CEACAM3
-
Official Full Name
carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 3 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the family of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAMs), which are used by several bacterial pathogens to bind and invade host cells. The encoded transmembrane protein directs phagocytosis of several bacterial species that is dependent on the small GTPase Rac. It is thought to serve an important role in controlling human-specific pathogens by the innate immune system. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. -
Synonyms
CEACAM3;carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 3;CGM1;CD66d;CD66d antigen;carcinoembryonic antigen CGM1;nonspecific cross-reacting antigen;carcinoembryonic antigen gene family member 1;CEA;W264;W282;CD66D;MGC119875
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Human Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- SUMO
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is CEACAM3 Protein?
CEACAM3 is like one of those unsung heroes in your immune system. Found mainly in granulocytes, a type of white blood cell, this protein helps spot and deal with bacterial invaders that sneak past our standard defenses. It basically tags certain bacteria, making it easier for the immune cells to gobble them up and get rid of them. Scientists are pretty intrigued by CEACAM3, especially when thinking about new ways to treat infections or even cancer. They're looking into how modifying this protein's activity might make it harder for cancer cells to dodge our immune system. So, while CEACAM3 might not be a name you hear every day, it’s got a big job keeping us healthy and could lead to some groundbreaking therapies in the future.What is the Function of CEACAM3 Protein?
The CEACAM3 protein acts like a frontline defender in our immune system, found mainly in granulocytes, a type of white blood cell. Its primary role is to identify and tag tricky bacteria that slip past other defenses, making them targets for destruction by immune cells. This tagging process is crucial for clearing infections efficiently. Beyond battling bacteria, scientists are exploring its potential in cancer treatment, considering how tweaking CEACAM3 might help the immune system target cancer cells more effectively. So, while it might not get much attention, CEACAM3 is vital in keeping us healthy and could lead to breakthroughs in medical treatments.CEACAM3 Related Signaling Pathway
The CEACAM3-related signaling pathway is like a communication hub within granulocytes, a type of white blood cell, that springs into action when CEACAM3 spots invading bacteria. Once activated, this pathway triggers a series of chemical reactions, effectively setting off the immune response to engulf and destroy the invaders. Researchers are keenly studying this pathway because understanding it better could lead to new therapies that boost our natural infection-fighting abilities or even adapt these mechanisms to target cancer cells. So, while it might sound complex, this pathway is crucial for our defense system and holds promise for advancing medical treatments.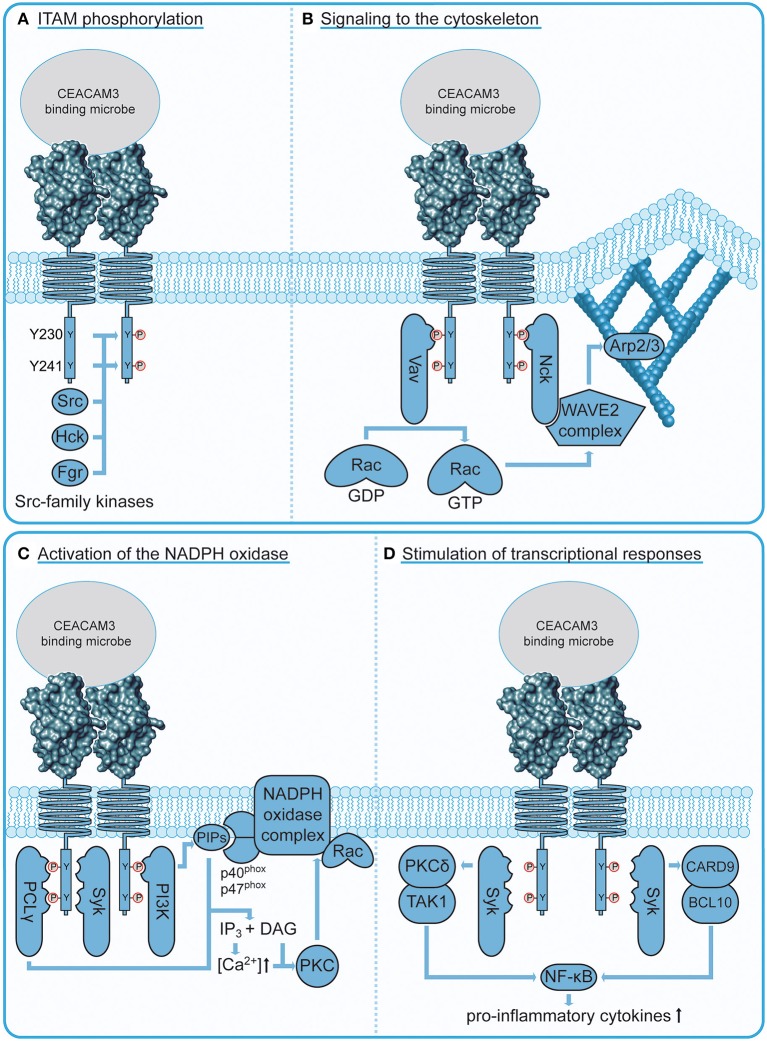
Fig1. CEACAM3 signaling connections. (Patrizia Bonsignore, 2020)
CEACAM3 Related Diseases
CEACAM3 plays a key role in the body’s fight against bacterial infections, so when it's not doing its job right, people might end up getting sick more easily from certain bacteria. Scientists are also exploring whether problems with CEACAM3 might relate to autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly targets the body’s own tissues. There's also interest in its link to cancer, as CEACAM3 helps the immune system recognize threats like cancer cells. By digging into how CEACAM3 works, researchers are aiming to uncover new treatments for infections, autoimmune issues, and even cancer, highlighting its importance in health research.Bioapplications of CEACAM3
CEACAM3 is grabbing attention because it's got some cool potential in various biological uses, especially since it's a key player in the immune system. What makes this protein such a big deal is that it helps white blood cells spot and wipe out certain bacteria that lead to infections. Scientists are looking into ways to use this ability not only to boost our ability to fight infections but also to develop new treatments for different diseases. For instance, CEACAM3's knack for identifying and flagging pathogens makes it a fascinating target for developing new drugs that can enhance immune responses or work as part of robust diagnostics to detect bacterial infections early. There’s also ongoing research into using insights gained from CEACAM3 to better understand how the immune system can be directed to recognize and kill cancer cells. This could lead to breakthroughs in cancer treatment by enhancing how therapies target tumor cells. All in all, CEACAM3 isn't just a part of our immune arsenal; it's a promising tool that scientists are hoping to leverage in the constant battle against diseases.Case Study
Case Study 1: Kuiper JWP. et al. J Cell Sci. 2023
CEACAM3 helps immune cells engulf specific bacteria without opsonins by activating Rac, a key player in cell structure changes. Using a CRISPR/Cas9 screen, researchers identified CYRI-B as a protein that hinders this phagocytosis process. Cells without CYRI-B showed enhanced engulfing activity, which reversed when CYRI-B was restored. This highlights CYRI-B's role as a negative regulator in the CEACAM3-mediated bacteria capture pathway.-
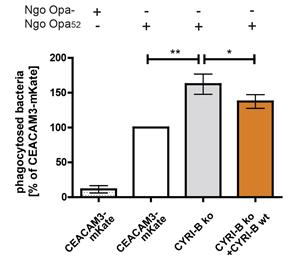 Fig1. CEACAM3-mediated phagocytosis was determined by flow cytometry.
Fig1. CEACAM3-mediated phagocytosis was determined by flow cytometry. -
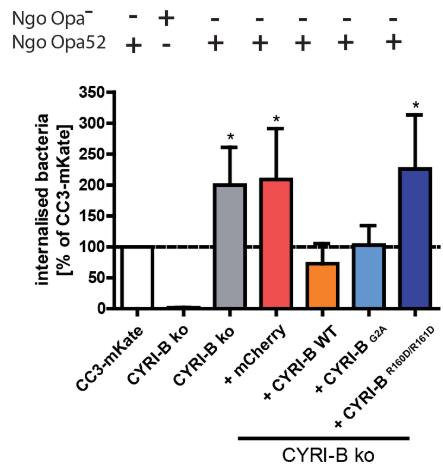 Fig2. CEACAM3-mediated phagocytosis of Ngo Opa52 or non-opaque gonococci (Ngo Opa−) by the complemented cell lines from B was quantified using gentamicin protection assays.
Fig2. CEACAM3-mediated phagocytosis of Ngo Opa52 or non-opaque gonococci (Ngo Opa−) by the complemented cell lines from B was quantified using gentamicin protection assays.
Case Study 2: Pils S. et al. PLoS One. 2012
CEACAM3 helps granulocytes recognize and ingest specific bacteria without opsonins through a sequence that gets activated by Src kinases. This activation triggers Rac, leading to actin changes necessary for engulfing bacteria. Our research found that proteins Nck1 and Nck2 bind to phosphorylated CEACAM3, aiding this process. Disrupting Nck1 or Nck2 hampers bacterial intake by affecting actin rearrangements facilitated by the WAVE2 complex.-
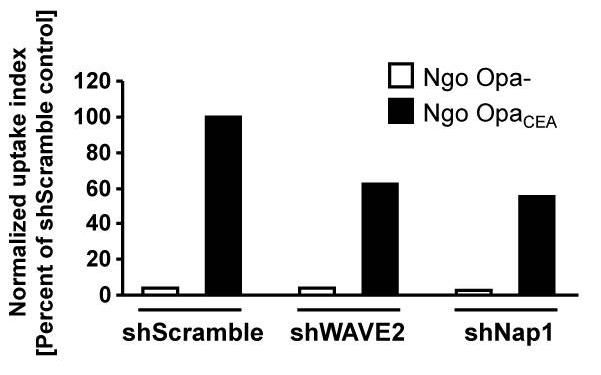 Fig3. 293 cells were co-transfected with CEACAM3 WT-GFP together with myc-WAVE2 ΔVCA or the empty vector.
Fig3. 293 cells were co-transfected with CEACAM3 WT-GFP together with myc-WAVE2 ΔVCA or the empty vector. -
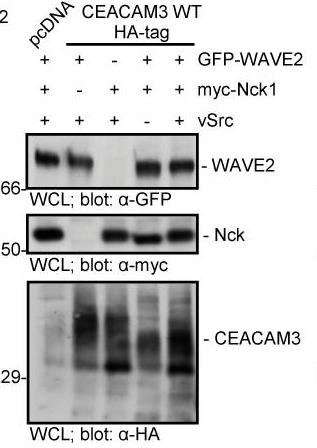 Fig4. 293 cells were co-transfected with GFP-WAVE2, myc-Nck1, CEACAM3 WT-HA and vSrc as indicated.
Fig4. 293 cells were co-transfected with GFP-WAVE2, myc-Nck1, CEACAM3 WT-HA and vSrc as indicated.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CEACAM3-0957H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CEACAM3-0957H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CEACAM3-0983H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CEACAM3-0983H)
Involved Pathway
CEACAM3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CEACAM3 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CEACAM3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
-
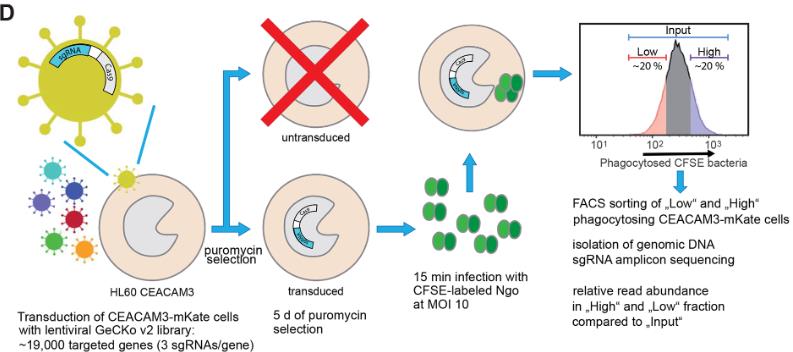 Fig1. Scheme depicting the workflow of the genome-wide screen using HL60 CEACAM3–mKate cells and lentiviral transduction with the GeCKo v2 library. (Johannes W P Kuiper, 2023)
Fig1. Scheme depicting the workflow of the genome-wide screen using HL60 CEACAM3–mKate cells and lentiviral transduction with the GeCKo v2 library. (Johannes W P Kuiper, 2023) -
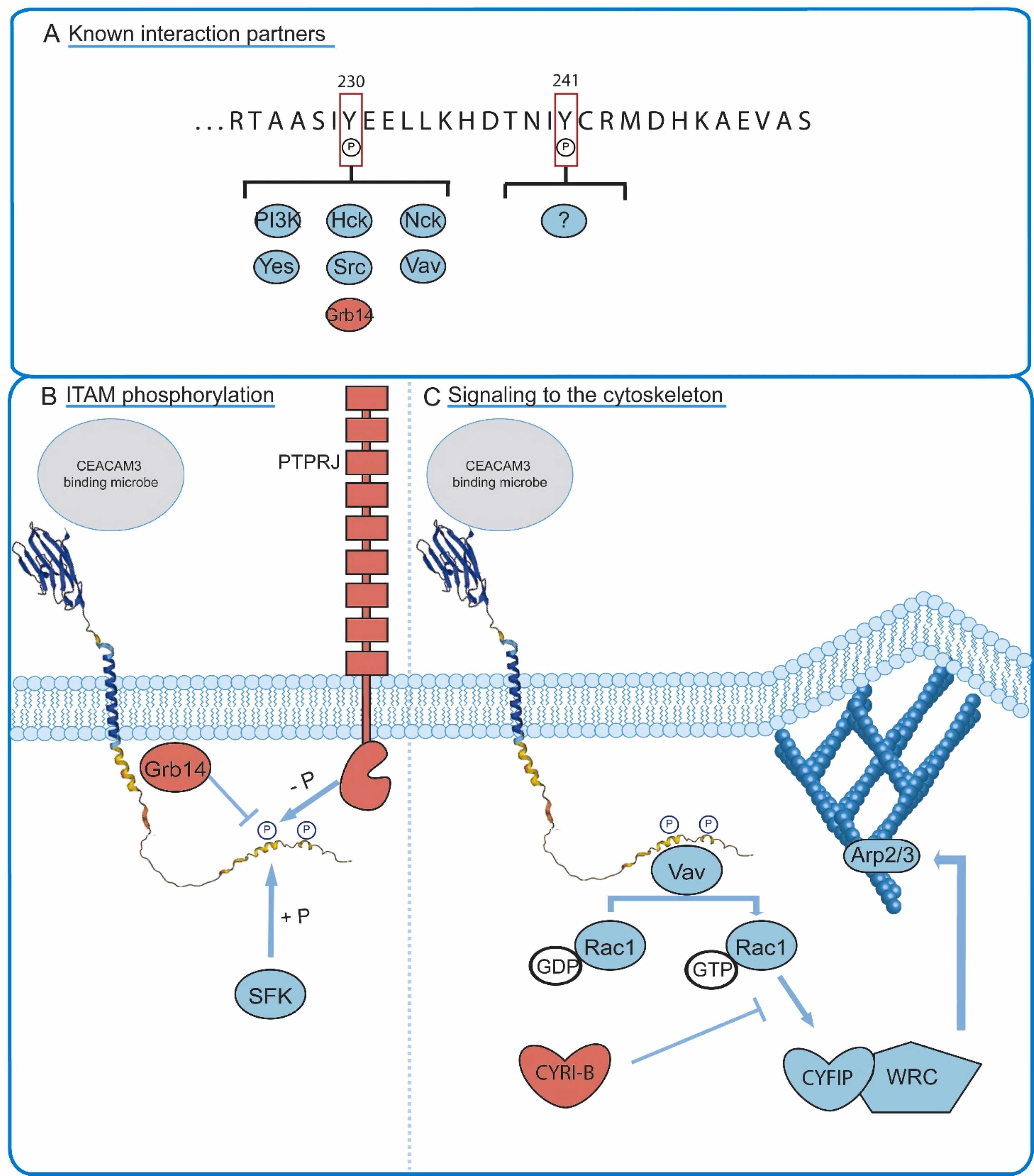 Fig2. Schematic overview of the negative regulation of CEACAM3. (Johannes W P Kuiper, 2024)
Fig2. Schematic overview of the negative regulation of CEACAM3. (Johannes W P Kuiper, 2024)
Protein Function
CEACAM3 has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CEACAM3 itself. We selected most functions CEACAM3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CEACAM3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
CEACAM3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CEACAM3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CEACAM3.
Resources
Research Area
ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related MoleculesMyeloid Lineage Markers
Immunoglobulin Superfamily CAMs
Epithelial Cell Markers and Intracellular Molecules
CD Antigen (Neutrophils)
Tumor Antigens
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wakabayashi-Nakao, K; Hatakeyama, K; et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 4 (CEACAM4) is specifically expressed in medullary thyroid carcinoma cells. BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH-TOKYO 35:237-242(2014).
- Panczyszyn, A; Wieczorek, M; et al. Role of CEACAM in neutrophil activation. POSTEPY HIGIENY I MEDYCYNY DOSWIADCZALNEJ 66:574-582(2012).


