RBPJ
-
Official Full Name
recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region -
Overview
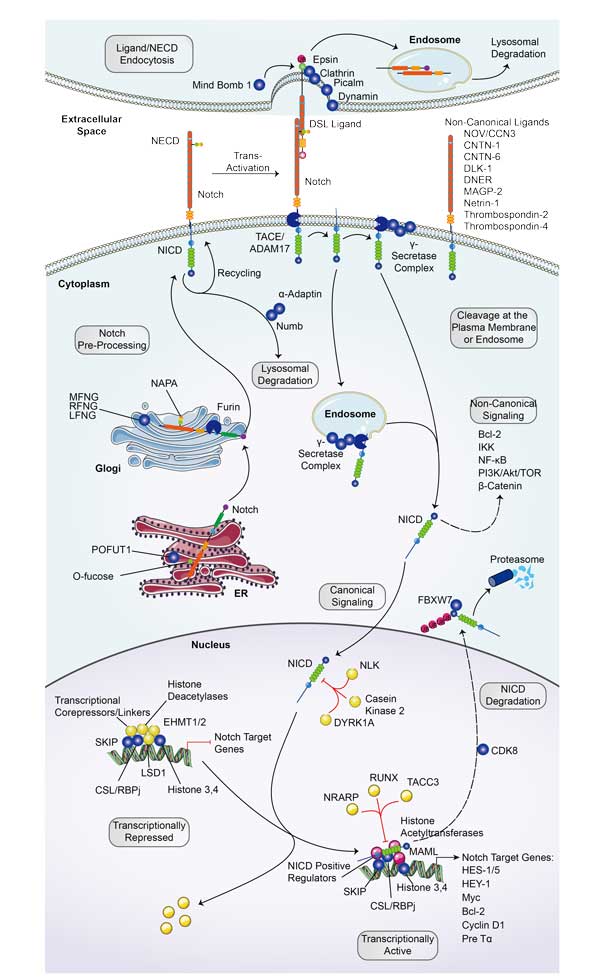
The protein encoded by this gene is a transcriptional regulator important in the Notch signaling pathway. The encoded protein acts as a repressor when not bound to Notch proteins and an activator when bound to Notch proteins. It is thought to function by recruiting chromatin remodeling complexes containing histone deacetylase or histone acetylase proteins to Notch signaling pathway genes. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene, and several pseudogenes of this gene exist on chromosome 9. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2013] -
Synonyms
RBPJ;recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region;SUH;csl;AOS3;CBF1;KBF2;RBP-J;RBPJK;IGKJRB;RBPSUH;IGKJRB1;recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless;CBF-1;RBP-JK;RBP-J kappa;H-2K binding factor-2;suppressor of hairless homolog;renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-30;immunoglobulin kappa J region recombination signal binding protein 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- GST
- His
- Myc&DDK
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
Involved Pathway
RBPJ involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RBPJ participated on our site, such as Notch signaling pathway,Epstein-Barr virus infection,Viral carcinogenesis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RBPJ were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Viral carcinogenesis | YWHAG,HIST1H2BC,HIST1H4A,BAD,H2-Q10,REL,IL6ST,HIST1H4K,SP100,C3 |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | RAN,PSMD4,AKAP8L,CD40,TAB1,POLR1D,IL10RB,RB1,ENTPD3,CCNA1 |
| Notch signaling pathway | NOTCH1B,APH1B,SNW1,JAG2B,DLK1,NOTCH3,MAML2,MFNG,RBPJA,DLL1 |
Protein Function
RBPJ has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RBPJ itself. We selected most functions RBPJ had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RBPJ. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein N-terminus binding | ERCC3,TAF11,KCNIP1,PEX14,PPP1CC,TSC1,DAXX,SLC6A3,EIF3E,RASSF1 |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | NR2F1B,DMRTC2,KLF9,ESR1,NR5A2,AHR1A,TBR1,BARX1,ESRRGA,CEBPD |
| protein binding | HHIP,NR5A2,HCFC1,UBE2B,TPD52L3,GGA3,NFKBID,SCARA5,CYHR1,HK2 |
| DNA binding | RCAN1,HMGA2,PKNOX1.1,RARGA,MAPK1,BANP,NKX3.2,ZFP865,ZBTB32,RABGEF1 |
| RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | ZBTB7A,HHEX,CTCFL,TBX15,SNAI3,GLI3,ISL1,MYOG,NKX2-8,NRF1 |
| recombinase activity | RAD51D,RAD51L1,XRCC3,RAD51C,RAD51,RAD51B,RAD51L3,XRCC2,DMC1 |
| chromatin binding | PRKCBB,MLH3,HMGB2B,CENPA,ENY2,CHD8,ERCC6,POLE,SP110,PRKCBP1L |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | PAX6A,ZNF274,NFIL3-3,BPTF,RORAB,ZNF187,NR4A1,NR5A2,ZFP161,POU2F1B |
| transcription factor binding | ATG7,SOST,APBB1,BCOR,NFYC,ARHGEF2,PPP1R13BB,E2F2,RARA,JUND |
Interacting Protein
RBPJ has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RBPJ here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RBPJ.
NOTCH1;ATXN1L;ATXN1;RITA1
RBPJ Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Guiu, J; Bergen, DJM; et al. Identification of Cdca7 as a novel Notch transcriptional target involved in hematopoietic stem cell emergence. JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MEDICINE 211:2411-2423(2014).
- Querol, L; Clark, PL; et al. Protein array-based profiling of CSF identifies RBPJ as an autoantigen in multiple sclerosis. NEUROLOGY 81:956-963(2013).