CDH11
-
Official Full Name
cadherin 11, type 2, OB-cadherin (osteoblast) -
Synonyms
CDH11;cadherin 11, type 2, OB-cadherin (osteoblast);cadherin-11;CAD11;OB;OB Cadherin;CDHOB;OSF-4
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- Mus musculus
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- GST
- Fc
- Flag
- His
- Strep II
- Non
- Avi
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is CDH11 protein?
CDH11 gene (cadherin 11) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 16 at locus 16q21. This gene encodes a type II classical cadherin from the cadherin superfamily, integral membrane proteins that mediate calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion. Mature cadherin proteins are composed of a large N-terminal extracellular domain, a single membrane-spanning domain, and a small, highly conserved C-terminal cytoplasmic domain. Type II (atypical) cadherins are defined based on their lack of a HAV cell adhesion recognition sequence specific to type I cadherins. Expression of this particular cadherin in osteoblastic cell lines, and its upregulation during differentiation, suggests a specific function in bone development and maintenance. The CDH11 protein is consisted of 796 amino acids and CDH11 molecular weight is approximately 88.0 kDa.
What is the function of CDH11 protein?
CDH11 plays a crucial role in cell-to-cell adhesion, helping to maintain tissue integrity and stability by binding to other cadherin molecules on adjacent cells. It is involved in the morphogenesis of various tissues, including the development of the skeleton, particularly in processes like chondrogenesis and osteogenesis. CDH11 is expressed in mesenchymal cells and is involved in their migration and differentiation, which is important during embryonic development and tissue repair. It is involved in the wound healing process, where it contributes to tissue repair by regulating cell migration and adhesion during the healing process. It may also play a role in the inflammatory response, potentially contributing to the pathogenesis of certain inflammatory diseases.
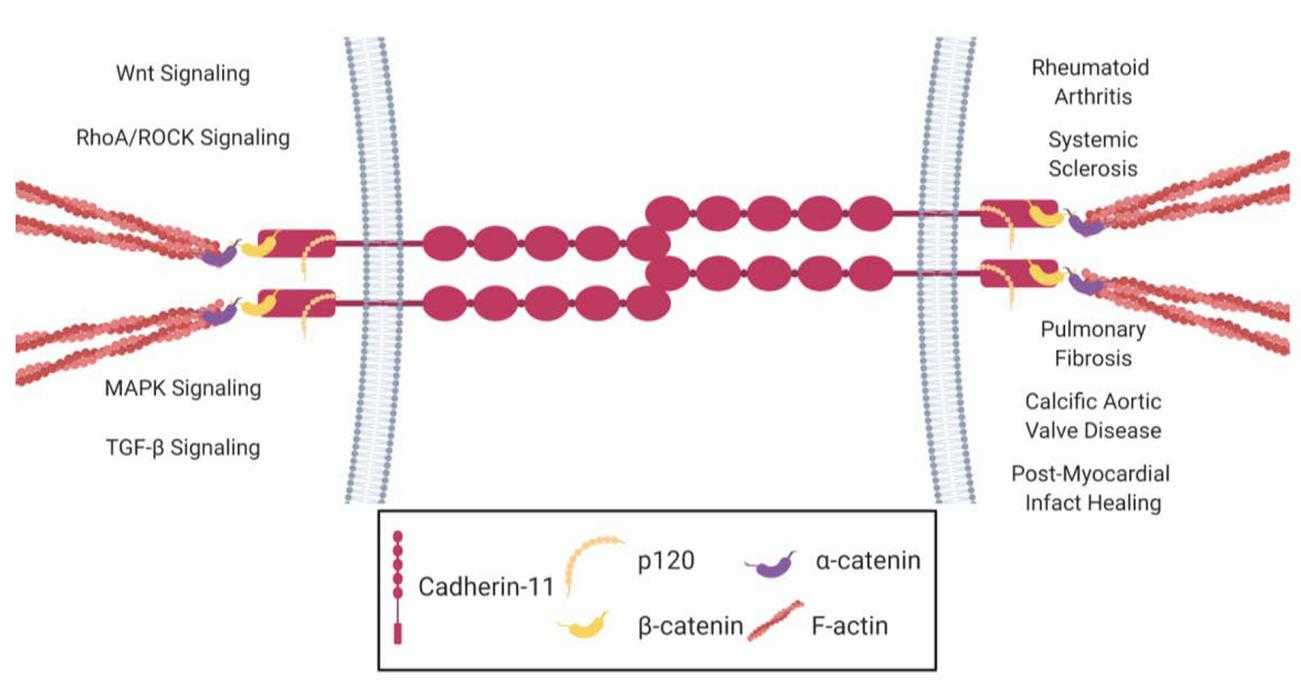
Fig1. Cadherin-11's role in signaling pathways and disease. (Lance A Riley, 2021)
CDH11 Related Signaling Pathway
The interaction of CDH11 with β-catenin can modulate the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, which is involved in cell fate determination, tissue regeneration, and oncogenesis. CDH11 may be involved in the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which includes the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and is important for cell growth, differentiation, and survival. The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway is a key regulator of cell survival, proliferation, and metabolism. CDH11 may interact with this pathway to influence cell fate decisions. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling is involved in various cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. CDH11 may be connected to this pathway in certain cell types. The Hippo pathway is a kinase cascade that regulates organ size and tissue homeostasis. CDH11 may influence this pathway to control cell proliferation and differentiation.
CDH11 Related Diseases
Abnormal expression of the CDH11 protein has been linked to a variety of diseases, ranging from abnormal bone and soft tissue development to cancer and inflammatory diseases. In bone diseases, CDH11 may be associated with certain types of bone deformities and chondrodysplasia. In the field of cancer, especially breast cancer and osteosarcoma, changes in CDH11 expression are closely associated with tumor aggressiveness, metastasis, and prognosis. In addition, CDH11's critical role in embryonic development means that its dysfunction can lead to congenital heart disease and other organ development defects. In inflammatory diseases, CDH11 may be involved in regulating the immune response, and its abnormalities may be related to inflammatory processes.
Bioapplications of CDH11
In tissue engineering, the cell adhesion properties of CDH11 contribute to the construction of extracellular matrix and promote cell proliferation and differentiation, accelerating wound healing and tissue regeneration. As a key molecule in cell signaling and cell-cell interactions, CDH11 can be used to screen for drugs that affect these processes, especially in the treatment of cancer and inflammatory diseases. Changes in CDH11 expression levels in a variety of cancers make it a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for cancer diagnosis, prognosis assessment, and the development of new therapies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ryota Shirai, 2024
Ewing sarcoma is the second most common bone cancer in children, and while patients who present with metastatic disease at the time of diagnosis have a dismal prognosis. Ewing sarcoma tumors are driven by the fusion gene EWS/Fli1, and while these tumors are genetically homogenous, the transcriptional heterogeneity can lead to a variety of cellular processes including metastasis. In this study, researchers demonstrate that in Ewing sarcoma cells, the canonical Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway is heterogeneously activated in vitro and in vivo, correlating with hypoxia and EWS/Fli1 activity. Ewing sarcoma cells predominantly express β-Catenin on the cell membrane bound to CDH11, which can respond to exogenous Wnt ligands leading to the immediate activation of Wnt/β-Catenin signaling within a tumor. Knockdown of CDH11 leads to delayed and decreased response to exogenous Wnt ligand stimulation, and ultimately decreased metastatic propensity.

Fig1. Co-Immunoprecipitation shows that CDH11 is bound to β-catenin in Ewing sarcoma cells.

Fig2. β-catenin knockdown in Ewing sarcoma cells do not lead to alteration of CDH11 expression.
Case Study 2: Yayu Liu, 2023
During epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cancer progression, tumor cells switch cadherin profile from E-cadherin to cadherin-11 (CDH11), which is accompanied by increased invasiveness and metastatic activity. However, the mechanism through which CDH11 may affect tumor growth and metastasis remains elusive. Here, researchers report that CDH11 was highly expressed in multiple human tumors and was localized on the membrane, in the cytoplasm and, surprisingly, also in the nucleus. Interestingly, β-catenin remained bound to carboxy-terminal fragments (CTFs) of CDH11, the products of CDH11 cleavage, and co-localized with CTFs in the nucleus in the majority of breast cancer samples. Binding of β-catenin to CTFs preserved β-catenin activity, whereas inhibiting CDH11 cleavage led to β-catenin phosphorylation and diminished Wnt signaling, similar to CDH11 knockout.
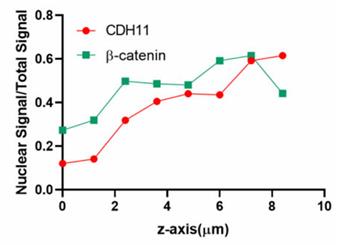
Fig3. Nuclear CDH11 and β-catenin signaling in the nucleus was quantified.

Fig4. Subcellular fractionation western blot revealing the distribution pattern of full-length CDH11 (CDH11-FL) and CDH11-CTFs in different subcellular fractions.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CDH11-1538H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CDH11-0972H)
Involved Pathway
CDH11 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CDH11 participated on our site, such as Adherens junctions interactions,Cell junction organization,Cell-Cell communication, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CDH11 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell-Cell communication | CDH9,CLDN3,KIRREL3L,KIRRELA,CDH12A,KIRREL,SIRPB1,NPHS1,CDH10,CDH18A |
| Cell-cell junction organization | CDH12A,CLDN16,CADM2B,CDH13,INADL,CTNND1,CADM2,CDH5,JUPA,ANG |
| Cell junction organization | CDH2,CADM2A,CDH18,CADM2B,CDH7,CDH8,F11R.2,CDH6,FERMT2,PARVB |
| Adherens junctions interactions | CDH4,CADM2A,PTBP3,CDH18A,CDH2,CADM2B,JUP,CDH17,CDH5,CDH3 |
Protein Function
CDH11 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CDH11 itself. We selected most functions CDH11 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CDH11. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| calcium ion binding | NCALDB,EFCAB9,PLCD1B,SERPINB1A,S100A7,PCDH12,CALML5,PLCB1,F9A,SYT5 |
Interacting Protein
CDH11 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CDH11 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CDH11.
CRK;ATF7IP;q81ye8_bacan
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wang, H; Leinwand, LA; et al. Roles of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and OB-cadherin in porcine cardiac valve myofibroblast differentiation. FASEB JOURNAL 28:4551-4562(2014).
- Assefnia, S; Dakshanamurthy, S; et al. Cadherin-11 in poor prognosis malignancies and rheumatoid arthritis: common target, common therapies. ONCOTARGET 5:1458-1474(2014).


