CCNG1
-
Official Full Name
cyclin G1 -
Overview
The eukaryotic cell cycle is governed by cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs) whose activities are regulated by cyclins and CDK inhibitors. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin family and contains the cyclin box. The encoded protein lacks the protein destabilizing (PEST) sequence that is present in other family members. Transcriptional activation of this gene can be induced by tumor protein p53. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene. -
Synonyms
CCNG1;cyclin G1;CCNG;cyclin-G1;CCNG 1;CCNG1_HUMAN;CYCG1;Cyclin G;Cyclin-G;OTTHUMP00000160918;OTTHUMP00000223690;OTTHUMP00000223692;OTTHUMP00000223697
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCNG1-3613H | Recombinant Human CCNG1 protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 1-46 aa | |
| CCNG1-0669H | Recombinant Human CCNG1 Protein, GST-Tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| CCNG1-1224R | Recombinant Rat CCNG1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| CCNG1-1331H | Recombinant Human Cyclin G1, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
|
|
| CCNG1-26094TH | Recombinant Human CCNG1, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 295 amino acids |
|
| CCNG1-28189TH | Recombinant Human CCNG1 | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 295 amino acids |
|
| CCNG1-2995M | Recombinant Mouse CCNG1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| CCNG1-824H | Recombinant Human CCNG1 Protein, DDK-tagged | Sf9 Cells | Human | Flag |
|
|
| CCNG1-825H | Recombinant Human CCNG1 Protein, GST-His-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST&His |
|
|
| CCNG1-9922Z | Recombinant Zebrafish CCNG1 | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| CCNG1-7707HCL | Recombinant Human CCNG1 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| CCNG1-1408M | Recombinant Mouse CCNG1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| CCNG1-1408M-B | Recombinant Mouse CCNG1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| CCNG1-2974HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CCNG1 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 295 amino acids |
|
| CCNG1-53HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CCNG1 Protein | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | Full L. 295 amino acids |
|
|
| CCNG1-882R | Recombinant Rat CCNG1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| CCNG1-882R-B | Recombinant Rat CCNG1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
Background
What is CCNG1 Protein?
The CCNG1 protein, also known as cyclin G1, is a bit of an atypical player in the cell cycle world. Unlike other cyclins that come and go with specific cell cycle stages, cyclin G1 doesn't follow the usual rules. It's controlled by the tumor suppressor protein p53, playing a part in cell cycle regulation and cellular responses to DNA damage. This means it helps manage how cells grow and divide, especially when they encounter stress or damage. Cyclin G1 comes into the spotlight in various cancers because its abnormal expression can disrupt normal cell cycle checkpoints, leading tumors to grow unchecked.What is the Function of CCNG1 Protein?
Cyclin G1, or CCNG1, is a member of the cyclin family crucial for cell cycle control. It doesn't function like most cyclins with direct cell cycle checkpoints but is influenced by the tumor suppressor p53. It's key in responding to DNA damage, affecting how cells grow and die. Cyclin G1 partners with other cell cycle proteins and can impact cell division and programmed cell death. Often found in high levels in various cancers, it might aid tumor growth and resistance to treatments. By exploring cyclin G1, researchers aim to find new cancer treatment targets due to its involvement in essential cell processes.
Fig1. Six proximal oncogenic mechanisms activating the CCNG1 oncogene. (Sant P Chawla, 2023)
CCNG1 Related Signaling Pathway
CCNG1, or cyclin G1, is a protein tied into important signaling pathways in cells. It often interacts with the well-known tumor suppressor p53. This relationship plays a role in controlling the cell cycle and how the cell responds to DNA damage. The cyclin G1 protein can impact tumor behavior by affecting the pathways that regulate cell growth and death. This makes it a key player in cancer-related processes, where it can promote tumor cell growth and adaptability. By targeting these pathways, researchers are looking to develop new strategies to treat cancers more effectively.CCNG1 Related Diseases
Cyclin G1, or CCNG1, is connected to several diseases, mainly because of its role in cell growth regulation with p53. It's often overexpressed in cancers like liver and breast cancer, aiding tumor growth and treatment resistance. Researchers think it might also be involved in other diseases where cell cycle control goes awry. By focusing on CCNG1, scientists hope to find new ways to target these diseases more effectively.Bioapplications of CCNG1
CCNG1, or cyclin G1, is gaining attention in the biomedical field, especially in cancer treatment research. Its role in helping cells manage their cycle means it could be a valuable target in developing drugs aimed at slowing down or stopping cancer cell growth. Scientists are exploring how to manipulate CCNG1 to enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy by making cancer cells more susceptible to treatment. Beyond cancer, understanding CCNG1's functions could open up new approaches in regenerative medicine, where controlling cell growth and division is crucial for tissue repair and recovery.Case Study
Case Study 1: Reimer CL. et al. J Biol Chem. 1999
Cyclin G, a newer member of the cyclin family, first came to light during searches for src kinase family members and p53 tumor suppressor targets. It's notably overexpressed in breast and prostate cancer cells. In normal breast cells, cyclin G levels peak during the S and G2/M phases of the cell cycle, but this pattern doesn't hold in cancer cells. When normal cells with functional p53 face DNA damage, cyclin G clusters at DNA replication sites with proteins like PCNA. However, cells lacking p53 don't show this response. This behavior suggests cyclin G could play a role in p53-related cell cycle control by interacting with replication site proteins.-
 Fig1. Western blot analysis was used to determine the level of Cyc G protein in normal cells.
Fig1. Western blot analysis was used to determine the level of Cyc G protein in normal cells. -
 Fig2. p53-dependent expression of Cyc G in different cell types.
Fig2. p53-dependent expression of Cyc G in different cell types.
Case Study 2: Liu Y. et al. Mol Med Rep. 2021
The study looked into how the long non-coding RNA OIP5-AS1 affects ovarian cancer. It turns out OIP5-AS1 is higher in cancer cells and tissues, and when it's reduced, cancer cell growth, movement, and energy production drop, while cell death increases. OIP5-AS1 interacts with miR-128-3p, acting like an oncogene by trapping this microRNA. It also boosts CCNG1 levels by targeting miR-128-3p. Lowering OIP5-AS1 curbs tumor growth in live models by influencing miR-128-3p and CCNG1 levels. This suggests OIP5-AS1 could be a key marker for diagnosing and treating ovarian cancer.-
 Fig3. Protein expression of CCNG1 was measured by western blotting in OVCAR-3 and SKOV3 cells.
Fig3. Protein expression of CCNG1 was measured by western blotting in OVCAR-3 and SKOV3 cells. -
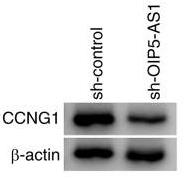 Fig4. CCNG1 protein expression was measured using western blotting.
Fig4. CCNG1 protein expression was measured using western blotting.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CCNG1-0669H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CCNG1-0669H)
Involved Pathway
CCNG1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CCNG1 participated on our site, such as p signaling pathway,MicroRNAs in cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CCNG1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MicroRNAs in cancer | NRAS,Casp3,PLAU,BMF,MARCKS,MDM4,MET,PDGFA,ABCB1,EZR |
| p signaling pathway | CD82B,PPM1DB,IGFBP3,MDM4,GTSE1,PERP,GADD45B,LRDD,CCNB2,EI24 |
-
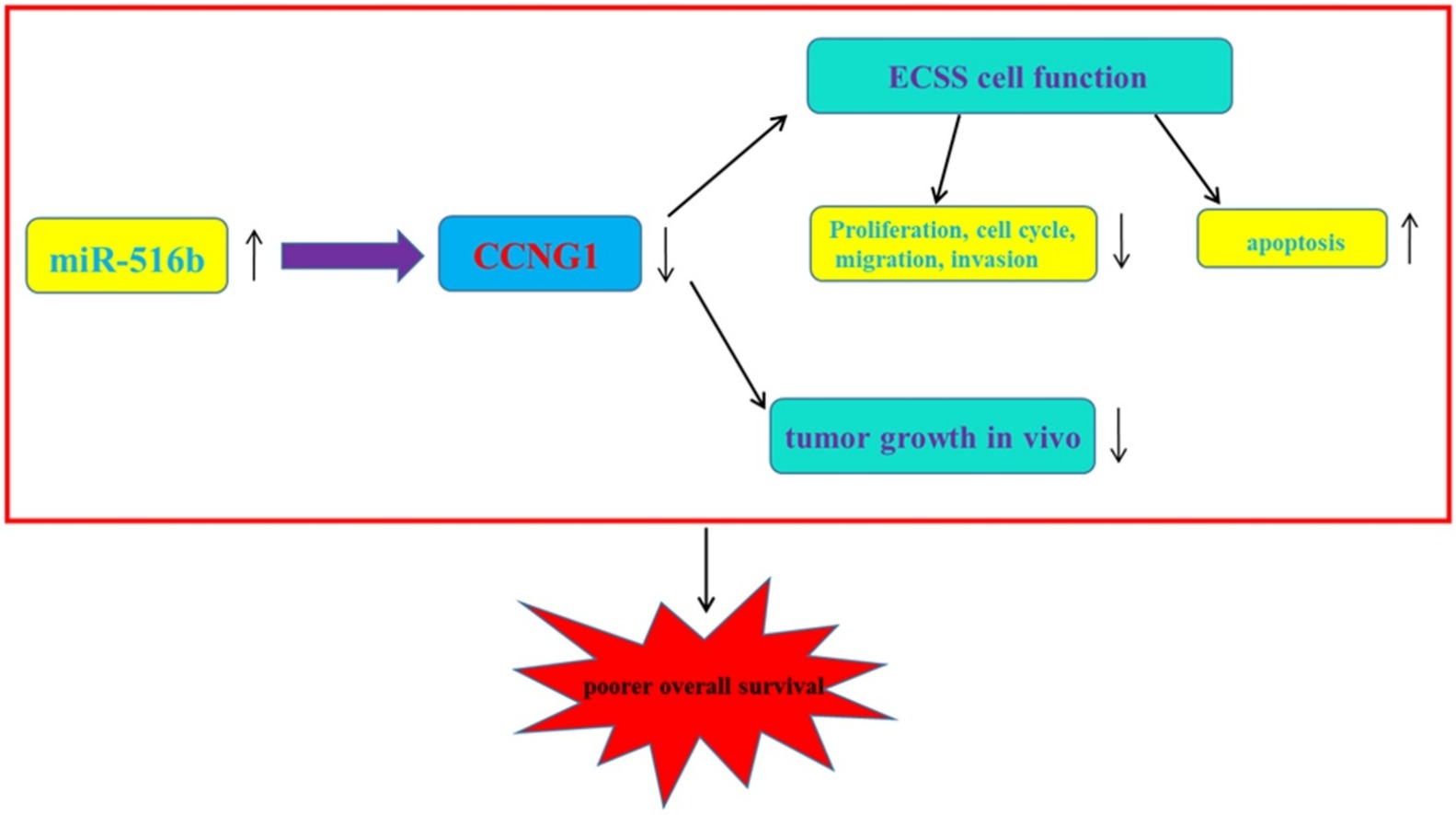 Fig1. miR-516b functions as a tumor suppressor by directly modulating CCNG1 expression in ESCC cells. (Yufeng Zhao, 2018)
Fig1. miR-516b functions as a tumor suppressor by directly modulating CCNG1 expression in ESCC cells. (Yufeng Zhao, 2018) -
 Fig2. C/EBPβ regulated the expression of LINC01133 by directly binding to its promoter region and subsequently activating CCNG1 expression. (Chen-Song Huang, 2018)
Fig2. C/EBPβ regulated the expression of LINC01133 by directly binding to its promoter region and subsequently activating CCNG1 expression. (Chen-Song Huang, 2018)
Protein Function
CCNG1 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CCNG1 itself. We selected most functions CCNG1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CCNG1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | HCLS1,DNAJB9,CSTF3,RFX4,PMM1,GIPC1,CCDC101,KISS1R,USP44,IPO4 |
Interacting Protein
CCNG1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CCNG1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CCNG1.
TNIP1;KRTAP10-7;KRT40;HMBOX1;SPERT;PNMA1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


