ASS1
-
Official Full Name
argininosuccinate synthase 1 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the penultimate step of the arginine biosynthetic pathway. There are;approximately 10 to 14 copies of this gene including the pseudogenes scattered across the human genome, among which;the one located on chromosome 9 appears to be the only functional gene for argininosuccinate synthetase. Mutations in;the chromosome 9 copy of this gene cause citrullinemia. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been;found for this gene. -
Synonyms
ASS1;argininosuccinate synthase 1;argininosuccinate synthase;Argininosuccinate synthetase 1;ASS;Ass-1;ASSA;ASSY_HUMAN;Citrulline aspartate ligase;Citrulline--aspartate ligase;CTLN1;citrullinemia
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- E.Coli/Yeast
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
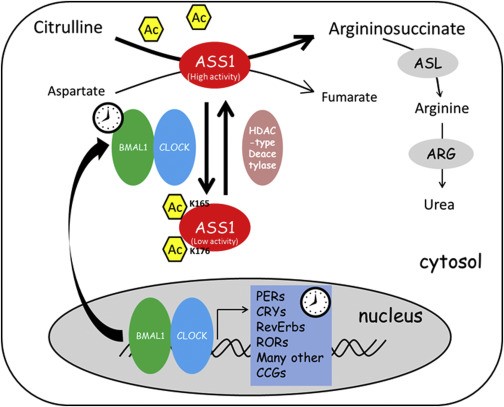
Fig1. A Proposed Model for CLOCK in Regulation of Arginine Biosynthesis and Ureagenesis via ASS1 Acetylation. (Ran Lin, 2017)
What is ASS1 protein?
ASS1 (argininosuccinate synthase 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 9 at locus 9q34. ASS1 is an enzyme that plays a key role in the arginine biosynthesis pathway. It catalyzes the conversion from citrulline to argininosuccinate, a limiting step in the synthesis of arginine. The function of ASS1 is critical for cell growth and proliferation because it is involved in protein synthesis as well as the production of a variety of biomolecules, including nitric oxide (NO), urea, creatine, polyamines, agmatine, proline, and glutamate. The ASS1 protein is consisted of 412 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 46.5 kDa.
What is the function of ASS1 protein?
ASS1 is one of the key enzymes in the urea cycle, which catalyzes the synthesis of Argininosuccinate. The biological functions of ASS1 protein mainly include the following aspects: First, ASS1 is one of the key enzymes in the urea cycle, which catalyzes the synthesis of Argininosuccinate and participates in the regulation and maintenance of the urea cycle. Secondly, ASS1 is highly expressed in the liver and is involved in amino acid metabolism and protein synthesis. In addition, ASS1 is also involved in biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis.
ASS1 Related Signaling Pathway
ASS1 is a key enzyme in the urea cycle responsible for catalyzing the synthesis of citrulline and aspartate into arginine succinic acid, which is essential for maintaining ammonia balance and arginine levels in the body. The expression of ASS1 can be directly activated by the transcription factor p53, which is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. ASS1 is involved in cellular metabolic processes by influencing the synthesis of arginine, including the synthesis of polyamines and proline, which play a role in cell proliferation and cell signaling.
ASS1 Related Diseases
ASS1 has been implicated in a variety of diseases, especially those related to arginine metabolism. Defects in the ASS1 gene can lead to citrullinemia, a disorder of the urea cycle caused by insufficient arginine synthesis, characterized by significantly elevated levels of citrullinine in plasma and hyperammonemia. In addition, ASS1 expression is down-regulated in a variety of tumors, such as melanoma, prostate cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, mesothelioma, pancreatic cancer, nasopharyngeal cancer, osteosarcoma and mucofibrosarcoma, which is associated with the occurrence and development of tumors and poor prognosis. Low expression of ASS1 makes tumor cells dependent on or addicted to extracellular arginine, and this property has been used to develop arginine deprivation therapy (ADT) targeting ASS1-deficient tumors.
Bioapplications of ASS1
ASS1 is expressed as a tumor suppressor in a variety of tumors. The discovery of new anti-tumor drugs based on ASS1, such as spinosyn A (SPA) and its derivative LM-2I, can activate ASS1 activity, reduce aspartic acid, inhibit de novo synthesis of pyrimidine, and then inhibit tumor proliferation. The expression status of ASS1 is correlated with the sensitivity of tumors to arginine deprivation therapy (ADT). Tumors with low ASS1 expression are exposed to increased dependence on external arginine, so they can be used as potential therapeutic targets.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Sanghwa Kim, 2021
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant cancers worldwide, and liver cancer has increased in mortality due to liver cancer because it was detected at an advanced stages in patients with liver dysfunction, making HCC a lethal cancer. Accordingly, this study aims to new targets for HCC drug discovery using HCC tumor spheroids. The researchers' comparative proteomic analysis of HCC cells grown in culture as monolayers (2D) and spheroids (3D) revealed that argininosuccinate synthase 1 (ASS1) expression was higher in 3D cells than in 2D cells due to upregulated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress responses. They investigated the clinical value of ASS1 in Korean patients with HCC. The mechanism underlying ASS1-mediated tumor suppression was investigated in HCC spheroids. ASS1-mediated improvement of chemotherapy efficiency was observed using high content screening in an HCC xenograft mouse model. Bidirectional interactions between ASS1 ER stress responses in HCC-derived multicellular tumor spheroids can limit HCC progression. ASS1 overexpression effectively inhibited tumor growth and enhanced the efficacy of in vitro and in vivo anti-HCC combination chemotherapy via activation of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP axis, but was not dependent on the status of p53 and arginine metabolism.
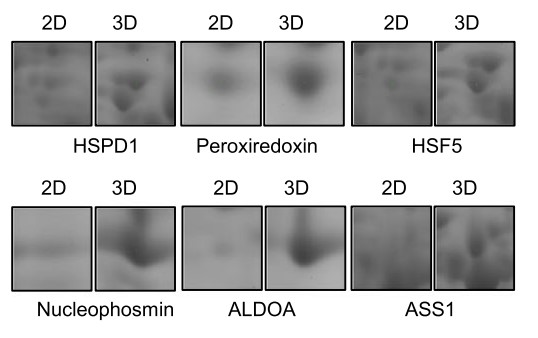
Fig1. Expression of ASS1 in 2D or 3D-culured system.
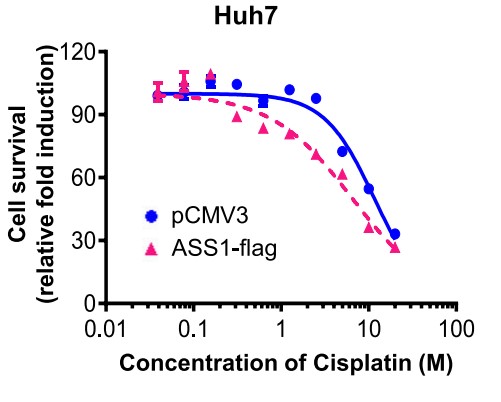
Fig2. ASS1 transfected in Huh7 cells treated with cisplatin at the indicated concentrations.
Case Study 2: Min Liu, 2022
Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 (PGAM1) is a crucial glycolytic enzyme, and its expression status has been confirmed to be associated with tumor progression and metastasis. However, the precise role and other biological functions of PGAM1 remain unclear. Here, the researchers report that PGAM1 expression is upregulated and related to poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer (BC). Functional experiments showed that knockdown of PGAM1 could suppress the proliferation, invasion, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of BC cells. Through RNA sequencing, they found that argininosuccinate synthase 1 (ASS1) expression was markedly upregulated in BC cells following PGAM1 knockdown, and it is required to suppress the malignant biological behavior of BC cells. Importantly, they demonstrated that PGAM1 negatively regulates ASS1 expression through the cAMP/AMPK/CEBPB axis. In vivo experiments further validated that PGAM1 promoted tumor growth in BC by altering ASS1 expression. Finally, immunohistochemical analysis showed that downregulated ASS1 levels were associated with PGAM1 expression and poor prognosis in patients with BC.
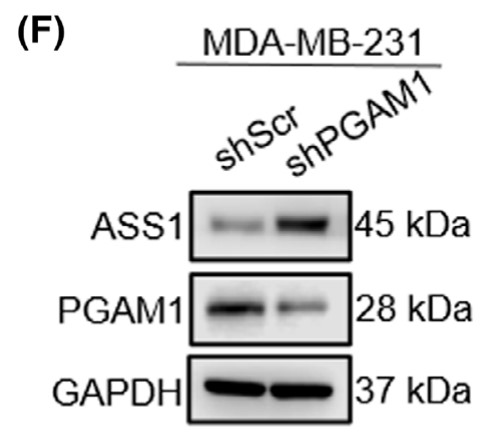
Fig3. The protein levels of PGAM1 and ASS1 measured by western blot.
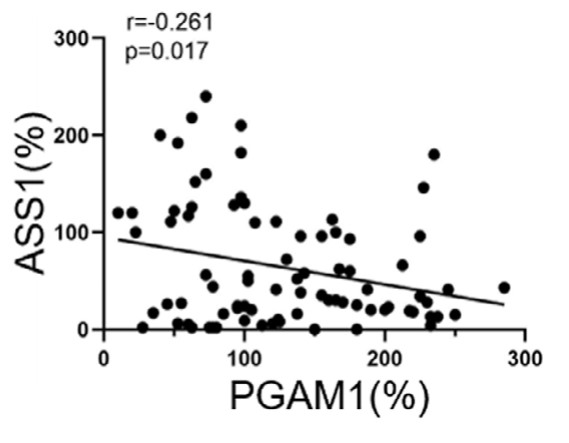
Fig4. The expression levels of PGAM1 were negatively related to the expression levels of ASS1.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ASS1-646H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ASS1-0626H)
Involved Pathway
ASS1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ASS1 participated on our site, such as Arginine biosynthesis,Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ASS1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Arginine biosynthesis | GLUD2,ARG2,GLUD1,GOT1,OTC,GOT2,GLSA,NOS1,ASL,GLULA |
| Metabolic pathways | LIPT2,NT5C3B,ATP6AP1B,CKB,RDH12,HYKK.2,LDHAL6B,AMPD3,NDUFA8,TYMS |
| Biosynthesis of amino acids | NAGS,BCAT2,GPT2L,TPI1,TKTL2,ALDOAA,ENO3,ENO1A,PFKP,MAT2A |
| Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | GFPT1,GOT2,ADSL,RIMKLA,CAD,AGXTB,ASNS,GLUL,GLSA,PPAT |
Protein Function
ASS1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,amino acid binding,argininosuccinate synthase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ASS1 itself. We selected most functions ASS1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ASS1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| poly(A) RNA binding | MRPS12,RPS19BP1,LYAR,SAP18,PUM2,ZC3H18,NOL10,PPP1R10,RPL35A,SNW1 |
| protein binding | ICAM4,EHD1,TAB1,RPS26,NR3C2,TH1L,AKR7A3,ASCL3,DSG1A,TBC1D10A |
| toxic substance binding | DSG1,GUCY2C,EPHX2,H2-AB1,NEFH,AZU1,A4GALT,CHRNA7,Alb,PHAX |
| identical protein binding | PTEN,IFI16,WRNIP1,SCUBE1,IGF2R,CDC42,ZNF703,TRP63,BAG2,MCM10 |
| ATP binding | PDPK1,SIK2,ULK1A,YTHDC2,UBE2G2,MAP2K1,DAPK2,RTCB,PANK2,MCM3L |
| amino acid binding | PAH,TPH2,OTC,TPH1A,TDO2,TH,TPH1B,GOT2,AARS2,DDC |
Interacting Protein
ASS1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ASS1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ASS1.
YWHAZ;Bles03;JAK2;MT2A;ARAF;PTPN1;MLH1;TERF1;CDR2;TERF2;yitU;ASCC2;AKTIP
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


