RBP3
-
Official Full Name
retinol binding protein 3, interstitial -
Overview
Interphotoreceptor retinol-binding protein is a large glycoprotein known to bind retinoids and found primarily in the interphotoreceptor matrix of the retina between the retinal pigment epithelium and the photoreceptor cells. It is thought to transport retinoids between the retinal pigment epithelium and the photoreceptors, a critical role in the visual process.The human IRBP gene is approximately 9.5 kbp in length and consists of four exons separated by three introns. The introns are 1.6-1.9 kbp long. The gene is transcribed by photoreceptor and retinoblastoma cells into an approximately 4.3-kilobase mRNA that is translated and processed into a glycosylated protein of 135,000 Da. The amino acid sequence of human IRBP can be divided into four contiguous homology domains with 33-38% identity, suggesting a series of gene duplication events. In the gene, the boundaries of these domains are not defined by exon-intron junctions, as might have been expected. The first three homology domains and part of the fourth are all encoded by the first large exon, which is 3,180 base pairs long. The remainder of the fourth domain is encoded in the last three exons, which are 191, 143, and approximately 740 base pairs long, respectively. -
Synonyms
RBP3;retinol binding protein 3, interstitial;retinol-binding protein 3;D10S64;D10S65;D10S66;Interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein;Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein;Interstitial retinol binding protein;Interstitial retinol-binding protein;IRBP;RBP 3;RBPI;RET3_HUMAN;Retinol binding protein 3;Retinol binding protein 3 interstitial;OTTHUMP00000019536
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Rat
- Bovine
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian cells
- Yeast
- HEK293
- Human Cells
- HEK293T
- His
- Non
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
- GST
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is RBP3 protein?
RBP3 gene (retinol binding protein 3) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10q11. RBP3, also known as IRBP, is a glycoprotein that is abundant in the retina. RBP3 mainly acts as A transport of retinol (a form of vitamin A) between photoreceptor cells and pigment epithelial cells in the retina and is essential for visual circulation. It supports the light sensing and light conversion process of the retina by binding and transporting retinol and its derivatives. The function of RBP3 is not limited to retinol transport, it may also be involved in the oxidative stress response of the retina, has antioxidant properties, and protects photoreceptor cells from light damage. The RBP3 protein is consisted of 1247 amino acids and RBP3 molecular weight is approximately 135.4 kDa.
What is the function of RBP3 protein?
RBP3 plays A vital role in the visual cycle by helping to transport retinol (a form of vitamin A) and its derivatives in the retina, maintaining the normal function of photoreceptor cells. In addition, RBP3 is involved in lipid transport between retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and photoreceptor cells. The thiol-dependent antioxidant activity of RBP3 contributes to the maintenance of fine REDOX balance in the normal retina. Thus, dysfunction of RBP3 may play a role in many retinal diseases, including diabetic retinopathy.

Fig1. Simplified composition of the retina with RPE, photoreceptors, Muller cells, and IPM represented. (Vineeta Kaushik, 2023)
RBP3 related signaling pathway
The RBP3-associated signaling pathways are primarily involved in the transport and metabolism of retinoic acid, an active form of vitamin A. RBP3 is a plasma protein that specifically binds retinol, helping it transport to cells and tissues that require retinoic acid. Within the cell, retinol is metabolized into retinoic acid, which regulates gene expression by binding to nuclear receptors, such as retinoic acid receptors and retinoflavin X receptors, affecting cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. The signaling pathway of RBP3 is therefore closely related to physiological processes such as the visual cycle, embryonic development, cell proliferation, and immune regulation.
RBP3 related diseases
Rbp3-associated diseases mainly involve those that affect the transport and metabolism of retinoic acid (the active form of vitamin A). Because RBP3 plays a key role in the transport and distribution of retinoic acid in the body, its abnormal expression or function may be associated with visual problems, developmental defects, skin diseases, and some types of cancer. For example, deficiencies in RBP3 may lead to visual impairments such as night blindness, while dysregulation of its expression may be associated with malignancies such as acute promyelocytic leukemia. In addition, as a component of the retinoic acid signaling pathway, dysfunction of RBP3 may also affect embryonic development, bone development, and the normal functioning of the immune system.
Bioapplications of RBP3
RBP3 is a protein that is specifically expressed in retinal photoreceptors and is essential for visual function. Studies have shown that rhRBP3 can prevent or stop the development of diabetic retinopathy. In experiments, by overexpressing rhRBP3 in mouse and rat models of diabetic retinopathy or injecting it directly into the retina, the progression of the lesions could be prevented or slowed. The mechanism of action of rhRBP3 involves binding to glucose transporter 1, slowing the uptake of glucose by eye cells, thereby avoiding the toxic effects of hyperglycemia. In addition, rhRBP3 reduces retinal dysfunction and elevated levels of inflammatory factors caused by high blood sugar. These findings support the potential therapeutic value of rhRBP3 in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy and may serve as a biomarker for the severity and progression of the disease.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Hisashi Yokomizo, 2019
The Joslin Medalist Study found that over 35% of individuals with type 1 diabetes for 50 years or more have little to no diabetic retinopathy (DR), hinting at natural protective factors. Proteomic analysis revealed higher levels of retinol binding protein 3 (RBP3), a photoreceptor-secreted retinol transporter, in these patients. RBP3 was inversely linked to DR severity and could counteract VEGF's harmful effects by inhibiting its receptor phosphorylation. RBP3 also reduced hyperglycemia-induced inflammation by binding to glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) and decreasing glucose uptake. Thus, RBP3's elevated levels might protect against DR progression by curbing glucose uptake and inflammation.
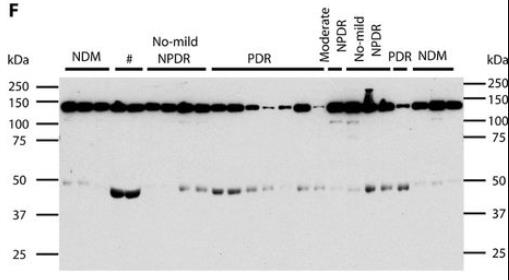
Fig1. Representative immunoblot (IB) for RBP3 expression in human vitreous.

Fig2. Effects of recombinant hRBP3 (rhRBP3) on VEGF-mediated retinal vascular permeability
Case Study 2: Ling Zhu, 2015
While studying Norrin protein in a transgenic mouse model with controllable Müller cell disruption, a decrease in a ~150 kDa protein, later identified as Inter-photoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP). IRBP's mRNA and protein levels dropped significantly after Müller cell disruption, leading to hyperfluorescent dots and A2E accumulation. Cone photoreceptor cell lines treated with stressed Müller cell medium showed reduced IRBP expression, suggesting Müller cells regulate IRBP via secreted factors, possibly TNFα. This indicates that IRBP downregulation due to Müller cell dysfunction might be an early indicator of photoreceptor degeneration in retinal diseases.
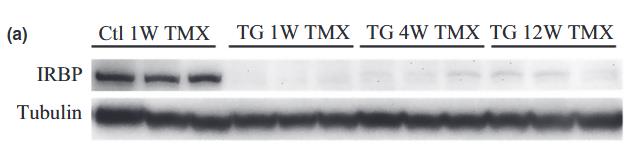
Fig3. Western blot analysis of IRBP expression in the control mice.

Fig4. Western blot analysis of IRBP expression in the control mice treated with or without LPS.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RBP3-511H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RBP3-102HFL)
Involved Pathway
RBP3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RBP3 participated on our site, such as Signal Transduction,The canonical retinoid cycle in rods (twilight vision),The retinoid cycle in cones (daylight vision), which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RBP3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Signal Transduction | WIPF3,RGS12,OPN4A,PMEPA1,APOC2,PTHLH,PAG1,UTS2D,ANXA1B,TAS2R3 |
| The canonical retinoid cycle in rods (twilight vision) | RDH12,RLBP1A,RLBP1B,RPE65A,RDH10,IRBP,SDR9C7,RBP4,RLBP1,RPE65B |
| the visual cycle I (vertebrates) | RBP5,DHRS4 |
| Visual phototransduction | NMT1A,RLN1,APOA4B.2,ABCA4A,IRBP,GUCA1E,BCO2,METAP2,NMT1B,MYO7A |
| The retinoid cycle in cones (daylight vision) | OPN1SW1,DHRS3,RLBP1B,RLBP1,IRBP,DHRS3A,RLBP1A,OPN1LW1,OPN1LW2 |
Protein Function
RBP3 has several biochemical functions, for example, retinal binding,retinoid binding,retinol binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RBP3 itself. We selected most functions RBP3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RBP3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| retinal binding | RBP5,RBP1,RBP7,RBP2,RBP2B,RBP4,CRABP1,CRABP2,RBP2A |
| retinoid binding | RBP2,LCN5,RBP5,PTGDS,CRABP1,CRABP2,RBP4L,RBP1 |
| serine-type peptidase activity | PARLA,KLK1B5,DPP6B,HPN,ST14,PREP,MCPT8,PRSS42,ELA2,TMPRSS11B |
| retinol binding | RBP4,ADH4,CRABP1,RLBP1,RBP1,CRABP2,ADH7,C8G,RBP2,RBP5 |
Interacting Protein
RBP3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RBP3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RBP3.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


