CDH13
-
Official Full Name
cadherin 13 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the cadherin superfamily. The encoded protein is localized to the surface of the cell membrane and is anchored by a GPI moiety, rather than by a transmembrane domain. The protein lacks the cytoplasmic domain characteristic of other cadherins, and so is not thought to be a cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein. This protein acts as a negative regulator of axon growth during neural differentiation. It also protects vascular endothelial cells from apoptosis due to oxidative stress, and is associated with resistance to atherosclerosis. The gene is hypermethylated in many types of cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011] -
Synonyms
CDH13;cadherin 13;CDHH;P105;cadherin-13;T-cad;T-cadherin;heart cadherin;H-cadherin (heart);cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- His
- T7
- Non
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDH13-11031H | Recombinant Human CDH13, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | C-term-350a.a. | |
| CDH13-1504M | Recombinant Mouse CDH13 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His | ||
| CDH13-2961H | Recombinant Human CDH13 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 364-713 aa | |
| Cdh13-721M |
Active Recombinant Mouse Cdh13 Protein, His-tagged
|
Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His | Met1-Gly693 |
|
| CDH13-0975H | Recombinant Human CDH13 Protein, GST-Tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| CDH13-1156C | Recombinant Chicken CDH13 | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| Cdh13-1947M | Recombinant Mouse Cdh13 protein, His & GST-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | GST&His | Tyr478-Asn690 |
|
| Cdh13-1948R | Recombinant Rat Cdh13 protein, His & GST-tagged | E.coli | Rat | GST&His | Tyr478-Asn690 |
|
| Cdh13-25R | Recombinant Rat Cdh13, Fc tagged | Human Cells | Rat | His | 1-692 a.a. |
|
| Cdh13-26R | Recombinant Rat Cdh13, His tagged | Human Cells | Rat | His | 1-692 a.a. |
|
| Cdh13-27R | Recombinant Rat Cdh13, LEVLFQ tagged | Human Cells | Rat | His | 1-692 a.a. |
|
| CDH13-3166M | Recombinant Mouse CDH13 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| CDH13-31H | Recombinant Human CDH13 protein, T7/His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&T7 | 139-693 a.a. |
|
| CDH13-775R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey CDH13 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cells | Rhesus macaque | His |
|
|
| Cdh13-991M | Recombinant Rat Cdh13 protein, hFc-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Fc | Met1-Ala692 |
|
| Cdh13-992M | Recombinant Mouse Cdh13 Protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His | 1-692 a.a. |
|
| CDH13-802RCL | Recombinant Rat CDH13 cell lysate | Human Cells | Rat | Non |
|
|
| CDH13-1269R | Recombinant Rat CDH13 protein(Met1-Ala692) | HEK293 | Rat | Non | Met1-Ala692 |
|
| Cdh13-148R | Recombinant Rat Cdh13 Protein, hFc-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Fc | Met1-Ala692 |
|
| Cdh13-1505M | Recombinant Mouse Cdh13 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| Cdh13-1505M-B | Recombinant Mouse Cdh13 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| CDH13-3137HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CDH13 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 713 amino acids |
|
| CDH13-3864H | Recombinant Human CDH13 Protein (Glu23-Ala692), C-His tagged | Mammalian Cells | Human | His | Glu23-Ala692 |
|
| CDH13-601R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque CDH13 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| CDH13-601R-B | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque CDH13 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque |
|
Background
What is CDH13 protein?
CDH13 gene (cadherin 13) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 16 at locus 16q23. This gene encodes a member of the cadherin superfamily. The encoded protein is localized to the surface of the cell membrane and is anchored by a GPI moiety, rather than by a transmembrane domain. The protein lacks the cytoplasmic domain characteristic of other cadherins, and so is not thought to be a cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein. This protein acts as a negative regulator of axon growth during neural differentiation. It also protects vascular endothelial cells from apoptosis due to oxidative stress, and is associated with resistance to atherosclerosis. The gene is hypermethylated in many types of cancer. The CDH13 protein is consisted of 713 amino acids and CDH13 molecular weight is approximately 78.3 kDa.
What is the function of CDH13 protein?
The CDH13 protein, also known as T-cadherin or H-cadherin, is an atypical member of the cadherin family. It is widely distributed mainly on the surface of normal cells, down-regulated in a variety of malignant tumors, and is associated with poor prognosis of tumors. The reexpression of CDH13 can inhibit the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells. In addition, CDH13 is involved in regulating adiponectin levels, affecting vascular remodeling, neointima formation, inflammatory response, and the development of atherosclerosis. CDH13 plays a central role in cell signaling by binding low-density lipoprotein and adiponectin and activating the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. It is thought that CDH13 may be a regulatory protein rather than an adhesion molecule because of its relatively weak connection to the outer membrane.
CDH13 Related Signaling Pathway
CDH13 controls cell migration, neurite growth, and axon guidance through its low-adhesion homologous or allogenic interactions. In the hippocampus, CDH13 is localized to the presynaptic compartment of inhibitory GABAergic neurons, specifically associated with Parvalbumin-positive neurons. CDH13 may play a role in the development of coronary artery disease through the cell-extracellular matrix interaction pathway, possibly as a biomarker. CDH13 plays a key role in the synaptic activity of GABAergic circuits in the hippocampus, influencing cognitive function and memory formation.

Fig1. Schematic diagram of the signaling pathways involved in the CDH13-induced inhibitory effect on human PC cells. (Dengfei Xu, 2020)
CDH13 Related Diseases
CDH13 protein has been implicated in a variety of diseases, mainly including neoplastic diseases and cardiovascular diseases. In terms of tumor, CDH13 expression is down-regulated in lung cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer and other malignant tumors, and is associated with poor tumor prognosis. The reexpression of CDH13 can inhibit the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells, indicating that it may have the characteristics of tumor suppressor gene. In addition, the polymorphism of CDH13 gene is significantly associated with metabolic syndrome, diabetes, atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. In terms of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders, the CDH13 gene has been linked to the risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and its comorbid disorders.
Bioapplications of CDH13
The application of CDH13 protein is mainly in the field of medical research and clinical diagnosis. As a tumor suppressor gene, CDH13 is down-regulated in a variety of malignancies, making it an important biomarker for cancer risk assessment and prognostic monitoring. In clinical diagnosis, the detection of CDH13 helps in the early detection and classification of cancer, such as the detection of CDH13 expression levels by immunohistochemical or molecular biological methods. In addition, the reexpression of CDH13 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells, which opens up the possibility of developing new cancer treatment strategies, such as gene therapy or drug intervention to restore or mimic the function of CDH13. In cardiovascular disease studies, the association of CDH13 with blood pressure, lipid levels, atherosclerosis, etc., suggests its potential application in cardiovascular health assessment.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Britt Mossink, 2022
Cadherin-13 (CDH13) has been associated with autism and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. CDH13 localizes at inhibitory presynapses, specifically of parvalbumin (PV) and somatostatin (SST) expressing GABAergic neurons. However, the mechanism by which CDH13 regulates the function of inhibitory synapses in human neurons remains unknown. Starting from human-induced pluripotent stem cells, researchers established a robust method to generate a homogenous population of SST and MEF2C (PV-precursor marker protein) expressing GABAergic neurons (iGABA) in vitro, and co-cultured these with glutamatergic neurons at defined E/I ratios on micro-electrode arrays. They identified functional network parameters that are most reliably affected by GABAergic modulation as such, and through alterations of E/I balance by reduced expression of CDH13 in iGABAs. And CDH13 deficiency in iGABAs decreased E/I balance by means of increased inhibition. Moreover, CDH13 interacts with Integrin-β1 and Integrin-β3, which play opposite roles in the regulation of inhibitory synaptic strength via this interaction.

Fig1. Average network burst shape of representative cultures from E/I 65:35 control and CDH13-deficient networks at DIV 49.

Fig2. Western blot showing co-immunoprecipitation of CDH13 with GABAAα1.
Case Study 2: Boris Dasen, 2023
Pericytes are mural cells that play an important role in regulation of angiogenesis and endothelial function. To date, classical N-cadherin is the only cadherin described on pericytes. Here, researchers demonstrate that pericytes also express T-cadherin (H-cadherin, CDH13). The aim of the study was to investigate T-cadherin function in pericytes. Expression of T-cadherin in pericytes from different tissues was performed by immunofluorescence analysis. Using lentivirus-mediated gain-of-function and loss-of-function in cultured human pericytes, they demonstrate that T-cadherin regulates pericyte proliferation, migration, invasion, and interactions with endothelial cells during angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. T-cadherin effects are associated with the reorganization of the cytoskeleton, modulation of cyclin D1, α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA), integrin β3, metalloprotease MMP1, and collagen expression levels, and involve Akt/GSK3β and ROCK intracellular signaling pathways.
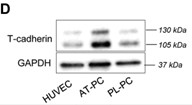
Fig3. Immunoblotting analysis of T-cadherin protein expression.

Fig4. T-cadherin effects on sprouting angiogenesis.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CDH13-0975H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CDH13-3864H)
Involved Pathway
CDH13 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CDH13 participated on our site, such as Adherens junctions interactions,Cell junction organization,Cell-Cell communication, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CDH13 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell junction organization | CDH12A,PLECA,FBLIM1,CDH5,CDH17,CDH24,CTNND1,LIMS1,CDH7,COL17A1 |
| Cell-Cell communication | CDH6,COL17A1A,CDH3,FBLIM1,DCC,INADL,PLECA,NPHS1,KIRREL,SIRPB1 |
| Adherens junctions interactions | CDH5,JUP,CDH18A,PVRL1A,ANG,CADM2A,CDH4,CDH2,CTNND1,CDH24 |
| Cell-cell junction organization | PVRL1A,CDH5,CADM2,CDH10,CDH18A,CDH10A,CDH12A,CADM2B,PVRL2L,CDH11 |
Protein Function
CDH13 has several biochemical functions, for example, adiponectin binding,cadherin binding,calcium ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CDH13 itself. We selected most functions CDH13 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CDH13. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| adiponectin binding | ADIPOR2,ADIPOR1 |
| low-density lipoprotein particle binding | SCARB1,CRP,SORL1,LIPC,PCSK9,COLEC12,ANKRA2,THBS1,MSR1,SCARF1 |
| calcium ion binding | PLSCR1,CBLC,CCBE1,PLCH1,PCDH2AB2,TBC1D9,CDH8,PCDH2G28,CASQ2,CDH5 |
| protein homodimerization activity | TFAP4,JAM3,FAP,ALDH1A3,PSPH,NOS2,SLC11A1,VPS25,GHR,CITED1 |
| lipoprotein particle binding | MAPT,APOE,GPIHBP1 |
| cadherin binding | OLFM4,TBC1D2,GNA13A,CTNNA1,CTNNAL1,MMP24,CTNND1,TRPC4,AKAP5,CTNNA2 |
Interacting Protein
CDH13 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CDH13 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CDH13.
AURKA;HMMR;CHEK2;PTPN1;CCND1;RAD51;CASP8;MAPK6
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Dai, J; Li, L; et al. Parallel detection and quantitative analysis of specific binding of proteins by oblique-incidence reflectivity difference technique in label-free format. SCIENCE CHINA-PHYSICS MECHANICS & ASTRONOMY 57:2039-2042(2014).
- Bosserhoff, AK; Ellmann, L; et al. Loss of T-Cadherin (CDH-13) Regulates AKT Signaling and Desensitizes Cells to Apoptosis in Melanoma. MOLECULAR CARCINOGENESIS 53:635-647(2014).



