OTUD5
-
Official Full Name
OTU domain containing 5 -
Synonyms
OTUD5;OTU domain containing 5;25402;ENSG00000068308;DUBA;Xp11.23;MGC104871, DKFZp761A052;OTU domain-containing protein 5;OTU domain-containing protein 5;deubiquinating enzyme A;deubiquitinating enzyme A;EC 3.4.19.12
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is OTUD5 Protein?
OTUD5, or OTU Deubiquitinase 5, is part of a cool family of cysteine proteases with an OTU domain, kind of like a specialized tool in your cell’s toolbox. This enzyme is known for its ability to remove ubiquitin from proteins, which plays a big role in a range of cell functions, from how cells grow to how cancer progresses. It’s been found to dampen Type I interferon-dependent immune responses by trimming ubiquitin chains on adapter proteins, which makes these proteins detach from their signaling partners, throwing a wrench in the interferon signaling works. OTUD5 also gets involved with the mTORC1 and mTORC2 pathways, helping to stabilize the β-TrCP1 protein and, in turn, promoting mTOR signaling. This action influences how cells grow and ties into cancer development. Interestingly, OTUD5 has a bit of a dual personality in cancer—it can either promote or suppress tumor growth, depending on the cancer type. So, it’s a key player in cell signaling, immune response modulation, and cancer progression, wearing many hats in its biological roles.What is the Function of OTUD5 Protein?
OTUD5, a deubiquitinating enzyme in the OTU family, plays a big part in several cellular processes such as DNA repair, gene regulation, and innate immunity. By trimming ubiquitin chains off certain proteins, it helps manage their stability and roles. For instance, OTUD5 downregulates type I interferon levels by cleaving ubiquitin linked to TRAF3. It also boosts antiviral and anti-tumor immunity by removing ubiquitin chains from STING. Additionally, OTUD5 influences gene transcription and can suppress tumor growth through its action on TRIM25. Its activity is shaped by the mTORC1 signaling pathway and involves phosphorylation and autophagic degradation processes. OTUD5 is closely tied to cancer development, with its effects varying across different types—sometimes promoting cancer and other times holding it back. This makes OTUD5 a key player in the complex web of cell signaling, immune responses, and cancer progression.OTUD5 Related Signaling Pathway
The OTUD5 protein plays a crucial role in various signaling pathways, especially when it comes to controlling immune responses and cellular growth. Basically, OTUD5 helps boost inflammatory immune responses by enhancing MyD88 oligomerization and forming the Myddosome complex. When OTUD5 gets knocked down in the NF-κB signaling pathway, it usually leads to less phosphorylation of TAK1, IKKα/β, and P65. Besides that, OTUD5 plays a role in stabilizing the β-TrCP1 protein through its deubiquitination function. In simple terms, the breakdown of a protein called DEPTOR, which usually inhibits mTORC1 and mTORC2 pathways, triggers mTOR signaling. There’s a continuous cycle where OTUD5 and the mTOR pathway boost each other. mTOR can directly energize OTUD5, influencing the way cells grow, divide, and clean themselves up through autophagy. In bladder cancer, OTUD5 ramps up mTORC1 signaling by deubiquitinating RNF186.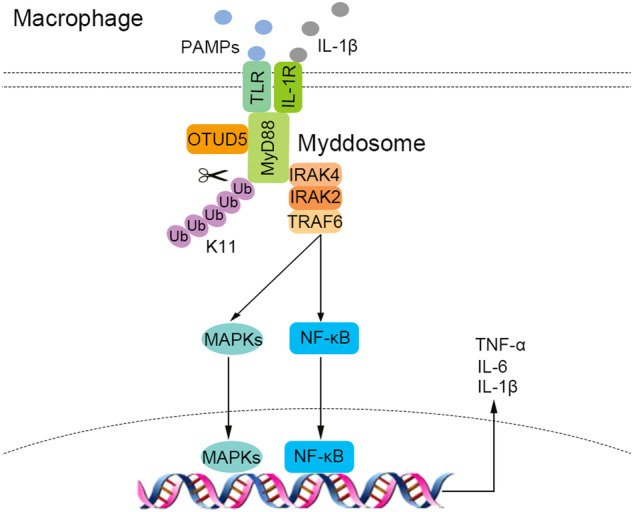
Fig1. Schematic model of OTUD5 participating in MyD88 oligomerization and Myddosome formation by inhibiting K11-linked polyubiquitination of MyD88. (Yaxing Liu, 2024)
OTUD5 Related Diseases
OTUD5 protein is tied to a bunch of diseases and plays roles in immune response, cell signaling, and tumor growth. For instance, it’s linked to a genetic disorder that messes with the nervous system, called X-linked MCAND. In diabetic kidney disease (DKD), OTUD5 has been found to ease inflammation and damage in podocytes, which can help with managing DKD. OTUD5 is also connected to some non-specific syndromic intellectual disabilities. When it comes to cancer, this protein regulates gene transcription and can put the brakes on tumor growth by deubiquitinating TRIM25. It’s involved in how non-small cell lung cancer cells grow, invade, and move around. Plus, OTUD5 is part of liver cancer progression by stabilizing SLC38A1 to boost tumor growth, and it plays a role in bladder cancer by tweaking the mTORC1 pathway. So, OTUD5’s involvement spans genetic diseases, kidney issues, neurological disorders, and various cancers, making it a potential target for treatments.Bioapplications of OTUD5
Recombinant OTUD5 protein is quite a big deal across research, industry, and medical fields. In research, it’s the go-to for digging into key biological processes like cell signaling, immune responses, and tumor growth, especially concerning innate immunity and gene expression roles. On the industrial side, OTUD5 is eyed as a prime target for crafting new treatment strategies due to its role in the mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling pathways, paving the way for fresh bioproducts and drugs. In medical research, its connection to various diseases, including autoimmune disorders and cancer, opens up new avenues and targets for cancer treatment and immune modulation. All in all, recombinant OTUD5 protein is crucial for advancing our scientific understanding and clinical applications in these areas.Case Study
Case Study 1: Lam SY. et al. Nat Commun. 2024
Proper repair of damaged DNA and keeping DNA damage responses in check at telomeres are crucial for maintaining genome stability. The DNA damage response (DDR) signaling is a series of kinase-driven phosphorylation activities, adjusted by both proteolytic and regulatory ubiquitination. The interaction between these two classes of post-translational modifications and how they affect DNA repair at unprotected telomeres is still not entirely clear. To dig deeper into this, we ran a genetic screen to pinpoint those in the ubiquitin system that rev up KAP1S824 phosphorylation—a strong DDR marker at vulnerable telomeres. Our findings show that the deubiquitinase OTUD5 enhances KAP1S824 phosphorylation by helping activate ATM through stabilizing the ubiquitin ligase UBR5, which is necessary for ATM activity triggered by DNA damage. Without OTUD5, KAP1S824 phosphorylation gets disrupted, hampering DNA repair at unguarded telomeres and DNA breaks in heterochromatin. We also discovered an unexpected role of the heterochromatin factor KAP1 in holding back DNA repair at telomeres.-
 Fig1. Immunoblot analysis of pKAP1S824 levels in OTUD5-depleted U2OS (sgOTUD5 KO1/KO3) and control (sgNT1), untreated or treated with ionizing radiation.
Fig1. Immunoblot analysis of pKAP1S824 levels in OTUD5-depleted U2OS (sgOTUD5 KO1/KO3) and control (sgNT1), untreated or treated with ionizing radiation. -
 Fig2. Immunoblot validation of OTUD5 depletion (sgOTUD5 g1/g1B) in NIH3T3 cells.
Fig2. Immunoblot validation of OTUD5 depletion (sgOTUD5 g1/g1B) in NIH3T3 cells.
Case Study 2: Cho JH. et al. Cell Death Differ. 2021
In simple terms, the mTOR signaling pathway is a key player in how cells grow and how cancer can progress, with its regulation being pretty complicated and filled with feedback actions. We’ve found that OTUD5, which is an enzyme breaking down ubiquitin, is a newly identified enhancer for both mTORC1 and mTORC2 pathways. Our research shows that OTUD5 boosts the stability of βTrCP1 proteins using its deubiquitinase activity. This process leads to the breakdown of DEPTOR, an inhibitory protein that normally dampens mTORC1 and mTORC2. Moreover, we observed that mTOR can directly phosphorylate and activate OTUD5’s DUB activity. Our RNA sequencing data revealed that OTUD5 influences gene expression tied to the mTOR pathway. When OTUD5 is reduced, cells display various mTOR-related characteristics like smaller size and more autophagy. This reduction also lessens the curled wing phenotype in Drosophila caused by a fly OTUD5 ortholog, Duba. Importantly, knocking down OTUD5 hinders the growth of cancer cells with mutations that activate the mTOR pathway.-
 Fig3. Whole-cell lysates from HEK293 cells stably expressing shCon or shOTUD5 were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
Fig3. Whole-cell lysates from HEK293 cells stably expressing shCon or shOTUD5 were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. -
 Fig4. HEK293T cells were transfected with empty vector, Myc-OTUD5 WT, or CS mutant.
Fig4. HEK293T cells were transfected with empty vector, Myc-OTUD5 WT, or CS mutant.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (OTUD5-4022H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (OTUD5-4022H)
Involved Pathway
OTUD5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways OTUD5 participated on our site, such as RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with OTUD5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | MAPK8,IL12BA,TP-1,IFNA7,IFNB,MAVS,TRADD,TRAF2,IRF3,MAP3K7 |
-
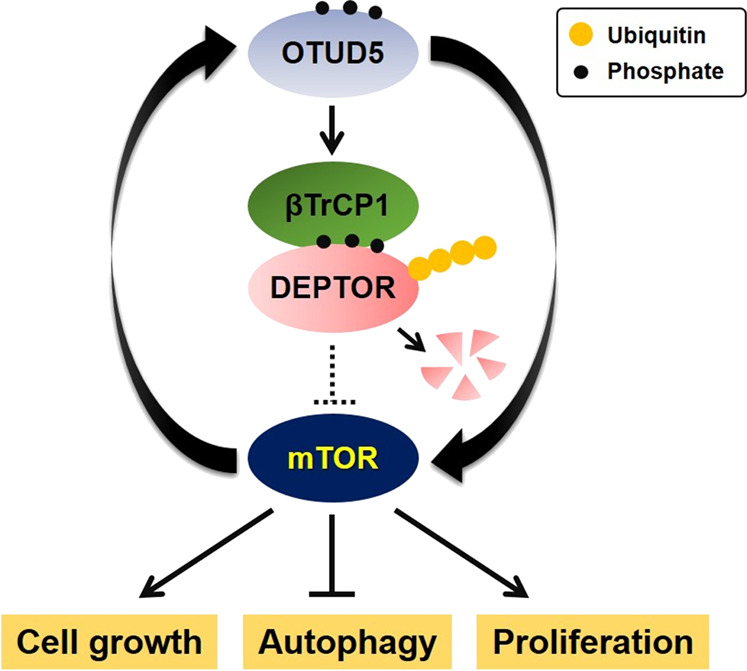 Fig1. Schematic overview for the positive feedback loop between OTUD5 and mTOR signaling pathway. (Jin Hwa Cho, 2021)
Fig1. Schematic overview for the positive feedback loop between OTUD5 and mTOR signaling pathway. (Jin Hwa Cho, 2021) -
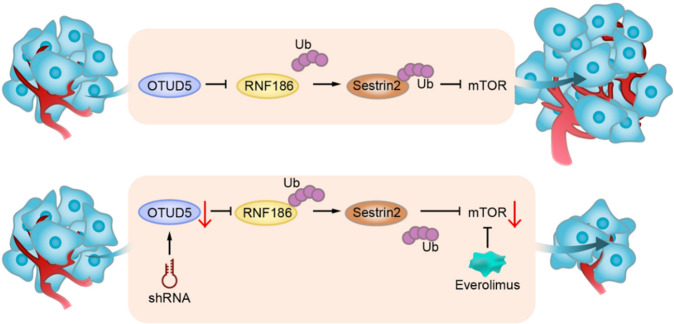 Fig2. OTUD5 plays a role in promoting bladder cancer proliferation through the OTUD5-RNF186-sestrin2-mTOR axis. (Tao Hou, 2022)
Fig2. OTUD5 plays a role in promoting bladder cancer proliferation through the OTUD5-RNF186-sestrin2-mTOR axis. (Tao Hou, 2022)
Protein Function
OTUD5 has several biochemical functions, for example, ubiquitin-specific protease activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by OTUD5 itself. We selected most functions OTUD5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with OTUD5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ubiquitin-specific protease activity | USP45,USP17L2,USP5,USP37,USP47,USP2A,USP8,ZRANB1,OTULIN,VCPIP1 |
Interacting Protein
OTUD5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with OTUD5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of OTUD5.
ipi00180730;TP53;GYS1;FLNA;VARS;PKLR;GPX4;USP11;GRB2;SET;LONRF2;CACYBP;CTPS2;LANCL2;ARPC3;thiF;metG
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



