RPS6
-
Official Full Name
ribosomal protein S6 -
Overview
Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species and approximately 80 structurally distinct proteins. This gene encodes a cytoplasmic ribosomal protein that is a component of the 40S subunit. The protein belongs to the S6E family of ribosomal proteins. It is the major substrate of protein kinases in the ribosome, with subsets of five C-terminal serine residues phosphorylated by different protein kinases. Phosphorylation is induced by a wide range of stimuli, including growth factors, tumor-promoting agents, and mitogens. Dephosphorylation occurs at growth arrest. The protein may contribute to the control of cell growth and proliferation through the selective translation of particular classes of mRNA. As is typical for genes encoding ribosomal proteins, there are multiple processed pseudogenes of this gene dispersed through the genome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
RPS6;ribosomal protein S6;S6;40S ribosomal protein S6;phosphoprotein NP33
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Insect Cell
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&GST
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPS6-307H | Recombinant Human RPS6, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | ||
| RPS6-1072Z | Recombinant Zebrafish RPS6 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| RPS6-14492M | Recombinant Mouse RPS6 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| RPS6-30769TH | Recombinant Human RPS6 | E.coli | Human | Non | Full L. 1-249 a.a. |
|
| RPS6-5171R | Recombinant Rat RPS6 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Rat | His |
|
|
| RPS6-6778C | Recombinant Chicken RPS6 | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| RPS6-567HCL | Recombinant Human RPS6 lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| RPS6-1102H | Recombinant Human RPS6 protein, His-GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&GST | 35-229aa |
|
| RPS6-171 | Recombinant RPS6 Protein, GST-tagged | Insect Cell | GST |
|
||
| RPS6-445HF | Recombinant Full Length Human RPS6 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 249 amino acids |
|
| RPS6-4830R | Recombinant Rat RPS6 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| RPS6-4830R-B | Recombinant Rat RPS6 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| RPS6-7791M | Recombinant Mouse RPS6 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| RPS6-7791M-B | Recombinant Mouse RPS6 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background

Fig1. Secondary structure and post–translational modification of RPS6. (Yong Weon Yi, 2021)
What is RPS6 protein?
RPS6 gene (ribosomal protein S6) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 9 at locus 9p22. Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species and approximately 80 structurally distinct proteins. This gene encodes a cytoplasmic ribosomal protein that is a component of the 40S subunit. The protein belongs to the S6E family of ribosomal proteins. It is the major substrate of protein kinases in the ribosome, with subsets of five C-terminal serine residues phosphorylated by different protein kinases. The protein may contribute to the control of cell growth and proliferation through the selective translation of particular classes of mRNA. As is typical for genes encoding ribosomal proteins, there are multiple processed pseudogenes of this gene dispersed through the genome. The RPS6 protein is consisted of 249 amino acids and RPS6 molecular weight is approximately 28.7 kDa.
What is the function of RPS6 protein?
The phosphorylation of RPS6 is catalyzed by multiple kinases, including p70 S6 Kinase (S6K1), and is a widely used biomarker for the activation of the mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway, which is central to the regulation of cell growth, proliferation, and metabolism. Moreover, RPS6 phosphorylation has been implicated in various physiological and pathological processes in the nervous system. It is used as a readout for neuronal activity and is associated with synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. In addition to its role in translation, RPS6 phosphorylation may have extratranslational functions, such as interacting with other cellular proteins and potentially affecting other cellular processes.
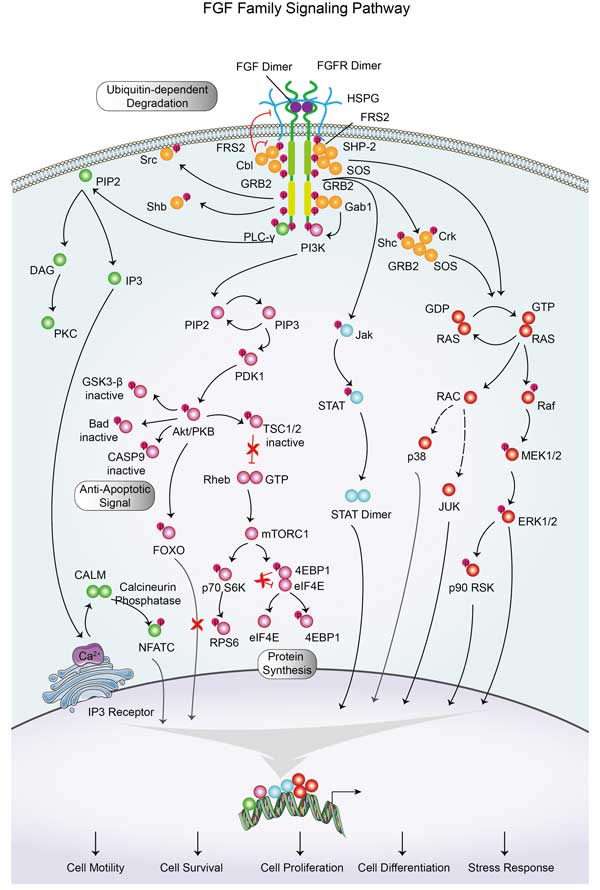
RPS6 Related Signaling Pathway
RPS6 cell signaling pathways are complex. RPS6 is one of the key substrates of mTOR Complex 1 (mTORC1). When mTORC1 is activated, it phosphorylates RPS6, which promotes protein synthesis and cell growth. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway influences the phosphorylation of RPS6 by activating mTORC1. AKT can activate mTORC1 directly or indirectly by inhibiting the TSC1/TSC2 complex, resulting in increased phosphorylation of RPS6. The Ras-MAPK signaling pathway can phosphorylate eIF4E through MNK kinase, which is an intersection of the signaling pathway where RPS6 is located, affecting translation initiation and cell proliferation. Phosphorylation of RPS6 may affect the expression of MDM2, TP53, CDKN1A and other genes, and participate in the regulation of p53 signaling pathway, thus affecting cell cycle and cell proliferation.
RPS6 Related Diseases
RPS6 is implicated in a variety of diseases, predominantly in the context of cancer. RPS6's role in cancers is highlighted by its association with tumor cell proliferation, with evidence suggesting that its knockdown can inhibit cancer cell growth. Furthermore, RPS6 has been implicated in non-cancerous diseases such as Diamond-Blackfan Anemia (DBA), a rare disorder characterized by a deficiency in the production of red blood cells, where mutations in RPS6 can affect ribosome assembly and function.
Bioapplications of RPS6
Given its involvement in mnay pathways, RPS6 is being explored as a potential therapeutic target for various diseases, including cancer, where its inhibition could lead to the suppression of tumor growth. Furthermore, RPS6's phosphorylation status is also considered a biomarker for the activity of the mTOR pathway, which can be useful for monitoring treatment responses, especially to mTOR inhibitors in cancer therapy. In addition to its direct role in disease, RPS6 is also studied for its potential as a biomarker in conditions like Diamond-Blackfan Anemia (DBA), a ribosomopathy where RPS6 mutations affect ribosome assembly.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kali A Smolen, 2023
Pathogenic mutations altering 13 different amino acids have been identified, with the E198K variant accounting for ∼40% of reported cases. However, the generation of a heterozygous E198K variant cell line to study the molecular effects of the pathogenic mutation has been challenging. Here, researchers use CRISPR-PRIME genomic editing to introduce a transition (c.592G>A) in a single PPP2R5D allele in HEK293 cells, generating E198K-heterozygous lines to complement existing E420K variant lines. They generate global protein and phosphorylation profiles of WT, E198K, and E420K cell lines and find unique and shared changes between variants and WT cells in kinase- and phosphatase-controlled signaling cascades. observed ribosomal protein S6 (RPS6) hyperphosphorylation as a shared signaling alteration, indicative of increased ribosomal protein S6-kinase activity. Treatment with rapamycin or an RPS6-kinase inhibitor (LY2584702) suppressed RPS6 phosphorylation in both, suggesting upstream activation of mTORC1/p70S6K. This data suggests ERK-dependent activation of mTORC1 in both E198K and E420K variant cells, with additional AKT-mediated mTORC1 activation in the E420K variant.

Fig1. LC-MS3 data for sites S240/244 and S235/236 of RPS6.

Fig2. Quantification of P-S240/244 of RPS6 normalized to total RPS6 for rapamycin.
Case Study 2: Ka-Wai Mok, 2014
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) is an emerging regulator of blood-tissue barriers that utilizes ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6) as the downstream signaling molecule. To explore the role of rpS6 in blood-testis barrier (BTB) function, a constitutively active quadruple rpS6 phosphomimetic mutant was constructed in mammalian expression vector and overexpressed in Sertoli cells cultured in vitro that mimicked the BTB in vivo. Using this quadruple phosphomimetic mutant, phosphorylated (p)-rpS6 was shown to disrupt IGF-1/insulin signaling, thereby abolishing Akt phosphorylation, which led to an induction of MMP-9. This increase in MMP-9 secretion perturbed the Sertoli cell tight junction permeability barrier by proteolysis-mediated downregulation of tight junction proteins at the BTB. These findings were confirmed by the use of a specific MMP-9 inhibitor that blocked the disruption of the tight junction permeability barrier by the rpS6 mutant.

Fig3. Overexpression of wild-type rpS6 per se perturbed the tight junction barrier.

Fig4. Immunoblot analysis of rpS6, p-rpS6, selected tight junction proteins and other proteins.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. Western blot (RPS6-171)
Involved Pathway
RPS6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RPS6 participated on our site, such as Ribosome,HIF- signaling pathway,mTOR signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RPS6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| HIF- signaling pathway | ANGPT2,PGK1,NFKB1,LDHA,CAMK2G,PIK3CA,EPO,PRKCG,PFKFB3,ENO2 |
| Insulin signaling pathway | INSRB,CALML5,PYGMA,TSC1A,PRKAR2AA,AKT2L,GRB2,PRKAR2A,PRKACB,PPP1CA |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | MET,FGF16,PPP2R2A,GH1,ATF4,GNG13,BCL2,TCL1B,HRAS,PPP2R2C |
| Ribosome | RPL15,RPL3L,MRPL17,RPL26,RPS27,RPL22L1,MRPL1,MRPS11,MRPL14,RPS20 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | CAMK2B,WNT9B,ACTB,MAPK13,PLCE1,ITGAV,CBL,ACTG1,VTN,MAPK11 |
| mTOR signaling pathway | AKT3A,RPS6KAL,PDPK1B,PIK3CG,CAB39L1,PRKAA2,PRR5,PTENB,RPS6KA6,CAB39L |
Protein Function
RPS6 has several biochemical functions, for example, poly(A) RNA binding,protein binding,protein kinase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RPS6 itself. We selected most functions RPS6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RPS6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| structural constituent of ribosome | RSL24D1,RPL7A,RPL39,RPL35,RPL5A,MRPS21,MRPL18,RPS3,RPL36,UBA52 |
| protein kinase binding | TRIM5,DCX,HNRNPA0,SMAD3,ACVRL1,NPM1,NEFH,SREBF1,CCNE1,TBC1D14 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | MRPS24,STAU2,DARS,RPS8,FASTKD5,NCBP2,RPP25,NXF3,RPP30,MRPL13 |
| protein binding | RTP4,UBAP2L,SP2,KRTAP9-2,DHX32,IMP4,TIE1,TBL3,SMAD4,TRAPPC10 |
Interacting Protein
RPS6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RPS6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RPS6.
STAU1;NCBP1;PASK;ESR1;PPP2R2B;AURKA;ATF4;RPS6KA2;RPS6KA1;RPS6KB2;MAP3K1
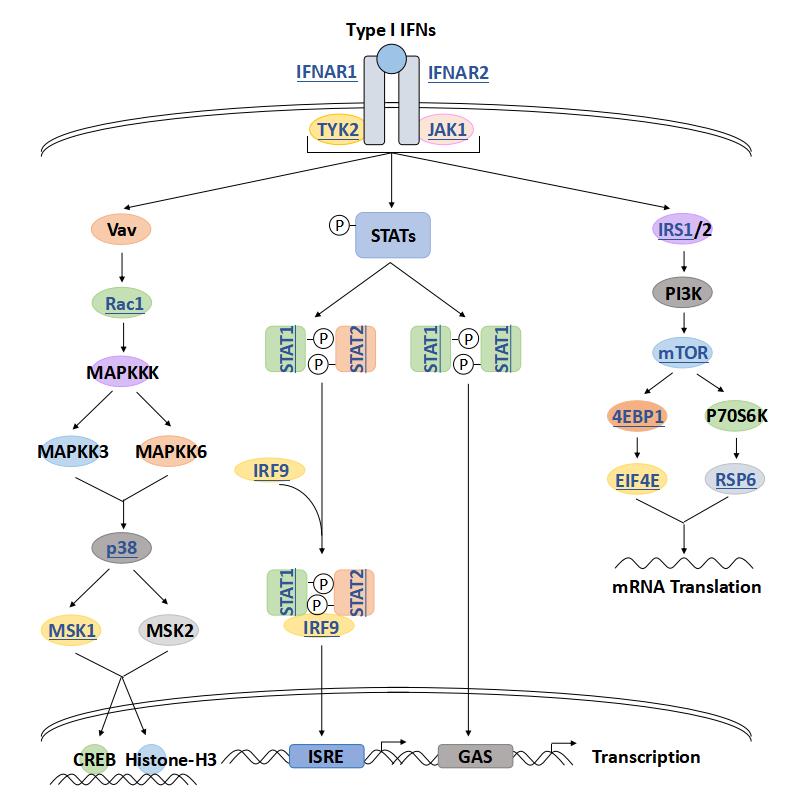
RPS6 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Osman, AM; van Loveren, H; et al. The immunosuppressant tributyltin oxide blocks the mTOR pathway, like rapamycin, albeit by a different mechanism. JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY 34:1361-1367(2014).
- von der Heyde, S; Bender, C; et al. Boolean ErbB network reconstructions and perturbation simulations reveal individual drug response in different breast cancer cell lines. BMC SYSTEMS BIOLOGY 8:-(2014).