biochemical functions, for example, N-acetylgalactosamine 4-O-sulfotransferase activity,N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase activity,chondroitin 4-sulfotransferase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CHST11 itself. We selected most functions CHST11 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CHST11. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chondroitin 4-sulfotransferase activity | CHST12 |
| N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase activity | CHST15 |
| N-acetylgalactosamine 4-O-sulfotransferase activity | HS3ST3B1B,SULT1ST1,CHST3B,SULT1D1,SULT1ST7,SULT2ST2,SULT1ST2,SULT2ST1,SULT6B1,HS6ST1B |
Interacting Protein
CHST11 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CHST11 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CHST11.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


