KIT
-
Official Full Name
v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog -
Overview
This gene encodes the human homolog of the proto-oncogene c-kit. C-kit was first identified as the cellular homolog of the feline sarcoma viral oncogene v-kit. This protein is a type 3 transmembrane receptor for MGF (mast cell growth factor, also known as stem cell factor). Mutations in this gene are associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumors, mast cell disease, acute myelogenous lukemia, and piebaldism. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
KIT;v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog;PBT;SCFR;C-Kit;CD117;mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit;p145 c-kit;proto-oncogene c-Kit;piebald trait protein;soluble KIT variant 1;tyrosine-protein kinase Kit;proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Kit;v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene-like protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Dog
- HEK293
- Human Cell
- E.coli
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- CHO
- Mammalian Cell
- Insect cell
- Insect Cell
- Mammalian cells
- His
- Fc
- GST
- Non
- hIgG4
- Flag
- His&T7
- His&Avi
- His&Fc
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&GST
Background
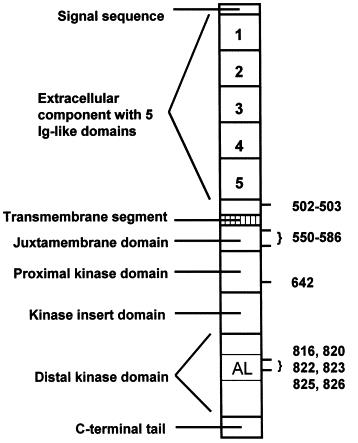
Fig1. Organization of Kit. (Robert Roskoski Jr, 2005)
What is KIT Protein?
KIT protein, which lots of folks call the CD117 antigen, is basically a receptor tyrosine kinase hanging out on certain cell surfaces. It's super important because it's like the traffic controller for how cells grow, survive, and become what they need to be, especially for germ cells, the cells involved in pigmentation called melanocytes, and those blood-forming hematopoietic cells. This protein links up with stem cell factor (SCF) and kicks off signaling like PI3K/AKT pathways, crucial for early development and keeping cells doing their thing. But when KIT malfunctions or mutates, it can be bad news, tying into issues like gastrointestinal stromal tumors, mastocytosis, and some leukemias, showing just how important it is in maintaining normal body functions and when things go wrong.
What is the Function of KIT Protein?
Now, the KIT protein's main gig as a receptor tyrosine kinase is all about handling processes like cell survival, growth, and differentiation. It's a big deal for the melanocytes, which deal with pigmentation, and hematopoietic stem cells, involved in making blood. Basically, when KIT hooks up with stem cell factor, it sets off a series of internal cell events, keeping things functioning nicely. But if KIT starts acting out due to mutations, it's like having a jammed accelerator; it tells the cells to keep growing uncontrollably, which is a path straight to cancer town.
KIT Related Signaling Pathway
The KIT protein is a receptor that sits on the surface of certain cells, like stem cells and others, playing a key role in cell signaling pathways. It primarily binds to stem cell factors, which kicks off a bunch of activities inside the cell. These activities include making sure cells survive, grow, and differentiate into various types. KIT signaling is crucial for melanocyte (the cells that give skin its color) survival, blood cell formation or hematopoiesis, and the development of germ cells involved in reproduction. Basically, KIT is like a switch that turns on vital processes within cells, helping them respond appropriately to the factors they encounter in their environment.
KIT Related Diseases
KIT protein, which you might also hear called CD117 or the stem cell factor receptor, is pretty crucial when it comes to how cells grow, change, and stay alive. When things go wrong with KIT, it can lead to some nasty stuff. Imagine systemic mastocytosis as a situation where you've got an overload of mast cells gathering in various parts of the body, often thanks to this specific hitch called the D816V mutation in the KIT gene. Then there's acute myeloid leukemia, or AML, where changes in the KIT gene ramp up the protein's activity, causing those leukemia cells to multiply like there's no tomorrow. You also have things like sinonasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (a mouthful, I know!) and testicular cancer, especially the type called seminomas, linked to KIT mutations. And don't forget gastrointestinal stromal tumors, or GISTs, where KIT gene mutations, especially in those exons 11 and 9, play a big role. Basically, when KIT is off the rails, it gets the signal pathways all hyped up, pushing cell growth and turning them into tumors, which is why figuring out how to tackle KIT is a big deal in cancer and blood disease research.
Bioapplications of KIT
Recombinant KIT proteins have found their way into a bunch of cool applications, particularly in research and industrial settings. In the world of science, they're a big deal for studying cell processes like growth and differentiation. They help researchers figure out how cells tick. On the industrial side of things, these proteins can be key in developing therapies for diseases where KIT is a player, acting as targets for drug discovery and development. In essence, these proteins are like the Swiss Army knives of biotechnology, doing a little bit of everything from aiding in basic science research to paving the way for new treatments in medicine.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Haiying Shen, 2024
Alzheimer's disease, which mainly affects older folks, leads to memory and cognitive issues. One thing causing trouble in this disease is stress in the cell's endoplasmic reticulum (ER), which is also seen in many brain disorders. Here, we zoom in on how stem cell factor (SCF), which works by latching onto a receptor called c-Kit, as well as the JAK2/STAT3 pathway, affect ER stress and cell suicide, or apoptosis, in Alzheimer's. We used L-glutamic acid to put stress on HT22 cells as a cell model for sporadic AD and examined APP/PS1 mice for familiar AD. To test the impact of SCF/c-Kit and JAK2/STAT3, we used a c-Kit blocker, ISCK03, and a JAK2/STAT3 blocker, WP1066. We measured how well cells survived and grew, and checked their stress and apoptosis markers using different lab techniques. Adding SCF helped brain cells thrive and fend off stress-related death from L-Glu. However, using ISCK03 or WP1066 undid these good effects of SCF, showing how these pathways play a role in managing cell stress and survival in Alzheimer's.
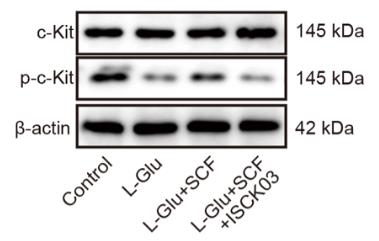
Fig1. Western blot detected p-c-Kit expression in cells.

Fig2. Western blot detected JAK2 and STAT3 phosphorylation in cells, with the addition of the c-Kit inhibitor ISCK03 to the cells.
Case Study 2: Yi Luan, 2024
The KITL-KIT interaction is key in kicking off oocyte activation via the PI3K-AKT-FOXO3 signaling route. Past studies using special Kit mutant models suggested KIT's major role in early follicle development. In our research, we looked at mice with total KIT expression loss in oocytes after birth using Gdf9-iCre. We examined their ovarian development, specific markers, hormone levels, and fertility. Surprisingly, unlike earlier prenatal models, these postnatal KIT-deleted mice didn't show early development issues. But, once fully mature, they faced a complete depletion of ovarian reserves and functionality, leading to smaller ovaries, delayed development, and signs of primary ovarian insufficiency like high FSH and low AMH levels. This ultimately led to infertility. Their ovaries had peculiar expressions of certain cell markers and unexpected widespread expression of p-SMAD3 and Ki67, along with dying cells throughout.

Fig3. Representative histology and 3, 3-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining illustrating KIT expression in the ovaries of CD-1 female mice at PD1.
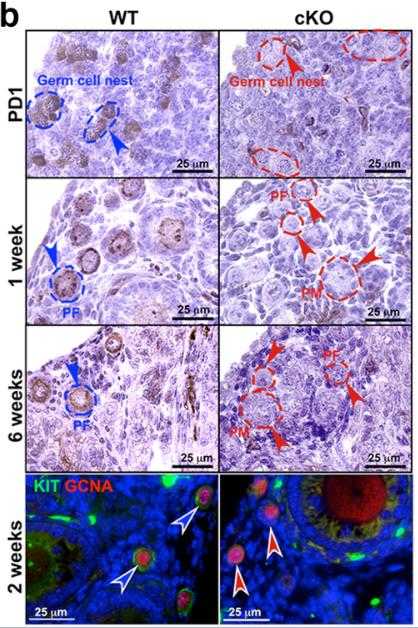
Fig4. Representative DAB staining and immunofluorescence assay with KIT in the ovaries from WT or cKO mice.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
KIT involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways KIT participated on our site, such as Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway,Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with KIT were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | PPP2R1A,IRS1,IGF1,FGF18,BCL2L1,VEGFB,THBS3,Fasl,FGF20,GNB3 |
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | CD44,IL7R,CD1D2,CR1,CSF3R,ITGA4,CD33,ITGB3,CD1B,HLA-DRA |
| Ras signaling pathway | GAB2,HRAS,REL,PLA2G3,MAPK10,PLA2G10,FGF5,FGF17,RASAL2,RAB5C |
| Rap signaling pathway | CALM3,FGFR2,PIK3R5,CALM1,AKT2,PRKCB,LCP2,PRKCI,RALB,FGF16 |
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | INS1,LPAR5,PLD2,PDGFA,PIK3CD,PIK3R1,FYN,PIK3R2,KRAS,GRM7 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | CCL25,GH2,Ifnlr1,IL22RA1,IL10RB,IL5RA,IFNE,CCL21B,PRLRA,IL4R |
| Melanogenesis | Adcy4,FZD7A,GNA15.1,MAP2K2B,NRAS,WNT7B,WNT8A,GNAQ,MC1R,CALML5 |
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | KRAS,PFKP,G6PD,PIK3R1,PIK3CG,MAP2K2,SLC2A1,SCO2,PIK3R2,PIK3R3 |
| Pathways in cancer | TP53,SFPI1,PRKCA,PAX8,RXRG,MAPK10,SMAD4,RASGRP3,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,CBLB |
Protein Function
KIT has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,cytokine binding,metal ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by KIT itself. We selected most functions KIT had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with KIT. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | LIMCH1A,ZFP292,SALL1A,ZNF485,ZFP385C,CACNA2D2,RYBPA,ARHGAP29,HINFP,GIT2 |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | BCR,PTK2B,JAK1,TTN,NTRK3A,KITB,ZNF143B,LCK,FGFR1,KIAA1804 |
| protein binding | SULT2B1,CIB4,NEUROD1,TAF6,PMM1,HMMR,BRD2,SRGAP3,MAP4K2,DLX2 |
| protease binding | LCN2,TIMP4,CST3,CAST,DPP4,PYCARD,FADD,Casp3,SERPINE1,BCL10 |
| ATP binding | MAP3K8,HSPH1,VPS4A,NTRK3A,LMTK3,GALK1,SRMS,CDK1,PANK4,ZRANB3 |
| protein homodimerization activity | ALDH1A3,OSTA,Anks6,KYNU,IKBKG,BNIP3L,MYOM3,NKX2,MIXL1,TARS |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | EPHA2,RET,EPHB2B,TEK,NPTNB,FGFR1A,FLT4,DDR1,IGF1RA,TRIM27 |
| receptor signaling protein tyrosine kinase activity | ERBB4A,KITB,INSR,ERBB2,TYRO3,EGFR,LYN,ERBB4,ERBB3B,SYK |
| cytokine binding | GBP1,ELANE,NOG,KITA,KITB,IL17F,PARK7,CRLF1,LIFR,NRP2 |
Interacting Protein
KIT has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with KIT here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of KIT.
PIK3R1;GRB2
Resources
Research Area
Cancer Drug TargetsEndothelial Cell Development Molecules
Cardiac Stem Cell Markers
Gamete Markers
Myeloid Lineage Markers
Germ Cell Markers
CD Antigen (Hematopoietic Stem Cell Markers)
Other Cytokines & Receptors
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)
Endothelial Cell Differentiation Markers
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) in the Akt Pathway
Negative Regulators of the Jak/STAT Pathway
Receptors in the Jak/STAT Pathway
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Markers
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Markers
Embryonic and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Markers
Leukemia Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Lung Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Ovarian Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Markers
Mesodermal Lineage Markers
MDSC Phenotyping - Negative Markers
Breast Cancer Biomarkers
Oncoprotein-Growth Factor Receptors
Related Services
Related Products
References

.jpg)
.jpg)

