SUMF1
-
Official Full Name
sulfatase modifying factor 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of sulfate esters by oxidizing a cysteine residue in the substrate sulfatase to an active site 3-oxoalanine residue, which is also known as C-alpha-formylglycine. Mutations in this gene cause multiple sulfatase deficiency, a lysosomal storage disorder. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. -
Synonyms
SUMF1;sulfatase modifying factor 1;sulfatase-modifying factor 1;FGE;UNQ3037;FGly-generating enzyme;C-alpha-formylglycine-generating enzyme 1;AAPA3037;MGC131853;MGC150436
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Human
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
Background

Fig1. The summary of reported mutations in SUMF1 gene. (Jingjing Zhang, 2022)
What is SUMF1 protein?
SUMF1 (sulfatase modifying factor 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3p26. SUMF1 is essential for the activity of multiple sulfatases. The SUMF1 protein plays a role in the endoplasmic reticulum within the cell, converting cysteine residues in sulfatase into C-alpha-formylglycine (fGly) through a special post-translational modification, a process that is necessary for sulfatase's maturation and activity. The SUMF1 protein is consisted of 374 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 40.6 kDa.
What is the function of SUMF1 protein?
The main function of SUMF1 is to make post-translational modifications to sulfatase in the endoplasmic reticulum of cells. This process involves the conversion of specific cysteine residues in sulfatase to C-alpha-formylglycine, which activates these enzymes. Sulfatases are a class of biomolecules capable of hydrolyzing sulfate-containing bonds, such as the sulfated parts of glycolipids and glycoproteins. This modification of SUMF1 protein is essential for the maturation and function of sulfatase.
SUMF1 Related Signaling Pathway
SUMF1 is primarily involved in regulating the activity of sulfatase through its function as an oxidase to convert the cysteine residue in sulfatase to 3-oxoalanine, also known as C-alpha-formylglycine (fGly). This process is essential for the maturation and function of sulfatase. Sulfatase is involved in a variety of biological processes, including the hydrolysis of glycolipids and the sulfated portion of glycoproteins, which affect multiple signaling and metabolic pathways. Although SUMF1 itself is not directly involved in the traditional signaling pathway, it indirectly affects the signaling and metabolic processes associated with these enzymes by modifying sulfatases.
SUMF1 Related Diseases
Abnormalities in SUMF1 are associated with Multiple Sulfatase deficiencies, including Multiple Sulfatase Deficiency (MSD). MSD is a rare inherited metabolic disorder characterized by affecting the central and peripheral nervous systems, resulting in intellectual impairment, developmental delays, skin lesions, and multiple organ dysfunction. Mutations in the SUMF1 gene can impair the function of the SUMF1 protein, which in turn affects the activity of sulfatase, leading to the accumulation of sulfated sugar chains, and these abnormal accumulations are directly related to the occurrence of diseases. In addition, SUMF1 is also associated with IgA nephropathy, Fragile X syndrome and other diseases.
Bioapplications of SUMF1
In terms of drug development, the SUMF1 protein is a potential therapeutic target, and its inhibitors or activators may have a positive effect on the treatment of diseases associated with sulfatase activity. Meanwhile, recombinant forms of SUMF1 protein are used in laboratory studies for a variety of biological experiments, including enzyme activity testing, protein interaction studies, and drug screening.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Alessandro Fraldi, 2007
The catalytic activity of sulfatases resides in a unique formylglycine residue in their active site generated by the post-translational modification of a highly conserved cysteine residue. This modification is performed by SUMF1 (sulfatase-modifying factor 1), which is an essential factor for sulfatase activities. In previous studies, the researchers have shown that SUMF1 has an enhancing effect on sulfatase activity when co-expressed with sulfatase genes in COS-7 cells. In the present study, they demonstrate that SUMF1 displays an enhancing effect on sulfatases activity when co-delivered with a sulfatase cDNA via AAV (adeno-associated virus) and LV (lentivirus) vectors in cells from individuals affected by five different diseases owing to sulfatase deficiencies or from murine models of the same diseases [i.e. MLD (metachromatic leukodystrophy), CDPX (X-linked dominant chondrodysplasia punctata) and MPS (mucopolysaccharidosis) II, IIIA and VI]. The SUMF1-enhancing effect on sulfatase activity resulted in an improved clearance of the intracellular GAG or sulfolipid accumulation. Moreover, they demonstrate that the SUMF1-enhancing effect is also present in vivo after AAV-mediated delivery of the sulfamidase gene to the muscle of MPSIIIA mice, resulting in a more efficient rescue of the phenotype. These results indicate that co-delivery of SUMF1 may enhance the efficacy of gene therapy in several sulfatase deficiencies.

Fig1. Effects of SUMF1 on ARSE activity upon LV transduction of CDPX cells.

Fig2. AAV-mediated transfer of SGSH with SUMF1 in MPSIIIA MEFs.
Case Study 2: Kanchan Kumari, 2021
Sulfatase enzymes catalyze sulfate ester hydrolysis, thus deficiencies of sulfatases lead to the accumulation of biomolecules resulting in several disorders. The essential factor responsible for this modification of sulfatase is Sulfatase-Modifying Factor 1 (SUMF1). However, the function and regulation of SUMF1 in cancer are not studied. In the present study, for the first time, the researchers have assessed the expression of SUMF1 in breast cancer and report the oncogenic behavior upon overexpression of SUMF1. Although increased expression or activity of SUMF1 is anticipated based on its function, the expression of SUMF1 was found to be reduced in breast cancer cells at both mRNA and protein levels. An estrogen receptor (ER) dependent expression of SUMF1 was observed and higher SUMF1 expression is associated with improved breast cancer patient survival in ER-positive cases. However, high SUMF1 expression leads to reduced median survival in ER-negative breast cancer patients. Putative binding sites for miRNAs-106b-5p, 128-3p and 148b-3p were found at 3'-UTR of SUMF1.
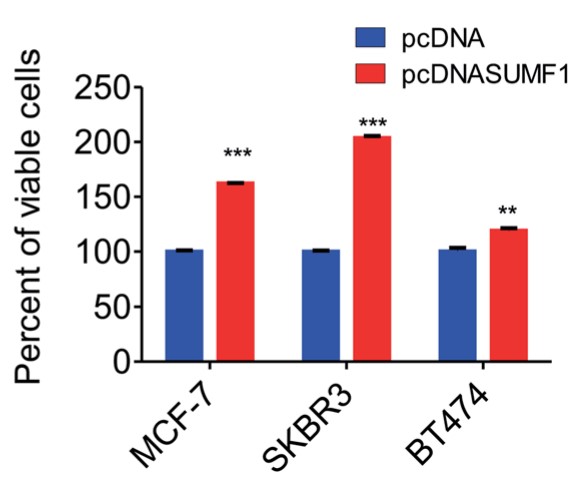
Fig3. Graph shows the quantification of crystal violet assay displaying the percent of viable cells in control and SUMF1 over-expressed cells.
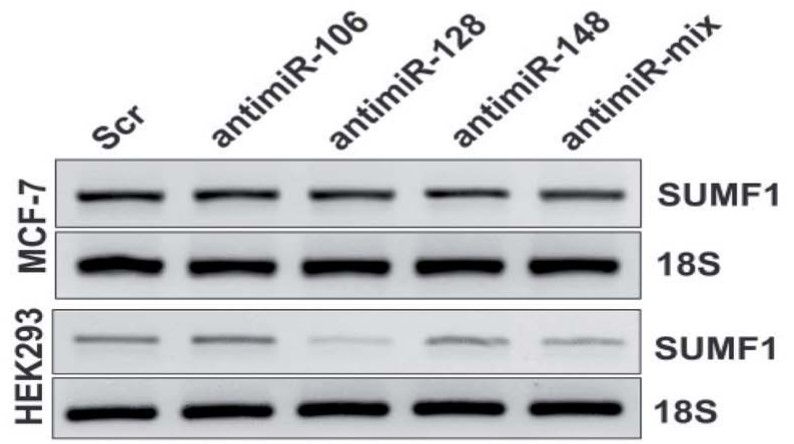
Fig4. Expression of SUMF1 in cells transfected with antimiR oligonucleotides against miR-106, 128 and 148 is displayed in the agarose gel as obtained using RT-PCR.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SUMF1-414HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SUMF1-5827H)
Involved Pathway
SUMF1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SUMF1 participated on our site, such as Lysosome, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SUMF1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Lysosome | CTSA,CTSM,ATP6V0A1B,ARSB,CTSBA,ATP6V0C,GLA,NPC2,LGMN,CTSSA |
Protein Function
SUMF1 has several biochemical functions, for example, metal ion binding,oxidoreductase activity,protein homodimerization activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SUMF1 itself. We selected most functions SUMF1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SUMF1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | ABO,MOB3A,NRXN2B,HRG,PKMYT1,PPP1CC,FUZ,RXRAB,PON3,ZMYND19 |
| protein homodimerization activity | TENM2,EFR3A,OSTA,TFAP2B,HSF2,ADD1,SYT10,VWF,TFAP2E,GDNF |
| oxidoreductase activity | C10orf33,CYP11C1,ETFDH,SCDB,DHRS7,P4HA1B,MOSC2,HEPHL1A,CYP1A1,SDR39U1 |
Interacting Protein
SUMF1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SUMF1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SUMF1.
q8clf6_yerpe;cona_canen;Hsd17b10;Lamp1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


