LIPA
-
Official Full Name
lipase A, lysosomal acid, cholesterol esterase -
Overview
This gene encodes lipase A, the lysosomal acid lipase (also known as cholesterol ester hydrolase). This enzyme functions in the lysosome to catalyze the hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides. Mutations in this gene can result in Wolman disease and cholesteryl ester storage disease. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014] -
Synonyms
LIPA;lipase A, lysosomal acid, cholesterol esterase;LAL;CESD;lysosomal acid lipase/cholesteryl ester hydrolase;sterol esterase;cholesteryl esterase;lysosomal acid lipase;cholesterol ester hydrolase;acid cholesteryl ester hydrolase
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Rat
- Burkholderia cepacia
- Bartonella Henselae
- Bacillus subtilis
- Rochalimaea henselae
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- Bacillus subtilis
- Insect Cell
- HEK293T
- Yeast
- E. coli or Yeast
- Mamanlian cells
- Myc&DDK
- His
- His&T7
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- GST
- Flag
Background
What is LIPA Protein?
LIPA gene (lipase A, lysosomal acid type) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10q23. LIPA is an enzyme that plays a role in the cellular lysosome and is primarily responsible for breaking down cholesterol esters and triglycerides. The activity of LIPA protein within the cell is regulated by a variety of factors, including its own post-translational modifications, such as glycosylation, and interactions with other proteins. The activity of LAL depends on its localization in the lysosome, and its function is not limited to its activity as a lipase, but may also be involved in other intracellular processes. The LIPA protein is consisted of 399 amino acids and LIPA molecular weight is approximately 45.4 kDa.
What is the Function of LIPA Protein?
The primary function of LIPA is to catalyze the hydrolysis of cholesterol esters and triglycerides, which are internalized by lipoprotein particles that enter cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis. The activity of LIPA protein is essential for the metabolism of intracellular cholesterol esters and triglycerides, and it is involved in the inhibition of hydroxymethylglutarate-CoA reductase after uptake of low density lipoprotein (LDL), as well as the activation of endogenous cellular cholesterol ester formation processes. This function of the LIPA protein is important for regulating cellular cholesterol levels and maintaining the balance of lipid metabolism.
LIPA Related Signaling Pathway
The LIPA protein catalyzes the hydrolysis of cholesterol esters and triglycerides in lysosomes, which is an important step in regulating intracellular cholesterol levels. LIPA protein plays a role in mediating the inhibition of hydroxylmethylglutarate-CoA reductase (HMGCR) and activation of endogenous cellular cholesterol ester formation after LDL (low density lipoprotein) uptake. The function of LIPA protein is not limited to its lipase activity, but may also be involved in other intracellular processes, including signaling pathways associated with ER stress. The activity and function of LIPA protein may be regulated by a variety of factors, including its post-translational modifications and interactions with other proteins.
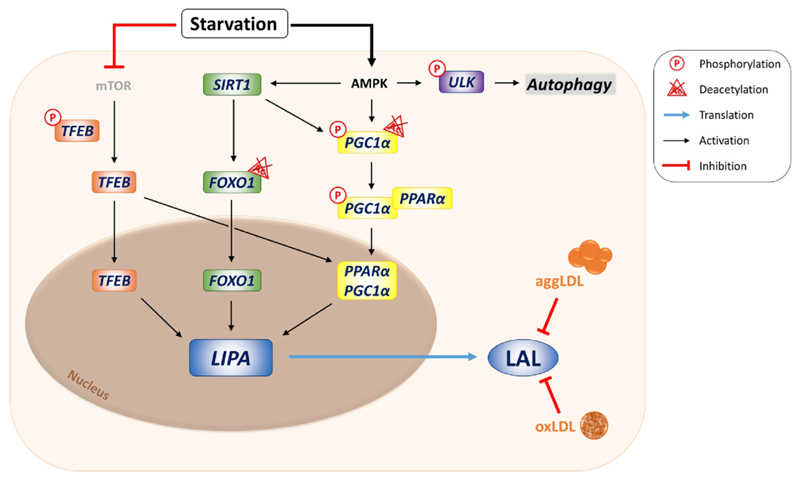
Fig1. Transcriptional regulation of lysosomal acid lipase (LAL). (Melanie Korbelius, 2023)
LIPA Related Diseases
Wolman's disease is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the LIPA gene that results in complete or near-complete loss of LAL activity. This causes cholesterol esters and triglycerides to accumulate in cellular lysosomes, affecting organ function, especially in the liver and spleen. Cholesteryl ester storage disease (CESD), also known as Ullrich-Turner syndrome, is a milder LiPA-related disorder, usually caused by certain mutations in the LIPA gene. Variations in the LIPA gene are associated with cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, which may be related to the role of LIPA protein in lipid metabolism.
Bioapplications of LIPA
For diseases with abnormal LIPA protein activity, such as Wolman's disease and cholesterol ester deposition disorder, enzyme replacement therapy can be used to provide functional LIPA proteins to help break down lipids accumulated in cells. The key role of the LIPA protein in lipid metabolism makes it a potential target for the development of drugs that regulate lipid metabolism, which may help treat cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Changes in LIPA protein or its activity may serve as biomarkers for certain metabolic diseases, contributing to early diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of the disease. For genetic diseases caused by mutations in the LIPA gene, gene therapy could be a potential treatment to restore the normal function of the LIPA protein by repairing or replacing the mutated gene.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Alexia B Collier, 2024
Ovarian cancer (OCa) is the most lethal form of gynecologic cancer, and the tumor heterogeneities at the molecular, cellular, and tissue levels fuel tumor resistance to standard therapies and pose a substantial clinical challenge. Here, researchers tested the hypothesis that the heightened basal endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) observed in OCa represents an exploitable vulnerability and may overcome tumor heterogeneity. The recent studies identified LIPA as a novel target to induce ERS in cancer cells using the small molecule ERX-41. However, the role of LIPA and theutility of ERX-41 to treat OCa remain unknown. Expression analysis using the TNMplot web tool, TCGA data sets, and immunohistochemistry analysis using a tumor tissue array showed that LIPA is highly expressed in OCa tissues, compared to normal tissues. ERX-41 treatment significantly reduced the cell viability and colony formation ability and promoted the apoptosis of OCa cells. Mechanistic studies revealed a robust and consistent induction of ERS markers, including CHOP, elF2α, PERK, and ATF4, upon ERX-41 treatment.
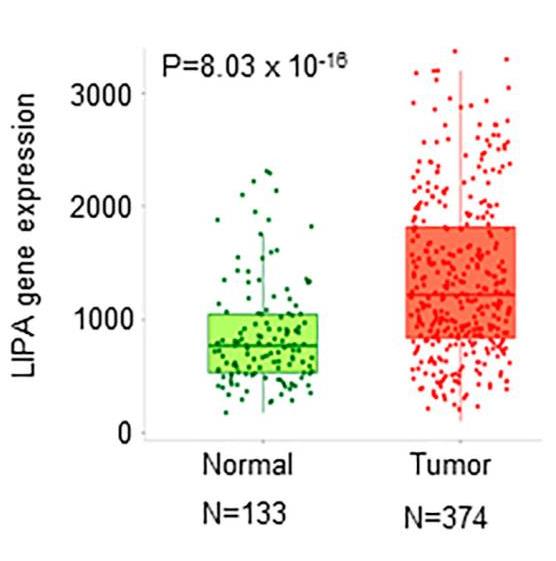
Fig1. Boxplots of LIPA gene expression in normal and tumor gene array data.

Fig2. The effect of the KO of LIPA in SKOV3 cells on the dose–response curve to ERX-41.
Case Study 2: Gyu-Lee Kim, 2017
More than 50% of sepsis cases are associated with pneumonia. Sepsis is caused by infiltration of bacteria into the blood via inflammation, which is triggered by the release of cell wall components following lysis. However, the regulatory mechanism of lysis during infection is not well defined. Mice were infected with Streptococcus pneumoniae D39 wild-type (WT) and lipase mutant (ΔlipA) intranasally (pneumonia model) or intraperitoneally (sepsis model), and survival rate and pneumococcal colonization were determined. LipA and autolysin (LytA) levels were determined by qPCR and western blotting. S. pneumoniae Spd_1447 in the D39 (type 2) strain was identified as a lipase (LipA). In the sepsis model, but not in the pneumonia model, mice infected with the ΔlipA displayed higher mortality rates than did the D39 WT-infected mice. Treatment of pneumococci with serum induced LipA expression at both the mRNA and protein levels. In the presence of serum, the ΔlipA displayed faster lysis rates and higher LytA expression than the WT, both in vitro and in vivo.
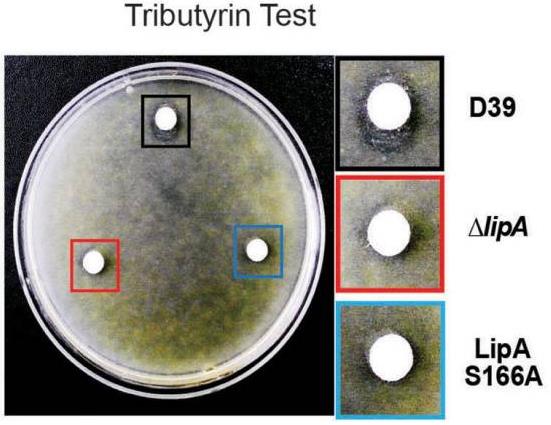
Fig3. S. pneumoniae D39 WT (Black square) had a clearer zone on the tributyrin THY agar plate than the ΔlipA (Red square) or LipA S166A (Blue square).

Fig4. Mice (n = 15) were infected i.n. with 1.5 × 107 CFU of the type 2 and 4 strains or 4.5 × 107 CFU of type 3, and survival time was recorded.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LIPA-627H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LIPA-2158H)
Involved Pathway
LIPA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LIPA participated on our site, such as Steroid biosynthesis,Lysosome, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LIPA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Lysosome | ATP6V0C,NAGPA,CTSW,GALNS,PSAP,SLC17A5,TCIRG1,CTPS1B,AP1S3,CD164 |
| Steroid biosynthesis | EBP,LSS,HSD17B7,CPN1,SOAT1,DHCR7,CELL,SQLE,FAXDC2,SC4MOL |
Protein Function
LIPA has several biochemical functions, for example, lipase activity,sterol esterase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LIPA itself. We selected most functions LIPA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LIPA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| lipase activity | PNPLA7,CEL.1,NOTUM1A,CES1C,DAGLB,LIPM,Aadacl3,LIPN,C2orf43,LIPK |
| sterol esterase activity | CES3,Cel,CES1,CES1D,CES5A,CEL.1 |
Interacting Protein
LIPA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LIPA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LIPA.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Frohnecke, N; Klein, S; et al. Protein-protein interaction studies provide evidence for electron transfer from ferredoxin to lipoic acid synthase in Toxoplasma gondii. FEBS LETTERS 589:31-36(2015).
- Zhao, FH; Zhu, FC; et al. Baseline prevalence and type distribution of human papillomavirus in healthy Chinese women aged 18-25 years enrolled in a clinical trial. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CANCER 135:2604-2611(2014).


