KISS1
-
Official Full Name
Kiss1 KiSS-1 metastasis-suppressor -
Overview
KiSS-1 gene encodes metastin, also known as kisspeptin or KiSS-1 peptide, which binds to a G protein-coupled receptor GPR54. KiSS-1 is dominantly expressed in brain (e.g. anteroventral periventricular nucleus, AVPV arcuate nucleus, ARC), placenta, and pancreas, etc. Metastin plays an important role in regulating the GnRH secretion in brain and MMP-9 expression in placenta, which is associated with development of puberty and sex maturation (e.g. Idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, IHH) as well as placentation (e.g. pre-eclampsia), respectively. Metastin was originally discovered as a tumor metastasis suppressor (e.g. melanoma, breast cancer). -
Synonyms
KISS1;KiSS-1 metastasis-suppressor;metastasis-suppressor KiSS-1;metastin;kisspeptin-1;0610012C01Rik;metastatin
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- CHO
- HEK293T
- His
- Non
- His&GST
- His&T7
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is KISS1 protein?
KISS1 gene (KiSS-1 metastasis suppressor) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q32. This gene is a metastasis suppressor gene that suppresses metastases of melanomas and breast carcinomas without affecting tumorigenicity. The encoded protein may inhibit chemotaxis and invasion and thereby attenuate metastasis in malignant melanomas. Studies suggest a putative role in the regulation of events downstream of cell-matrix adhesion, perhaps involving cytoskeletal reorganization. A protein product of this gene, kisspeptin, stimulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)-induced gonadotropin secretion and regulates the pubertal activation of GnRH neurons. The KISS1 protein is consisted of 138 amino acids and KISS1 molecular weight is approximately 14.7 kDa.
What is the function of KISS1 protein?
KiSS-1 protein, as a transfer suppressor, is an endogenous ligand that binds to the G protein-coupled receptor GPR54. In cancer biology, KiSS-1/GPR54 plays a role in inhibiting tumor metastasis by influencing tumor cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis. KiSS-1 also plays an important role in regulating physiological processes such as pubertal initiation, adult fertility, hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis feedback, and trophoblast invasion. Reduced KiSS-1 expression is associated with advanced and poor prognosis in a variety of cancers, making it a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis, therapeutic target identification, and prognostic judgment.
KISS1 related signaling pathway
By binding to its G protein-coupled receptor GPR54 (also known as KISS1R), KISS1 protein is involved in regulating a variety of physiological processes, including the initiation of puberty, reproductive function, and tumor suppression. In cancer biology, the KISS1/GPR54 system plays a role in inhibiting tumor metastasis by affecting the ability of tumor cells to prolifate, invade and metastasize. Studies have shown that decreased KISS1 expression is associated with advanced and poor prognosis in a variety of cancers, and that up-regulation or activation of KISS1 may inhibit tumor spread by inhibiting NF-kB signaling pathways and regulating apoptosis and autophagy processes. However, the role of KISS1 in different cancers may vary depending on the tissue environment, and its specific role in cancer progression is still being studied in depth.
KISS1 related diseases
The KISS1 protein plays a role in a variety of diseases, especially in cancer treatment and reproductive function. As a metastasis suppressor, KISS1 is reduced in many cancers, including melanoma, breast cancer, and prostate cancer, and is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis. Kisspeptin, which encodes Kisspeptin, is involved in regulating puberty initiation, reproductive hormone secretion, gonadal function and placental function by binding to the G-protein-coupled receptor GPR54. In addition, KISS1 plays a key role in regulating the feedback mechanism of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis (HPG axis), affecting reproductive processes such as ovulation, fertilization, and embryo implantation. In cancer therapy, the up-regulation or activation of KISS1 may inhibit the spread of tumors by inhibiting the NF-kB signaling pathway and regulating apoptosis and autophagy processes, making it a potential target for cancer therapy.

Fig1. KiSS1 in response to antitumor drugs. (Cristina Corno, 2019)
Bioapplications of KISS1
The protein encoded by the KISS1 gene and its derived peptide hormone Kisspeptin have important biological applications in a variety of diseases. In addition, KISS1 expression and activity have potential clinical application value in cancer diagnosis, therapeutic target identification and prognosis judgment. The KISS1 gene and the Kisspeptin it encodes provide new therapeutic strategies and drug development directions in the field of reproductive system diseases and tumor therapy, such as the treatment of certain types of cancer and reproductive dysfunction through drugs targeting the KISS1/GPR54 signaling pathway. Therefore, KISS1/GPR54 system has a wide range of prospects in medical research and clinical applications.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Lingna Chen, 2024
To explore the role of KISS-1/GPR54 signaling pathway in recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA), the researchers collected villi tissue from RSA patients and used the human trophoblast cell line HTR-8/SVneo. The levels of KISS-1 and GRP54 were detected by real-time quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry, and the expressions of ZO-1 and ZEB1 were analyzed by Western blot. Cell proliferation capacity was assessed by CCK-8 and clonogenesis assays, while Transwell assays were used to test cell migration and invasion capacity. The results showed that the expression of KISS-1 was decreased in the villi tissue of RSA patients. KISS-1 overexpression significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of trophoblast cells. In terms of molecular mechanism, after KISS-1 overexpression, ZEB1 expression decreased while ZO-1 expression increased. Silencing of GPR54 negates the role of KISS-1 in HTR-8/SVneo cells.
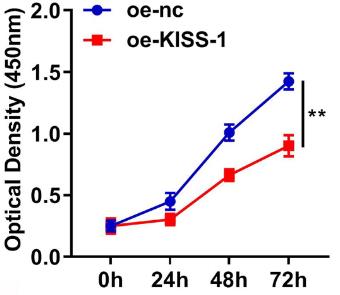
Fig1. After oe-KISS-1 transfection, the cell viability was tested with a CCK-8 assay.

Fig2. KISS-1 modulated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by targeting GPR54.
Case Study 2: Natalya Kaverina, 2017
Breast cancer metastasis is a key stage in the progression of the disease, and KISS1 expression is associated with inhibiting the development of metastasis. Lower levels of KISS1 mRNA and protein were found in breast cancer cells with brain metastases. Studies have also shown that astrocytes in normal adult brain promote the metastasis and transformation of breast cancer cells by secreting CXCL12, and can reduce KISS1 expression by inducing microRNA-345 (MIR345). In addition, ectopic expression of KISS1 down-regulates key autophagy regulators ATG5 and ATG7, acting synergically with autophagy inhibitors, suggesting that autophagy plays a role in KISs1-mediated breast cancer metastasis. KISS1 expression in human breast cancer tissues is inversely correlated with the expression of MMP9 and IL8 (associated with metastasis invasion mechanisms), further confirming KISS1's role as a potential regulator of metastasis. This conclusion is supported by the experimental results that KISS1 overexpression can reverse the invasive phenotype of MDA-MB-231Br cells.
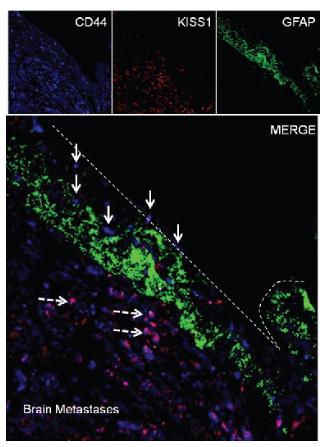
Fig3. Immunofluorescence staining of brain metastatic specimen for KISS1 (red).

Fig4. KISS1 expression reverses autophagy induction in the model of MDA-MB-231Br cells lacking KISS1 expression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (KISS1-1646H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (KISS1-3135H)
Involved Pathway
KISS1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways KISS1 participated on our site, such as Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors),G alpha (q) signalling events,GPCR downstream signaling, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with KISS1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Signal Transduction | GPR65,DHRS3A,CDC42EP2,RAMP1,RYK,DISP2,GPBAR1,WDR35,SOX32,TMED5 |
| GPCR downstream signaling | NPB,PDE10A,RGS7,OBSCN,PROKR1A,DGKA,PLEKHG2,ANXA1A,SOUL4,OXGR1A.1 |
| GPCR ligand binding | NTS,OXER1,OPN4A,ADORA2A,PTHLHA,RAMP3,FPR-RS4,S1PR5B,EMR4,UTS2D |
| Signaling by GPCR | OR52B4,RCA2.1,PENKA,SOUL4,OR2AP1,PTH2,RGS6,ARHGEF16,CXCR7B,EMR3 |
| Peptide ligand-binding receptors | CCBP2,RLN2,GAL,CX3CR1,NMBB,PROKR2,NMBA,FPR-RS6,KEL,PYYA |
| Gastrin-CREB signalling pathway via PKC and MAPK | ARHGEF25,EDN3,GCGB,QRFP,GPR65,ANXA1C,MGLL,RASGRP2,EDNRAB,OPN4 |
| Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) | RGS1,ADRA1D,GPR17,CCRL2,INSL3,DRD3,CCR7,SSTR1,NPFFR2,OXTRL |
| G alpha (q) signalling events | NMU,ADRA1D,QRFP,TAC3,NTS,EDNRB,NMB,NMBB,TRPC7,ANXA1 |
Protein Function
KISS1 has several biochemical functions, for example, kisspeptin receptor binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by KISS1 itself. We selected most functions KISS1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with KISS1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | UBR2,ARHGEF38,MBNL1,OPRD1,NAPA,CEP63,NBR1,PPP4R1,HEYL,TLR3 |
Interacting Protein
KISS1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with KISS1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of KISS1.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Han, YG; Liu, GQ; et al. KISS1 can be used as a novel target for developing a DNA immunocastration vaccine in ram lambs. VACCINE 33:777-782(2015).
- Papaoiconomou, E; Lymperi, M; et al. Kiss-1/GPR54 Protein Expression in Breast Cancer. ANTICANCER RESEARCH 34:1401-1407(2014).


