BANF1
-
Official Full Name
barrier to autointegration factor 1 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene was first identified by its ability to protect retroviruses from intramolecular integration and therefore promote intermolecular integration into the host cell genome. The protein forms a homodimer which localizes to both the nucleus and cytoplasm and is specifically associated with chromosomes during mitosis. This protein binds to double stranded DNA in a non-specific manner and also binds to LEM-domain containing proteins of the nuclear envelope. This protein is thought to facilitate nuclear reassembly by binding with both DNA and inner nuclear membrane proteins and thereby recruit chromatin to the nuclear periphery. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. -
Synonyms
BANF1;barrier to autointegration factor 1;barrier-to-autointegration factor;BAF;breakpoint cluster region protein 1;NGPS;BCRP1;D14S1460;MGC111161
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is BANF1 Protein?
BANF1, short for Barrier to Autointegration Factor 1, is a protein found in many cells. It's like a guardian for our DNA, playing a critical role in managing how our genetic material gets organized and protected. By binding to DNA, it helps keep the structure of our cells' nuclei intact and prevents unwanted DNA from integrating into our chromosomes. This function makes it important not just for regular cell maintenance, but also for responding to stress, like during infections or when alien DNA tries to sneak in. Scientists have also noticed its increased activity in various cancers, including gastric cancer, hinting at a broader role in cell growth or survival.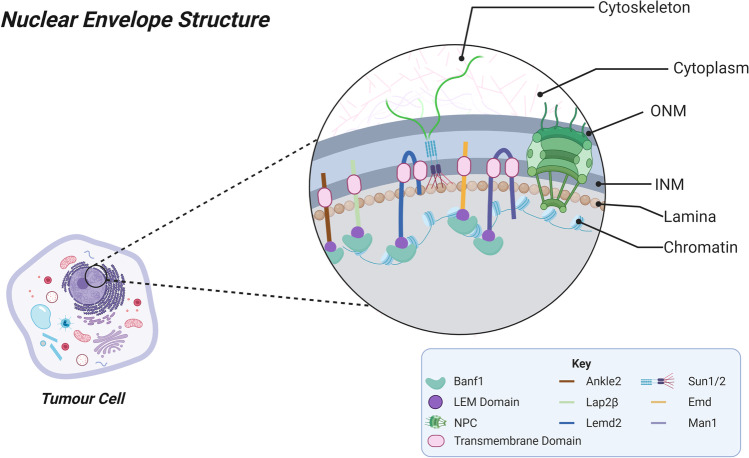
Fig1. Nuclear envelope structure. (Maddison Rose, 2022)
What is the Function of BANF1 Protein?
BANF1 is like a DNA bodyguard in our cells. This protein binds to DNA and helps organize and protect the nucleus, the cell's control center. It stops rogue DNA from messing up our genetic material, preventing chaos within our chromosomes. BANF1 is crucial for normal cell upkeep and plays a key role when the cell faces stress, like infections. Researchers have found that BANF1 seems to work overtime in some cancers, suggesting it might aid in cell survival or growth when things go awry.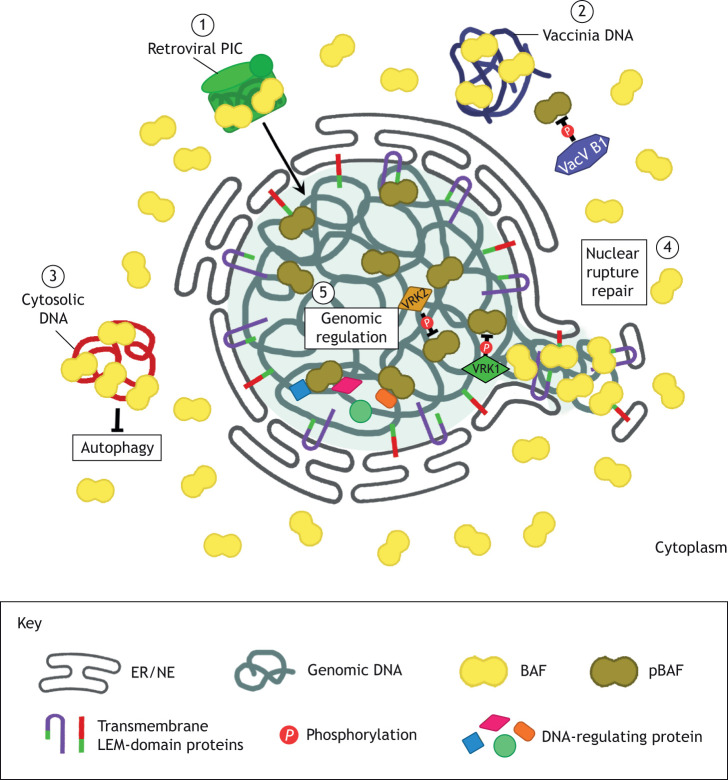
Fig2. BAF performs various roles in an interphase cell. (Rhiannon M Sears, 2020)
BANF1 Related Signaling Pathway
BANF1 is involved in various cellular processes, primarily by interacting with DNA and nuclear components. One key pathway it influences is the DNA damage response. When DNA gets damaged, BANF1 helps coordinate repair mechanisms, ensuring that the genetic material is fixed properly. It also plays a role in managing how DNA is packed within the nucleus, which affects how genes are expressed. Additionally, BANF1's activity has been linked to pathways that control cell growth and division. This connection becomes particularly interesting when looking at cancer, where BANF1 might contribute to unchecked cell proliferation by tweaking these signaling routes.BANF1 Related Diseases
BANF1 is linked to a few health issues, particularly when its usual functions go awry. In the world of cancer, BANF1 often shows up more active than normal. This heightened activity could help cancer cells grow and spread, making it a target of interest for researchers. Beyond cancer, mutations or changes in BANF1 function are also tied to conditions affecting the immune system, as this protein plays a part in DNA repair and cellular responses to stress. Disorders involving premature aging, like progeria, have been connected to problems with nuclear structure, where BANF1 is a key player. These associations make understanding BANF1 crucial in both cancer research and studying certain genetic diseases.Bioapplications of BANF1
BANF1 is a protein with interesting potential in the field of biotechnology and medicine. Given its role in DNA organization and nucleus integrity, scientists are exploring its use in gene therapy and cancer treatment. By understanding how BANF1 regulates cell growth and repair mechanisms, researchers aim to develop strategies that could halt cancer progression or assist in repairing genetic disorders. Its ability to interact with DNA also makes it a candidate for studying viral infections, as it could potentially be harnessed to prevent viruses from integrating their DNA into host cells, providing a novel antiviral approach. Overall, BANF1's functions open doors to innovative therapies and diagnostic tools.Case Study
Case Study 1: Xu Y. et al. Aging (Albany NY). 2024
Gastric cancer is pretty common and usually comes with a poor outlook. We dove into sequencing data to find unique genes linked to this cancer, mainly focusing on BANF1, a gene that's highly active in many cancers, including gastric. The findings suggest BANF1 could be a sign of patient outcomes and might influence immune cell behavior. Researchers ran lab tests and confirmed its high activity in gastric cancer cells, and knocking down BANF1 significantly slowed down cell growth and spread. In mouse models, reducing BANF1 led to notably slower tumor growth.-
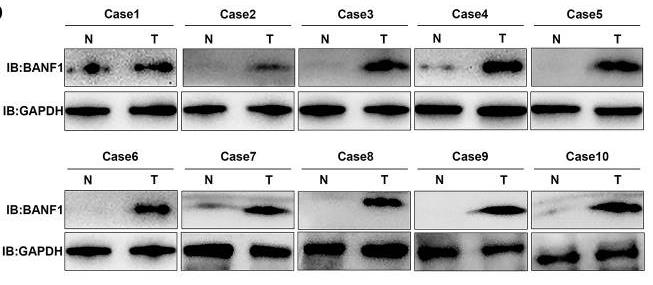 Fig1. WB detection of BANF1 protein expression in 10 pairs of GC tissues.
Fig1. WB detection of BANF1 protein expression in 10 pairs of GC tissues. -
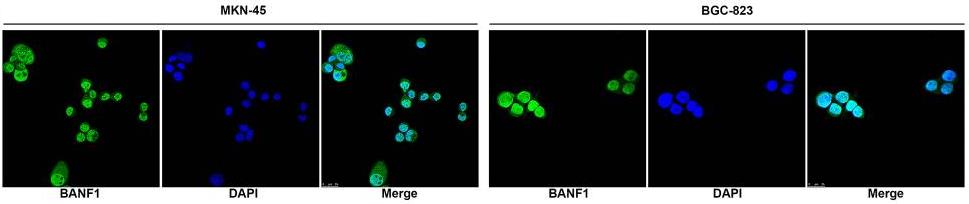 Fig2. Immunofluorescence staining showed the expression and localization of BANF1 protein in MKN-45 and BGC-823 cells.
Fig2. Immunofluorescence staining showed the expression and localization of BANF1 protein in MKN-45 and BGC-823 cells.
Case Study 2: Kobayashi S. et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015
Understanding how cells detect foreign DNA helps fight infections and respond to transfected DNA. Researchers developed a method using DNA-coated beads in live cells to track this process. BAF binds to foreign DNA immediately, forming a protective membrane to avoid autophagy. Without BAF, this fails, leading to increased autophagy. BAF may play a role in membrane remodeling upon detecting DNA.-
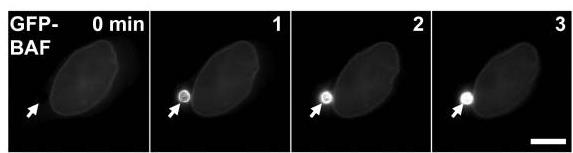 Fig3. Time-lapse images of GFP-BAF around anti–GFP-beads (anti–GFP-beads) incorporated into HeLa/GFP-BAF cells.
Fig3. Time-lapse images of GFP-BAF around anti–GFP-beads (anti–GFP-beads) incorporated into HeLa/GFP-BAF cells. -
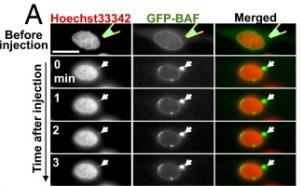 Fig4. Time-lapse images of GFP-BAF before and after the injection of exogenous circular dsDNA.
Fig4. Time-lapse images of GFP-BAF before and after the injection of exogenous circular dsDNA.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (BANF1-068H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (BANF1-068H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (BANF1-563H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (BANF1-563H)
Involved Pathway
BANF1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways BANF1 participated on our site, such as 2-LTR circle formation,APOBEC3G mediated resistance to HIV-1 infection,Autointegration results in viral DNA circles, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with BANF1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Clearance of Nuclear Envelope Membranes from Chromatin | VRK1,LEMD3,VRK2,TMPO |
| Cell Cycle, Mitotic | ARPP19B,SMC4,E2F3,HAUS2,TCTN2,TMPO,CENPN,CDKN2B,KIF18A,DCTN3 |
| 2-LTR circle formation | PSIP1,gag,HMGA1 |
| Early Phase of HIV Life Cycle | CCR5,gag,PSIP1,PPIA |
| Autointegration results in viral DNA circles | gag,HMGA1,PSIP1 |
| Cell cycle | ZBTB17,ATM,CDC14B,DIDO1,ACD,DCTN3,CDC25A,CUL1A,ESCO2,E2F4 |
| Disease | HDAC5,FDX1,AP1M2,HEY2,STX1B,OPN1MW,FMOD,OGN,GPC5,AMN |
| APOBEC3G mediated resistance to HIV-1 infection | PSIP1,gag,HMGA1,APOBEC3G,PPIA |
-
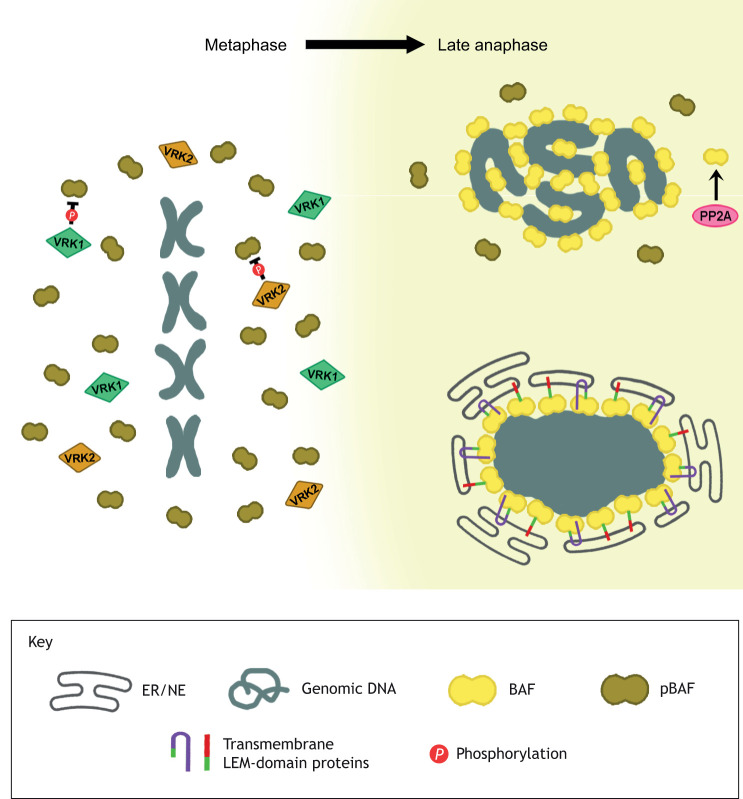 Fig1. BAF is required for the formation of a single nucleus following cell division. (Rhiannon M Sears, 2020)
Fig1. BAF is required for the formation of a single nucleus following cell division. (Rhiannon M Sears, 2020) -
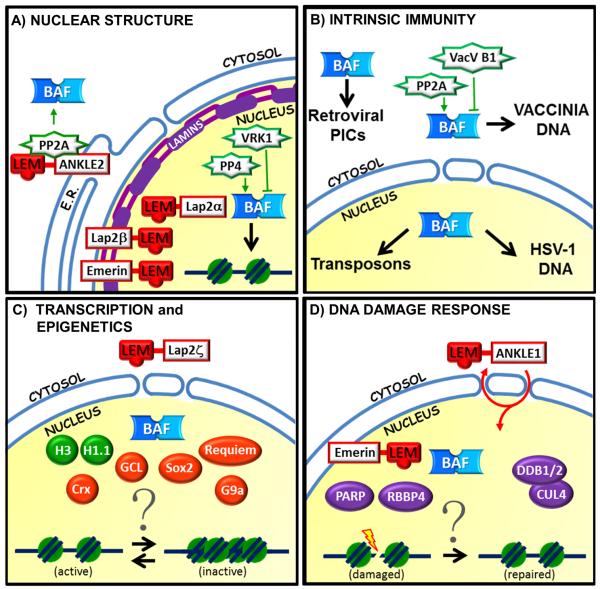 Fig2. Overview of BAF-associated proteins in different functional pathways. (Augusta Jamin, 2015)
Fig2. Overview of BAF-associated proteins in different functional pathways. (Augusta Jamin, 2015)
Protein Function
BANF1 has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by BANF1 itself. We selected most functions BANF1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with BANF1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | SATB1,ARMC2,KCNG4,CASP9,MITD1,FES,PROC,ISG20L2,AZIN2,ACTL6A |
| DNA binding | TBX6,HIST3H2A,TCF3,SIM1B,SHPRH,ZBED2,RAD51B,PC,POLA2,ZNF74 |
Interacting Protein
BANF1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with BANF1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of BANF1.
xav939;HLA-B;EMD;CDK5RAP3;ssdna_dcdgm;AIM2;PTBP3;RPL10;ATP6V1A
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


