PKM2
-
Official Full Name
pyruvate kinase, muscle -
Overview
Pyruvate kinase, a glycolytic enzyme, catalyses the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate. In mammals, the M1 isoform (PKM1) is expressed in most adult tissues. The M2 isoform (PKM2), an alternatively-spliced variant of M1, is expressed during emb -
Synonyms
PKM2;pyruvate kinase, muscle;pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2;OIP3;PK3;THBP1;p58;OIP-3;tumor M2-PK;PK, muscle type;pyruvate kinase 2/3;OPA-interacting protein 3;pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme;thyroid hormone-binding protein 1;cytosolic thyroid
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKM2-946H | Recombinant Human PKM2 protein(Ser2-Pro531), His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 2-531 a.a. | |
| PKM2-34H | Active Recombinant Human PKM2 Protein, N-His tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
|
Background
What is PKM protein?
PKM (pyruvate kinase M1/2) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 15 at locus 15q23. This gene encodes a protein involved in glycolysis. The PKM gene can produce two major isoforms through alternative splicing: PKM1 and PKM2. The encoded protein is a pyruvate kinase that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, generating ATP and pyruvate. This protein has been shown to interact with thyroid hormone and may mediate cellular metabolic effects induced by thyroid hormones. This protein has been found to bind Opa protein, a bacterial outer membrane protein involved in gonococcal adherence to and invasion of human cells, suggesting a role of this protein in bacterial pathogenesis. The PKM protein is consisted of 531 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 57.9 kDa.
What is the function of PKM protein?
PKM is a key glycolytic enzyme, which mainly plays a role in the glycolysis process of cells. PKM1/2 catalyzes the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvate, and in the process produces ATP. In addition to its metabolic function, PKM1/2 has multiple biological functions, including being involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and tumorigenesis as a transcription factor for gene expression. Through its non-enzymatic activity, PKM1/2 is able to enter the nucleus and affect the expression of multiple genes, especially in tumor cells. In addition, the activity and expression levels of PKM1/2 are controlled by multiple regulatory mechanisms, including gene transcription, post-translational modification, and subunit assembly, which ensure that cells are able to adjust their metabolic pathways according to energy requirements and metabolic status.
PKM Related Signaling Pathway
PKM (Pyruvate Kinase M), particularly its isoform PKM2, is involved in several signaling pathways that contribute to various cellular processes, including metabolism, cell growth, and tumorigenesis. PKM2 can interact with and phosphorylate the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, and this phosphorylation prevents the binding of ubiquitin E3 ligase to Bcl-2, thereby inhibiting the degradation of Bcl-2 and ultimately inhibiting apoptosis. By affecting the stability of Bcl-2, PKM2 indirectly participates in the signaling of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, which is essential for the degradation and stabilization of proteins within the cell. Studies have shown that dysregulation of mirnas contributes to cancer development by altering the proportion of PKM isoforms expressed.
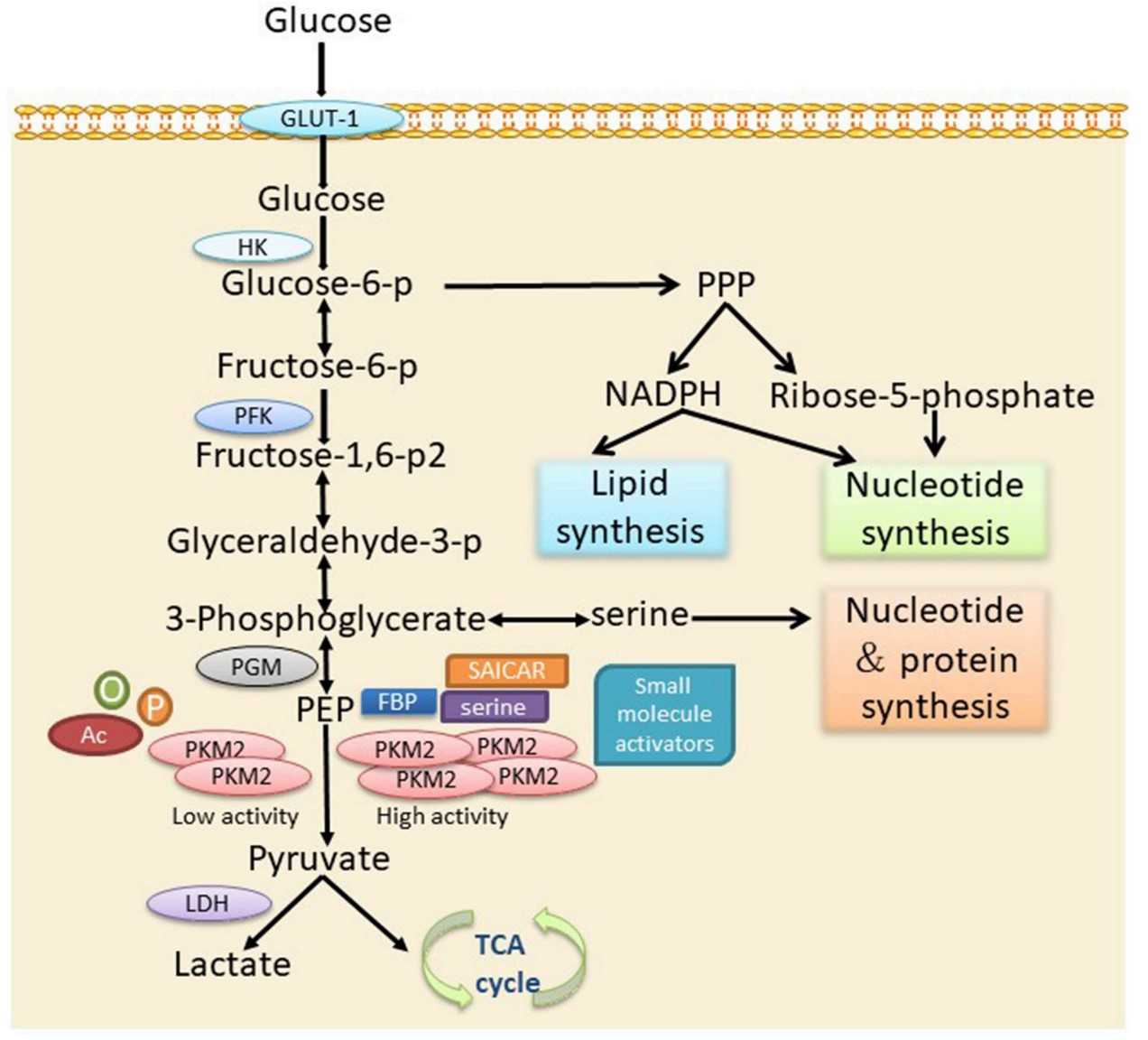
Fig1. The role of PKM2 in cellular metabolism via the glycolytic pathway. (Danyi Xu, 2019)
PKM Related Diseases
The expression of PKM2 was significantly increased in various tumor cells, and it was involved in the expression, regulation, autophagy and cell cycle progression of tumor cell proliferation related genes. Studies have shown that PKM2 plays a role in the activation of inflammation in diabetic nephropathy, and the activation of PKM2 is related to the activation of inflammatory bodies and the release of inflammatory factors in high glucose environment. PKM1 is expressed in the heart and is associated with cardiac remodeling and function.
Bioapplications of PKM
Due to the role of PKM in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, in-depth study of its structure and function could facilitate drug design and development targeting this enzyme, especially in the development of anti-tumor drugs. In the field of biotechnology, the production of biofuels or bio-based chemicals is enhanced by engineering PKM to improve the glycolysis efficiency of microbial production strains.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xin Zhou, 2024
Patients with hypopharyngeal carcinoma (HPC) have a poor prognosis mainly because of lymphatic metastasis. This research aimed to determine the PKM2 role in lymphatic metastasis in HPC and the underlying molecular mechanism contributing to this phenomenon. PKM2 in HPC was studied for its expression and its likelihood of overall survival using TCGA dataset. Western blotting, qRT-PCR, and IHC were employed to confirm PKM2 expression. Methods including gain- and loss-of-function were used to examine the PKM2 role in HPC metastasis in vitro and in vivo. In vitro and in vivo studies also confirmed lymphatic metastasis's mechanism. In vitro research showed that knocking down PKM2 decreased tumor cell invasion, migration, and proliferation while promoting apoptosis and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition, but overexpressing PKM2 had the reverse effect. Animal studies suggested that PKM2 may facilitate tumor development and lymphatic metastasis.

Fig1. Western blotting analysis of the expression of PKM2 in FaDu cell line.

Fig2. qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of key EMT-related genes in vector and PKM2 groups in vitro.
Case Study 2: Verena Boschert, 2022
The enzyme pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) plays a major role in the switch of tumor cells from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis, one of the hallmarks of cancer. Different allosteric inhibitors or activators and several posttranslational modifications regulate its activity. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a common disease with a high rate of recurrence. To find out more about PKM2 and its modulation in HNSCC, the researchers examined a panel of HNSCC cells using real-time cell metabolic analysis and Western blotting with an emphasis on phosphorylation variant Tyr105 and two reagents known to impair PKM2 activity. The results show that in HNSCC, PKM2 is commonly phosphorylated at Tyrosine 105. Its levels depended on tyrosine kinase activity, emphasizing the importance of growth factors such as EGF (epidermal growth factor) on HNSCC metabolism. Furthermore, its correlation with the expression of CD44 indicates a role in cancer stemness. Cells generally reacted with higher glycolysis to PKM2 activator DASA-58 and lower glycolysis to PKM2 inhibitor Compound 3k, but some were more susceptible to activation and others to inhibition.
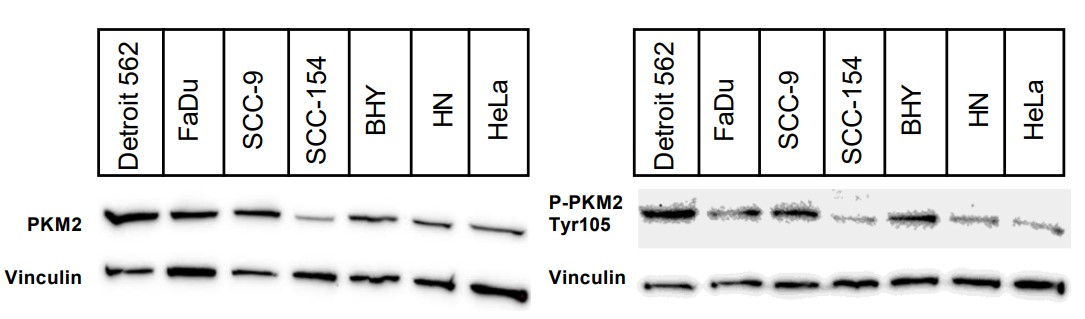
Fig3. Western blots of indicated cell lysates with an antibody specific for PKM2 (left) or P-PKM2 Tyr105 (right).
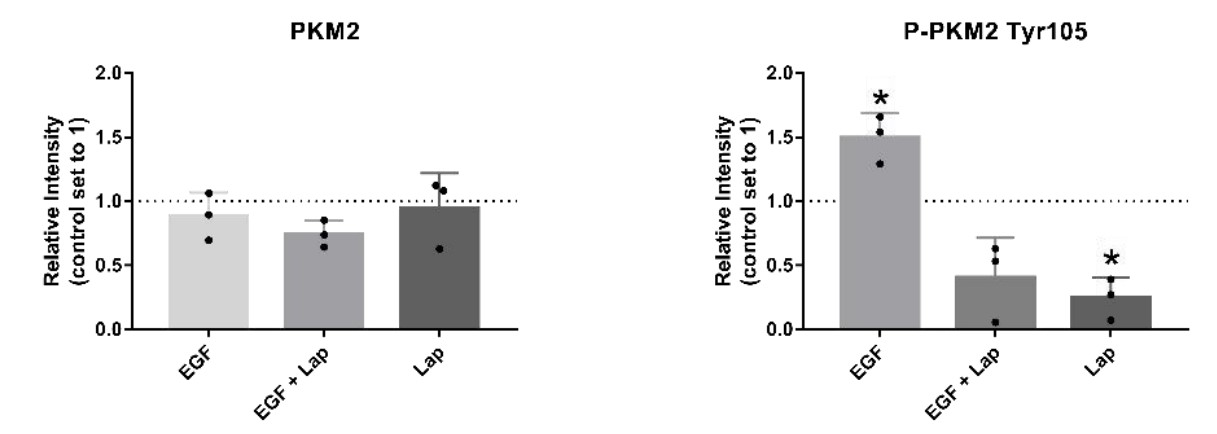
Fig4. EGF stimulation and lapatinib treatment have an impact on levels of P-PKM2 (Tyr105).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PKM2-11H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SRC-1100H)
Involved Pathway
PKM2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PKM2 participated on our site, such as Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis,Purine metabolism,Pyruvate metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PKM2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Purine metabolism | TM9SF1,PDE3B,PNP5A,HPRT1,ADA,Adcy4,PKM,ADAL,GUCY2E,PDE1C |
| Type II diabetes mellitus | SLC2A2,MAPK10,PIK3CA,INS-IGF2,INS2,HK3,INS,ADIPOQ,MTOR,PIK3R5 |
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | G6PD,LDHA,PGAM1,MAPK1,PDGFRB,SLC2A2,KRAS,PIK3CG,SIRT3,G6PDX |
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | ADH4,ALDH7A1,LDHAL6B,PFKP,ENO3,PGK1,G6PC3,ADH1,BPGM,MINPP1B |
| Carbon metabolism | HIBCH,ACAT1,TKTL1,PKMA,PDHB,ESD,H6PD,PKMB,AGXT,ME3 |
| Pyruvate metabolism | LDHC,ackA,PDHA2,PKLR,PDK3,ACSS2,LDHBA,ACAT1,ALDH9A1B,PKM |
| Viral carcinogenesis | UBE3A,MAPK1,HIST1H4A,BAK1,HPN,SKP2,CCND2,RHOA,HIST1H2BC,GTF2H2C_2 |
| Metabolic pathways | AMY1A,NT5C3L,NME2,LAP3,AZIN2,ARG1,ENOPH1,Amy1,BPGM,HEXB |
| Biosynthesis of amino acids | PFKMB,ALDOCB,PGAM1A,GOT2,TAT,GPT,PFKMA,SHMT1,IDH3G,IDH3A |
Protein Function
PKM2 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,MHC class II protein complex binding,kinase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PKM2 itself. We selected most functions PKM2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PKM2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| poly(A) RNA binding | EEF2,RPS13,DAP3,LRPPRC,ADARB1,PAN3,TIA1,EIF5B,RTN4,THRAP3 |
| magnesium ion binding | SIK3,IRAK4,RNASEH1,ALPP,FARSB,PPM1AB,IDH1,PPM1NB,PAPOLA,ATP11A |
| protein binding | ERH,MARCH2,USP47,OLA1,ABHD16A,NIPSNAP1,TNIP1,ADAM9,H3F3C,PGLS |
| ATP binding | ACVR1L,ATP13A,GTF2F2B,PTK7A,CLCN3,TRIP13,Ckmm,STK31,FGFR4,RLN1 |
| kinase activity | BMPR2A,CCL3,DCLK2,PRKCDA,NME2B.2,AKT3A,EGFRA,PHKG1A,MARCKSB,CDK14 |
| pyruvate kinase activity | PKMA,PKMB,PKLR,PKM |
| MHC class II protein complex binding | HLA-DMB,HSPA8,ATP1B1,HLA-DOB,HSP90AA1,CD74,YWHAE,HLA-DRB1,MS4A1,CD81 |
| potassium ion binding | ATP1A1,SLC24A2,PKLR,SLC24A5,PKMB,KCNJ11,PKM,SLC24A4A,PKMA,PDXK |
Interacting Protein
PKM2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PKM2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PKM2.
ARAF;polg_hcvco;E7;E7;DAPK1;TINF2;ARRB2;ARRB1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Oricchio, E; Papapetrou, EP; et al. A Cell Engineering Strategy to Enhance the Safety of Stem Cell Therapies. CELL REPORTS 8:1677-1685(2014).
- Li, WJ; Liu, J; et al. Sensitizing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Taxol with Shikonin in Human Breast Cancer Cells. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).


