TP53BP1
-
Official Full Name
tumor protein p53 binding protein 1 -
Overview
May have a role in checkpoint signaling during mitosis. Enhances TP53-mediated transcriptional activation. Plays a role in the response to DNA damage. -
Synonyms
TP53BP1;tumor protein p53 binding protein 1;p202;53BP1;tumor suppressor p53-binding protein 1;p53BP1;p53-binding protein 1;tumor protein 53-binding protein, 1;tumor protein p53-binding protein, 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- CHO
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Protein Modification
- His
- GST
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- GFP
Background
What is TP53BP1 Protein?
TP53BP1, or Tumor Protein p53 Binding Protein 1, is a fascinating protein that plays an important role in our cells, especially when it comes to fixing DNA damage. Think of it as a vital player in the repair crew that comes into action when our DNA strands break, which can happen due to various stresses or environmental factors. TP53BP1 helps to maintain the stability of our genome by working alongside other proteins, including the well-known tumor suppressor protein p53. This collaboration is crucial for activating repair pathways and ensuring the cell either repairs itself correctly or, if the damage is too severe, moves towards cell death to prevent potential problems like cancer. Besides being a repair agent, TP53BP1 is also involved in processes like cellular senescence and immune responses, making it essential for healthy cellular function and protection against disease development.What is the Function of TP53BP1 Protein?
TP53BP1, also known as p53 Binding Protein 1, is like a guardian for our DNA. Its main job is to help repair DNA when it gets broken, which is super important because DNA breaks can lead to serious issues if not fixed. When there's damage, TP53BP1 jumps in to make sure the DNA repair teams are on point and working efficiently. It teams up with the tumor suppressor p53 and other proteins to activate the right repair pathways. Essentially, TP53BP1 helps keep our genetic information stable. Beyond repair work, it's also involved in managing how cells age and in the immune response, making sure cells behave properly and stay healthy. So, it's a key player in preventing disorders like cancer by protecting the integrity of our genetic material.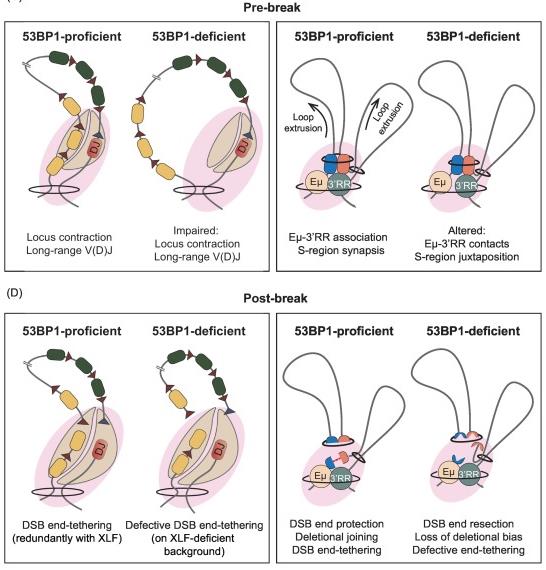
Fig1. 53BP1’s potential roles during antigen receptor locus diversification. (Eleni Kabrani, 2023)
TP53BP1 Related Signaling Pathway
The TP53BP1-related signaling pathway is all about DNA repair and maintaining genomic stability. When our DNA gets damaged, say from UV light or chemicals, TP53BP1 jumps into action. It recognizes the broken DNA ends and helps organize a repair crew. This process is key because if the damage isn't fixed, it could lead to cancer or other genetic diseases. TP53BP1 works closely with the p53 protein, which is famous for its role in preventing tumors. This collaboration ensures that if the damage is repairable, the correct repair pathway kicks in. If not, the cell may be directed to self-destruct to prevent any harmful mutations from passing on. Besides DNA repair, TP53BP1 also plays a part in how cells age and respond to stress, making it crucial for overall cellular health and integrity.TP53BP1 Related Diseases
TP53BP1, which stands for Tumor Protein P53 Binding Protein 1, plays a big role in how our cells fix damaged DNA. When DNA breaks, TP53BP1 steps in to help patch things up. If it doesn't work right, things can go awry, leading to various health issues. One of the main problems is cancer. When DNA errors pile up because they're not getting fixed, it sets the stage for cancerous growths. This is especially true for breast cancer, where faulty TP53BP1 means more DNA damage slips through the cracks, contributing to tumor development. But it's not just cancer; other genetic disorders linked to DNA repair issues can also involve TP53BP1. Its interactions with other proteins in the DNA repair toolkit underscore its importance in keeping our cells running smoothly.Bioapplications of TP53BP1
TP53BP1, or Tumor Protein P53 Binding Protein 1, is kicking up some dust in the world of biology. In cancer research, folks are excited about how this protein might take on tumors. By digging into how TP53BP1 helps repair DNA, scientists are coming up with new treatments that could make cancer therapies a lot more effective. But it doesn't stop at cancer—TP53BP1 is also being looked at for gene therapy. It's got this knack for keeping DNA in line, which makes it a hot topic for fixing genetic issues. Researchers are also eyeing it for regenerative medicine, where it's all about patching up and replacing damaged tissues. With its role in DNA repair, TP53BP1 isn't just sitting on the sidelines; it's part of the action, helping to drive forward some pretty cool medical breakthroughs.Case Study
Case Study 1: Kelliher JL. et al. Nat Commun. 2024
H2AX is crucial for DNA repair by bringing in key proteins to fix damage. Its phosphorylation at S139, known as γH2AX, is well-known for aiding repair, but its C-terminal tail is less understood. Researchers figured out how H2AX activates the essential MDC1-RNF8-RNF168 pathway for recruiting repair players like 53BP1 and BRCA1. Surprisingly, H2AX can also directly attract 53BP1 through a unique C-terminal region, bypassing the usual pathway. This happens via interaction with 53BP1's Oligomerization-Tudor domains. Additionally, this γH2AX-linked recruitment boosts resistance to camptothecin in H2AX-deficient cells.-
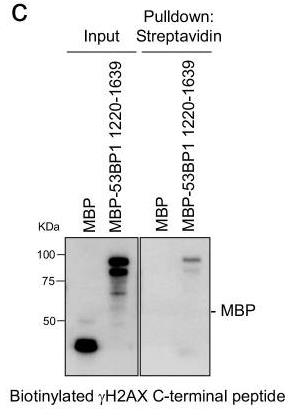 Fig1. Pulldown assay with purified recombinant proteins MBP or MBP-53BP1 IRIF formation fragment.
Fig1. Pulldown assay with purified recombinant proteins MBP or MBP-53BP1 IRIF formation fragment. -
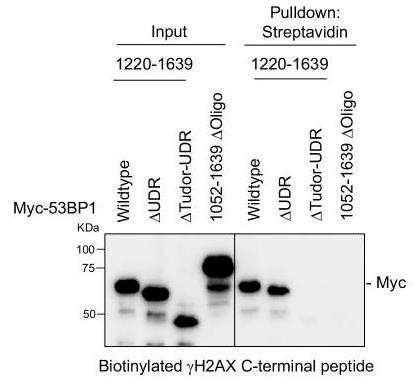 Fig2. Pulldown assay of Myc-53BP1 IRIF wildtype or deletion mutants using biotinylated phosphorylated S139 H2AX C-terminal tail peptide.
Fig2. Pulldown assay of Myc-53BP1 IRIF wildtype or deletion mutants using biotinylated phosphorylated S139 H2AX C-terminal tail peptide.
Case Study 2: Oda T. et al. Cell Prolif. 2023
Cellular senescence, associated with aging diseases, can result from DNA damage. DNA breaks, caused by stressors like cancer drugs, lead to p53 accumulation, essential for DNA repair and apoptosis. While p53's role is known, its regulation in senescence is less clear. Here 53BP1 buildup in the nucleus is necessary for senescence triggered by DNA damage through p53 activation. Reducing 53BP1 in fibroblasts lowers p53 activity and slows senescence. Blocking 53BP1 accumulation using certain inhibitors can prevent this form of senescence.-
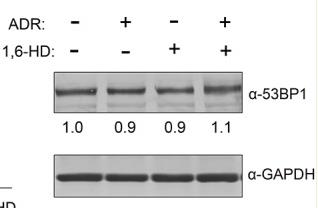 Fig3. Whole cell lysates from the cells treated with 1,6-hexanediol and/or ADR immunoblotted with anti-53BP1 antibodies.
Fig3. Whole cell lysates from the cells treated with 1,6-hexanediol and/or ADR immunoblotted with anti-53BP1 antibodies. -
 Fig4. Western blot of OUMS/Tet-on sh53BP1 whole cell lysates immunoblotted with anti-RNA168 and anti-53BP1 antibodies.
Fig4. Western blot of OUMS/Tet-on sh53BP1 whole cell lysates immunoblotted with anti-RNA168 and anti-53BP1 antibodies.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TP53BP1-001H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TP53BP1-001H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TP53BP1-641H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TP53BP1-641H)
Involved Pathway
TP53BP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TP53BP1 participated on our site, such as Cell Cycle,Cell Cycle Checkpoints,DNA Double Strand Break Response, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TP53BP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell Cycle Checkpoints | UBE2V2,RNF168,CHEK2,KAT5,HUS1,HTATIP,BABAM1,UIMC1,CDKN1B,MCM8 |
| G2/M Checkpoints | HUS1,THRSP,RAD9A,RAD9,RAD9B,RAD1,FAM175A,BABAM1,RAD17,BRE |
| DNA Repair | TOPBP1,ERCC8,FUZ,YY1,NFRKB,KIAA0146,RNF4,RIF1,RAD9A,INO80E |
| DNA Double Strand Break Response | FAM175A,BAZ1B,BARD1,BRE,SMARCA5,BABAM1,EYA4,UBE2V2,UIMC1,EYA3 |
| G2/M DNA damage checkpoint | FAM175A,UIMC1,BRCC3,BARD1,RNF168,BRE,BABAM1,THRSP |
| HDR through Homologous Recombination (HR) or Single Strand Annealing (SSA) | RTEL1,FUZ,GEN1,BABAM1,THRSP,PPP4CA,RAD51AP1,RAD1,BRE,WRN |
| DNA Double-Strand Break Repair | PARP2,FUZ,GEN1,TDP1,BARD1,RBBP8,HTATIP,EYA4,TOPBP1,HUS1 |
| Cell cycle | SMC1B,ARPP19A,RAD50,ANAPC5,CDC23,ORC6L,POT1,MAD1L1,BUB1,YWHABB |
-
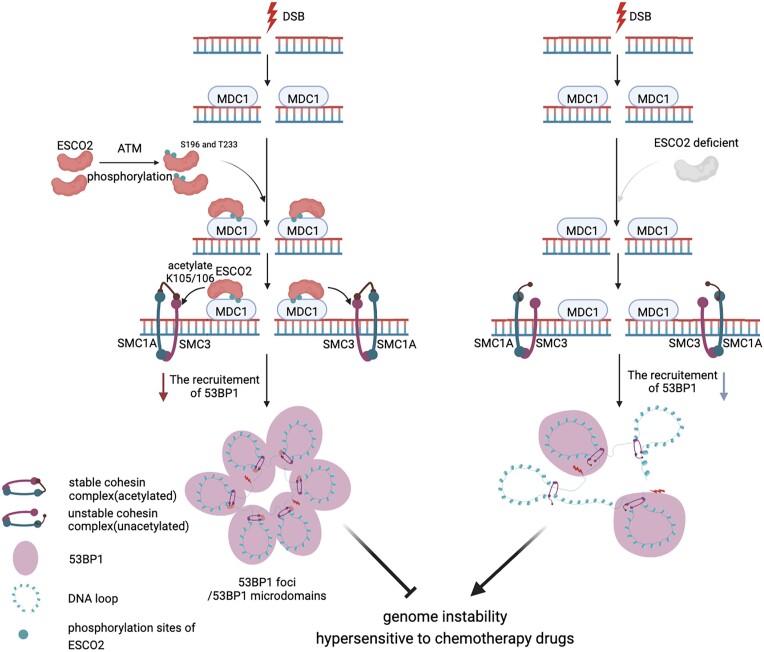 Fig1. Model for the role of the ATM–ESCO2–SMC3 axis in the DNA damage response. (Jianfeng Fu, 2023)
Fig1. Model for the role of the ATM–ESCO2–SMC3 axis in the DNA damage response. (Jianfeng Fu, 2023) -
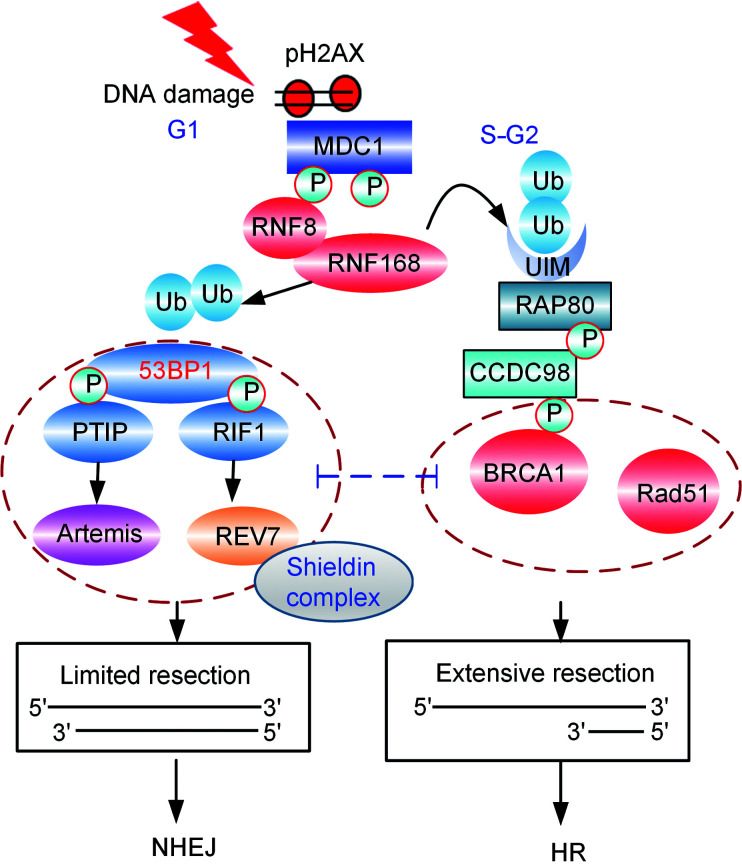 Fig2. Regulation of double-strand break repair pathway choice. (Fan Zhang, 2021)
Fig2. Regulation of double-strand break repair pathway choice. (Fan Zhang, 2021)
Protein Function
TP53BP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA polymerase II activating transcription factor binding,RNA polymerase II transcription cofactor activity,damaged DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TP53BP1 itself. We selected most functions TP53BP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TP53BP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| telomeric DNA binding | XRCC5,TINF2,TERT,TEN1,POT1A,TERF2,CTC1,CDAN1,PIF1,TERF1 |
| protein binding | CD36,U2AF1,LYL1,THAP11,EMID2,TMEM74,LILRA4,MATN3,SULT4A1,GNPDA1 |
| damaged DNA binding | APTX,TP63,RPA3,PCNA,UNG,ERCC1,POLB,XRCC5,RAD23AA,OGG1 |
| p53 binding | BANP,BCL2L12,CDK5,STK11,TP53RK,GSK3B,ZNF346,HSPD1,SETD7,ZFP385C |
| RNA polymerase II activating transcription factor binding | EOMES,JUN,SIN3A,SMAD3,PITX2,EP300,NEUROD1,T,TBX6,NHLH2 |
| methylated histone binding | GLYR1,MSH6,CDYL2,JHDM1D,CBX7,TDRD3,CBX4,ING1,WDR92,UHRF1 |
| RNA polymerase II transcription cofactor activity | MED13L,PPARGC1B,MED7,MDT-19,MED31,MED17,TDG,MED22,PPARGC1A,MED10 |
Interacting Protein
TP53BP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TP53BP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TP53BP1.
H2AFX;HIST2H4B;PAXIP1;HIST1H3D
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


