CAV1
-
Official Full Name
caveolin 1, caveolae protein, 22kDa -
Overview
The scaffolding protein encoded by this gene is the main component of the caveolae plasma membranes found in most cell types. The protein links integrin subunits to the tyrosine kinase FYN, an initiating step in coupling integrins to the Ras-ERK pathway and promoting cell cycle progression. The gene is a tumor suppressor gene candidate and a negative regulator of the Ras-p42/44 mitogen-activated kinase cascade. Caveolin 1 and caveolin 2 are located next to each other on chromosome 7 and express colocalizing proteins that form a stable hetero-oligomeric complex. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy. Alternatively spliced transcripts encode alpha and beta isoforms of caveolin 1. -
Synonyms
CAV1;caveolin 1, caveolae protein, 22kDa;CAV, caveolin 1, caveolae protein, 22kD;caveolin-1;cell growth-inhibiting protein 32;CGL3;BSCL3;VIP21;MSTP085
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Dog
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- His
- Non
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- Myc
Background
What is CAV1 Protein?
CAV1, or Caveolin-1, is crucial for forming caveolae—tiny pockets in cell membranes. It acts like a framework, helping these structures take shape. Besides giving structure, CAV1 influences several cellular processes, like how cells grow and survive. Scientists are keen on CAV1 because it's connected to conditions like cancer and heart disease. Due to its role in cell signaling and transport, it's a promising target for new treatments. By studying CAV1 further, researchers aim to find therapies that could tackle various health challenges.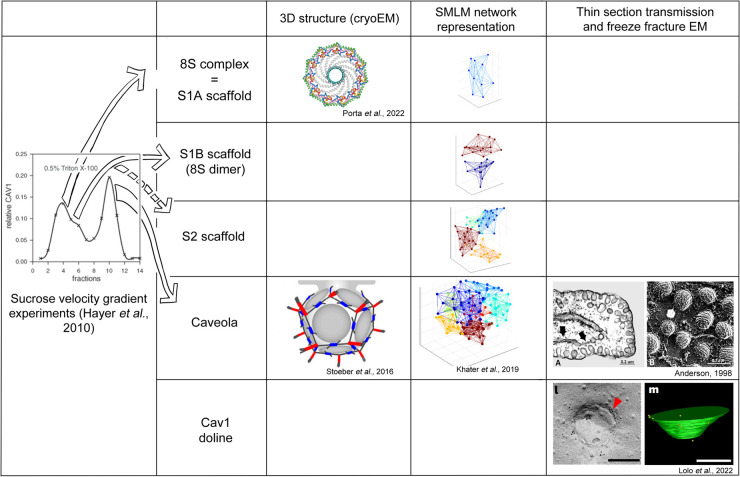
Fig1. Cav1 oligomeric structures by cryoEM, SMLM network analysis, and electron microscopy. (John E Lim, 2024)
What is the Function of CAV1 Protein?
CAV1, or Caveolin-1, plays a big role in shaping caveolae—those small invaginations on the cell membrane. Acting like a support beam, it helps these structures form and provides stability. Beyond just architecture, CAV1 is deeply involved in important cell functions, like signaling pathways that manage how cells grow, move, and survive. This protein also influences how cells take in substances and respond to environmental stress. It's a hot topic in research due to its links to diseases like cancer and cardiovascular disorders. Understanding CAV1’s multifaceted role might open doors to new treatments and therapies for these health issues.CAV1 Related Signaling Pathway
CAV1, or Caveolin-1, plays a key role in several signaling pathways that influence cell function. It helps manage how signals cross the cell membrane, affecting growth, division, and survival. Acting as a gatekeeper, CAV1 is involved in pathways related to insulin signaling, cancer growth, and lipid balance. Because of this, CAV1 interests researchers looking at diseases like cancer, where it could impact tumor growth, and metabolic disorders, where it might change cell energy management. Understanding these pathways could lead to more targeted treatments.CAV1 Related Diseases
CAV1, or Caveolin-1, is linked to a variety of diseases due to its role in cell signaling and structure. In cancer, CAV1 can influence tumor growth and spread, either promoting or suppressing it depending on the context. It's also associated with cardiovascular diseases because it affects how blood vessels function and respond to stress. Researchers have found links between CAV1 and metabolic disorders like diabetes, where it impacts glucose and fat metabolism. Additionally, CAV1 could play a role in pulmonary conditions and fibrosis due to its involvement in maintaining cellular environments. Understanding CAV1's role in these diseases might pave the way for new treatment strategies.Bioapplications of CAV1
CAV1, or Caveolin-1, holds significant promise in bioapplications due to its role in various cell functions. In cancer therapy, targeting CAV1 could influence tumor behavior, potentially slowing growth or preventing spread. Its impact on blood vessel function makes it a candidate for cardiovascular treatments, possibly improving vascular health and response. In metabolic research, manipulating CAV1 might help manage or prevent diabetes by affecting how cells process glucose and fat. Additionally, its role in cell signaling suggests potential in developing treatments for lung diseases and fibrosis. Exploring CAV1’s functions could lead to innovative strategies across these health areas.Case Study
Case Study 1: Simón L. et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024
Metastasis is a major cancer killer, and better therapies are essential. Cancer cells often rely on aerobic glycolysis for energy to spread. Researchers found that Caveolin-1 (CAV1) enhances this process. Using 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) to inhibit glycolysis reduced the spread in melanoma and breast cancer cells. CAV1-driven mobility relies on Src/Akt signaling, which 2-DG blocks. Inhibiting Akt also lowered lung metastasis in CAV1-rich melanoma cells.-
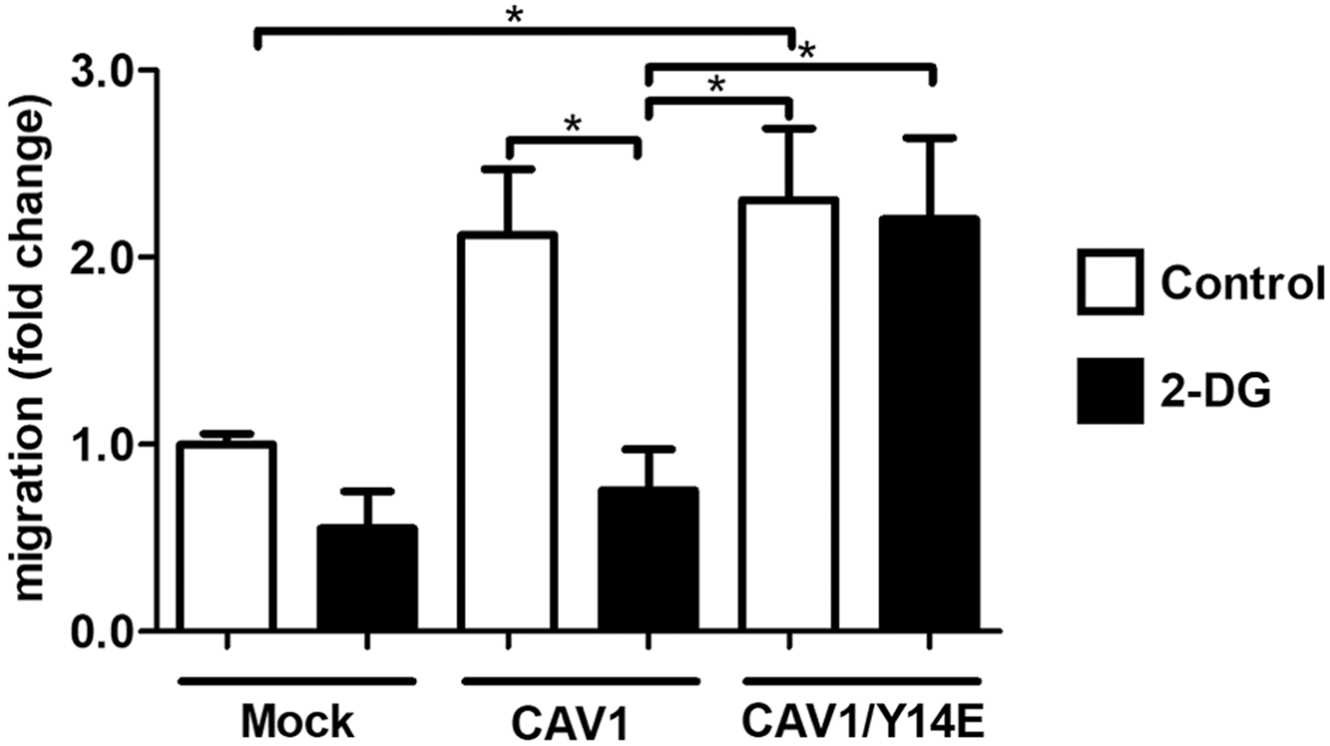 Fig1. The glycolysis inhibitor 2-DG failed to prevent phosphomimetic CAV1/Y14E-enhanced migration.
Fig1. The glycolysis inhibitor 2-DG failed to prevent phosphomimetic CAV1/Y14E-enhanced migration. -
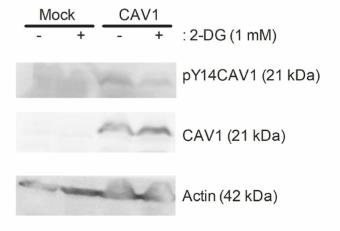 Fig2. Western blot analysis of pY14CAV1 and CAV1 in extracts from B16-F10(Mock) and (CAV1) cells.
Fig2. Western blot analysis of pY14CAV1 and CAV1 in extracts from B16-F10(Mock) and (CAV1) cells.
Case Study 2: Goutas A. et al. Cells. 2021
In osteoarthritic chondrocytes, Cav-1 overexpression disrupts DNA repair under oxidative stress, likely due to cell aging. In young mesenchymal stem cells, Cav-1 adjusts under stress, but this mechanism is lost as they age, leading to persistent DNA damage. Reducing Cav-1 causes sustained damage and aging through autophagy. Lowering Atg5 together with Cav-1 can prevent this stress-induced aging, suggesting Cav-1’s role in DNA repair is crucial; without it, cells may age.-
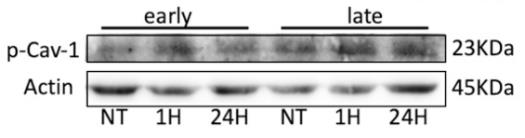 Fig3. Representative immunoblot showing p-Cav-1 levels from cell lysates of early- and late-passage WJ-MSCS.
Fig3. Representative immunoblot showing p-Cav-1 levels from cell lysates of early- and late-passage WJ-MSCS. -
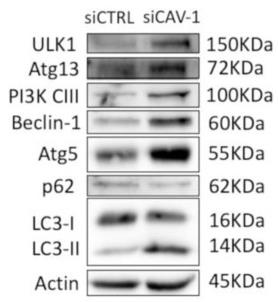 Fig4. Characteristic immunoblot showing protein levels of key molecules of autophagy in early passage cells treated with control siRNA (siCTRL) or siRNA against Cav-1.
Fig4. Characteristic immunoblot showing protein levels of key molecules of autophagy in early passage cells treated with control siRNA (siCTRL) or siRNA against Cav-1.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CAV1-0389H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CAV1-0389H)
High Bioactivity
-
.jpg) Fig2. Activity Data (CAV1-0389H)
Fig2. Activity Data (CAV1-0389H)
Involved Pathway
CAV1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CAV1 participated on our site, such as Endocytosis,Focal adhesion,Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CAV1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Proteoglycans in cancer | COL21A1,PIK3R2,WNT16,FAS,LUM,HRAS,ERBB3,ARHGEF1,FZD3,VTN |
| Viral myocarditis | CD40,HLA-DMB,MYH7,HLA-DRA,FYN,HLA-DMA,HLA-DQA1,H2-AB1,RAC2,CD86 |
| Focal adhesion | BRAF,HRAS,DIAPH1,VAV3B,ACTN4,RHOAC,PXNA,AKT2,TNC,ITGB1B.2 |
| Endocytosis | SH3GLB1A,CSF1RA,SMAD3,IL2RB,DNM2A,CHMP1B,PDCD6IP,SH3GL3,ADRB3A,PRKCI |
| Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | SEPT11,DOCK1,ITGB1,SEPT3,GAB1,CD2AP,DNM3,CAV3,CDC42,SEPT2 |
-
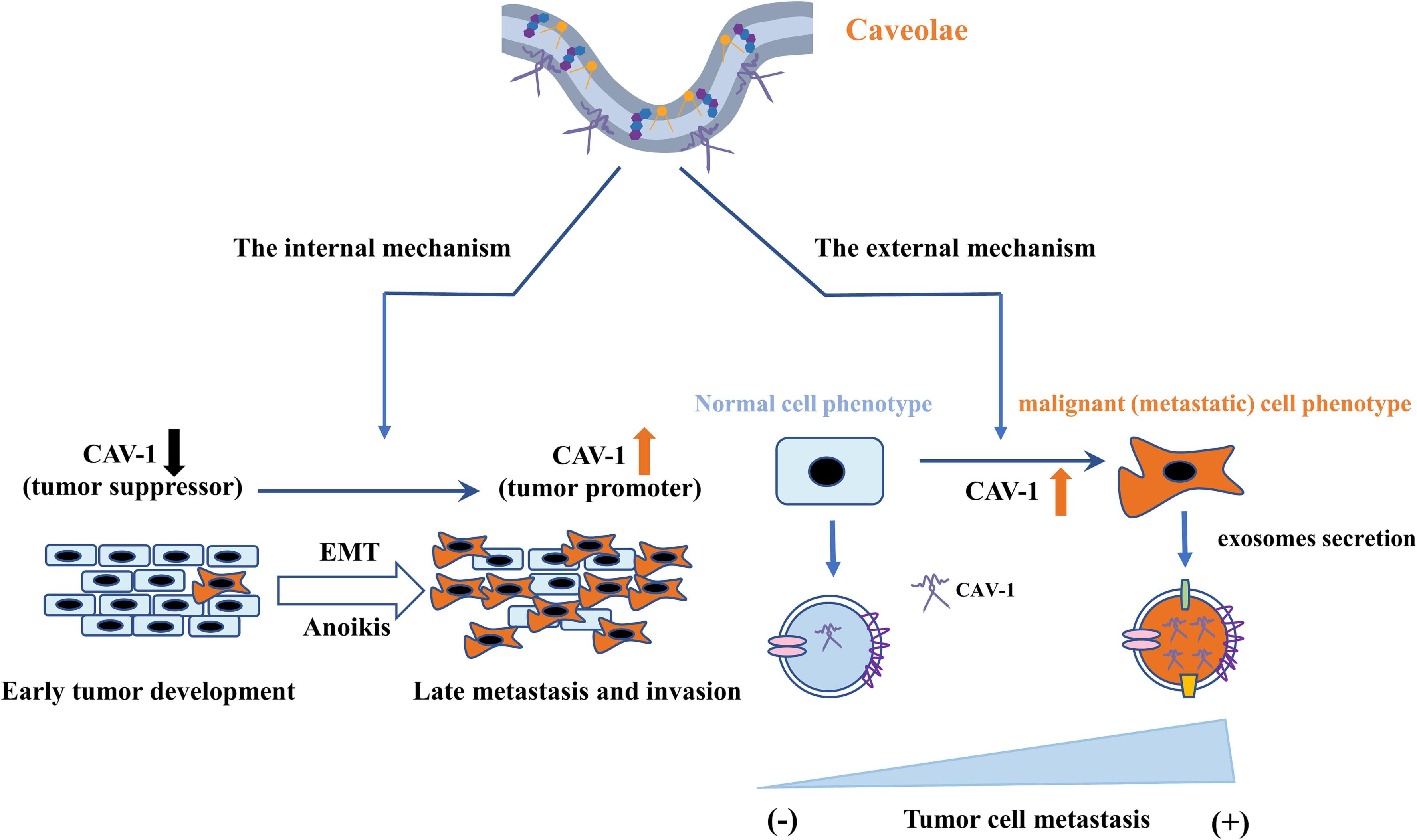 Fig1. Cell internal and external mechanisms of caveolin-1 (CAV-1) mediating tumor development. (Xiangfu Jiang, 2023)
Fig1. Cell internal and external mechanisms of caveolin-1 (CAV-1) mediating tumor development. (Xiangfu Jiang, 2023) -
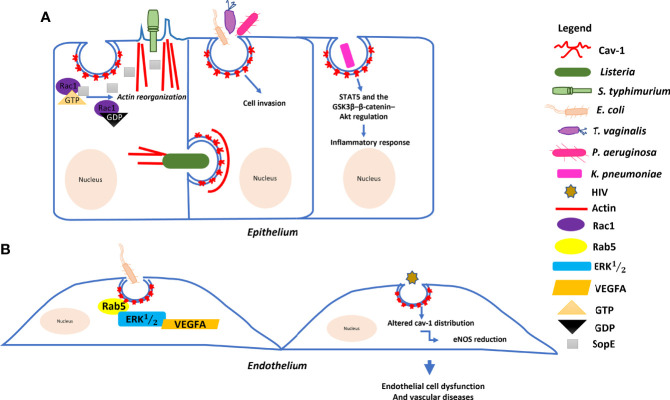 Fig2. Model of the molecular mechanism underlying the role of Cav–1 in bacterial and HIV invasion. (Pamella Silva Lannes-Costa, 2022)
Fig2. Model of the molecular mechanism underlying the role of Cav–1 in bacterial and HIV invasion. (Pamella Silva Lannes-Costa, 2022)
Protein Function
CAV1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATPase binding,MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding,RNA polymerase I transcription factor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CAV1 itself. We selected most functions CAV1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CAV1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding, bridging | FBXW7,CBX5,PSMC6,ST13,CUX1,COL1A2,ANK2,TJP2,FLRT3,FSCN1A |
| ion channel binding | YES1,PKD2,ARRB1,YWHAE,PRKCSH,HTT,PACS1A,SRC,ACTN1,CALM2 |
| enzyme binding | NPC2,UGT1A6,APBA3,EIF4E,STUB1,TSPAN33,PPP3CA,USP22,LDB1,NOTCH1 |
| protein complex scaffold | SLC9A3R1,HOMER1,GNB2L1,PKP2,SMARCD1,CAV2,ITSN1,MAGI1B,WWC2,ARRB2 |
| Rac GTPase binding | RAB7A,ARHGAP4A,DOCK7,PAK1,SRGAP3,EPS8,SRGAP2,ARHGAP4,CDKL5,HACE1 |
| cholesterol binding | NPC1,APOA5,SYP,STARD6,ERLIN2,ERLIN1,APOA1A,OSBPL3,ABCG1,APOE |
| protein kinase binding | SHC4,PTEN,PLK1,RNF138,PPP1R15A,JTB,MAPT,CALM3,E2F1,ILK |
| patched binding | PTCH1,CCNB1,SMO,SETD6,IHH,BBS1,Shh,DHH |
| identical protein binding | REG3B,DYNLT3,IIGP1,SDCBP,PRMT1,AGXT2,HJURP,FADD,PYCARD,PLIN5 |
Interacting Protein
CAV1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CAV1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CAV1.
PTPN1;EGFR;TXNRD1;ID1
Resources
Research Area
Uptake and Transport Molecules on Endothelial CellsUptake and Transport Molecules in VSMC
Muscle Stem Cell Markers
Myogenesis Markers
Phospholipases, Small GTPases, and Other Molecules in the Akt Pathway
Focal Adhesion Adaptor and Scaffold Proteins
Myogenic Precursor Markers
Caveolin-mediated Endocytosis
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Biswas, SK; Brako, L; et al. Massive formation of square array junctions dramatically alters cell shape but does not cause lens opacity in the cav1-KO mice. EXPERIMENTAL EYE RESEARCH 125:9-19(2014).


