KAT5
-
Official Full Name
K(lysine) acetyltransferase 5 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the MYST family of histone acetyl transferases (HATs) and was originally isolated as an HIV-1 TAT-interactive protein. HATs play important roles in regulating chromatin remodeling, transcription and other nuclear processes by acetylating histone and nonhistone proteins. This protein is a histone acetylase that has a role in DNA repair and apoptosis and is thought to play an important role in signal transduction. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
KAT5;K(lysine) acetyltransferase 5;TIP;ESA1;PLIP;TIP60;cPLA2;HTATIP;ZC2HC5;HTATIP1;histone acetyltransferase KAT5;K-acetyltransferase 5;cPLA2 interacting protein;cPLA(2)-interacting protein;60 kDa Tat-interactive protein;Tat interacting protein, 60kDa;histone acetyltransferase HTATIP;HIV-1 Tat interactive protein, 60kDa
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Sf21 Insect Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- Insect cell
- E.coli
- HEK293T
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
- Flag
Background
What is KAT5 Protein?
KAT5 gene (lysine acetyltransferase 5) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q13. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the MYST family of histone acetyl transferases (HATs) and was originally isolated as an HIV-1 TAT-interactive protein. HATs play important roles in regulating chromatin remodeling, transcription and other nuclear processes by acetylating histone and nonhistone proteins. This protein is a histone acetylase that has a role in DNA repair and apoptosis and is thought to play an important role in signal transduction. The KAT5 protein is consisted of 513 amino acids and KAT5 molecular weight is approximately 58.6 kDa.
What is the Function of KAT5 Protein?
The KAT5 protein, also known as TIP60, is an important histone acetyltransferase that acts as a catalytic subunit of the NuA4 complex and is involved in a variety of biological processes, including gene transcription activation, DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, and mitosis. KAT5 regulates a variety of cellular functions by acetylating histones and other non-histone proteins, such as BMAL1, ATM, and AURKB. In addition, the role of KAT5 in neurodegenerative diseases includes influencing the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells, as well as participating in chromatin remodeling and gene expression regulation. KAT5 also showed cardioprotective effects, alleviating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating STUB1 expression. In terms of tumor development, O-GlcNAcylation of KAT5 promotes tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
KAT5 Related Signaling Pathway
In terms of signaling pathways, Tip60 is involved in a variety of cellular signaling processes. For example, it is able to participate in transcriptional regulation by interacting with HIV-1 Tat and is involved in the activation of ATM kinase during DNA damage repair. Specifically, Tip60 is able to be activated in response to DNA damage and, by binding to the FATC domain of ATM, acetylates the K3016 site of ATM, thereby activating ATM kinase and initiating a downstream repair response. In addition, tyrosine phosphorylation of Tip60 enhances its binding to H3K9me3, which is critical for ATM kinase activation and cell survival.
KAT5 Related Diseases
KAT5 protein, also known as TIP60, is associated with a variety of diseases, especially the occurrence, development and metastasis of tumors. KAT5 plays an important role in tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, metabolism and DNA damage repair. For example, in prostate cancer, reduced KAT5 expression correlates with disease progression. In addition, KAT5 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in liver cancer through acetylation of the SPZ1-TWIST complex. In breast cancer, KAT5 inhibits the migration and invasion of tumor cells by mediating acetylation of cortactin. Abnormal expression of KAT5 is also associated with aggressiveness and metastasis of thyroid cancer. In addition to tumors, de novo variants of the KAT5 gene have been linked to syndromes that cause facial deformities, cerebellar atrophy, sleep disorders, and epilepsy.
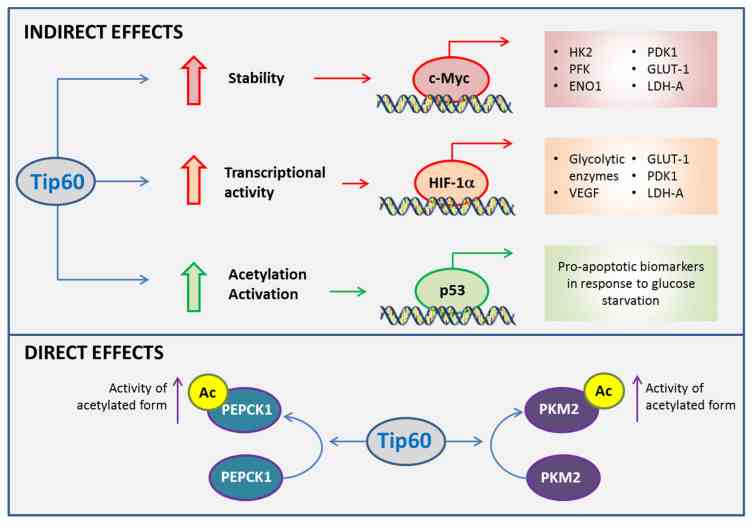
Fig1. Roles of Tip60 in cancer metabolism. (Kah Ni Tan, 2020)
Bioapplications of KAT5
As a histone acetyltransferase, KAT5 protein is mainly involved in gene expression regulation and chromatin remodeling, and is an important object of epigenetic research. At the application level, the study of KAT5 protein contributes to the in-depth understanding of biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and the occurrence and development of diseases (such as cancer), and provides theoretical and experimental basis for the development of diagnostic markers for diseases, the selection of therapeutic targets and the creation of new drugs. For example, in cancer therapy research, regulating abnormal cell proliferation and gene expression by inhibiting the activity of KAT5 protein has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy. In addition, the function of KAT5 protein has also been applied to stem cell technology, regenerative medicine and developmental biology, providing key molecular mechanism information for related research.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Carla L Esposito, 2023
DNA methylation is a fundamental epigenetic modification regulating gene expression. Aberrant DNA methylation is the most common molecular lesion in cancer cells. However, medical intervention has been limited to the use of broadly acting, small molecule-based demethylating drugs with significant side-effects and toxicities. To allow for targeted DNA demethylation, researchers integrated two nucleic acid-based approaches: DNMT1 interacting RNA (DiR) and RNA aptamer strategy. Bio-Layer Interferometry measurements were performed using a BLItz system and AR2G tips functionalized with KAT5. By combining the RNA inherent capabilities of inhibiting DNMT1 with an aptamer platform, they generated a first-in-class DNMT1-targeted approach - aptaDiR. Molecular modelling of RNA-DNMT1 complexes coupled with biochemical and cellular assays enabled the identification and characterization of aptaDiR. This RNA bio-drug is able to block DNA methylation, impair cancer cell viability and inhibit tumour growth in vivo.
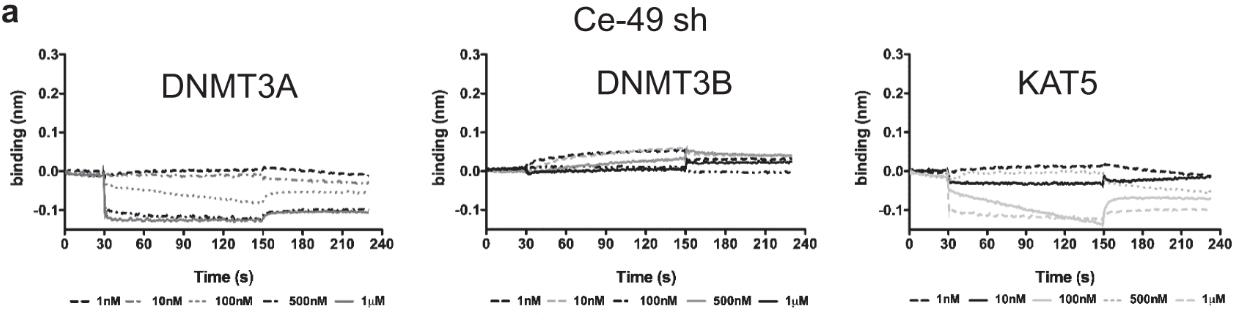
Fig1. Binding measured by bio-layer interferometry of Ce-49 sh to KAT5 protein (right panels) immobilized on separate biosensors.
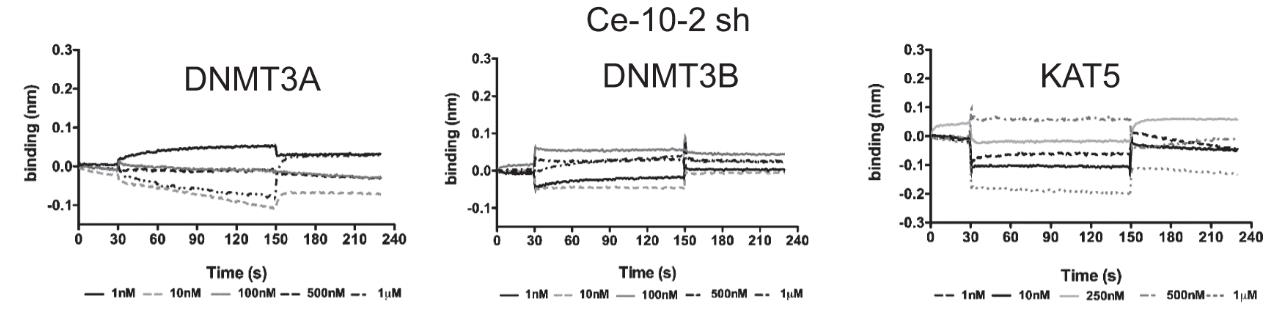
Fig2. Binding measured by bio-layer interferometry of Ce-10-2 sh to KAT5 protein (right panels) immobilized on separate biosensors.
Case Study 2: Fan Xuan, 2024
The lysine acetyltransferase KAT5 is a pivotal enzyme responsible for catalyzing histone H4 acetylation in cells. In addition to its indispensable HAT domain, KAT5 also encompasses a conserved Tudor-knot domain at its N-terminus. However, the function of this domain remains elusive, with conflicting findings regarding its role as a histone reader. In this study, researchers have employed a CRISPR tiling array approach and unveiled the Tudor-knot motif as an essential domain for cell survival. The Tudor-knot domain does not bind to histone tails and is not required for KAT5's chromatin occupancy. However, its absence leads to a global reduction in histone acetylation, accompanied with genome-wide alterations in gene expression that consequently result in diminished cell viability. Mechanistically, we find that the Tudor-knot domain regulates KAT5's HAT activity on nucleosomes by fine-tuning substrate accessibility.

Fig3. Western blot analysis of the H4-PanAc, H4, and KAT5 protein levels of whole cell lysates from the indicated cell lines.

Fig4. Heatmaps of HA-KAT5 ChIP-seq signal densities centered on transcription starting sites (TSS) across a ±5 kb window of all genes.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (KAT5-021H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (KAT5-5258H)
Involved Pathway
KAT5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways KAT5 participated on our site, such as ATF-2 transcription factor network,Androgen receptor signaling pathway,C-MYC pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with KAT5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell cycle | BARD1,MYBL2,CCND2A,DULLARD,DPF1,CENPO,NUDC,NINL,HDAC6,MND1 |
| Cell Cycle Checkpoints | MCM10,CDK5RAP2,YWHAQ,THRSP,UBE2V2,RAD9B,BARD1,MCM8,BRE,BABAM1 |
| Androgen receptor signaling pathway | ETV5A,RAD9A,KDM1A,EFCAB6,NR0B2A,KAT7,GNB2L1,RNF14,CTNNB2,RANBP9 |
| Cellular responses to stress | AMBRA1A,HMGA1B,TXNRD2,HIST1H1B,DYNLL2,WIPI1,SUZ12B,HMGA1,BAG5,EGLN1B |
| ATF-2 transcription factor network | GADD45A,RUVBL2,DDIT3,DUSP1,DUSP5,HRK,MAPK14,CREB1,DUSP10,KCNA3 |
| Cellular Senescence | LMNB1,HMGA1-RS1,CBX8A,TERF1,Txn1,HIST1H1E,PHC3,RNF2,RBBP7,POT1A |
| C-MYC pathway | ACTL6A,MYC,RUVBL2,HBP1 |
| Chromatin modifying enzymes | SETD3,RBBP4,KAT7B,DMAP1,BRD1,KAT7A,SMARCC2,SMARCA2,COPRS,BRPF3 |
Protein Function
KAT5 has several biochemical functions, for example, acetyltransferase activity,androgen receptor binding,histone acetyltransferase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by KAT5 itself. We selected most functions KAT5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with KAT5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | DNAJA2L,NEK8,HCCS,ZBTB2B,ACSM4,ATMIN,CBS,PDXK,PDE11A,DNMT3B |
| protein binding | GADD45G,DMD,DNM2,THOC1,PPP4R4,MTPAP,LRDD,CD27,HBA2,DLAT |
| histone acetyltransferase activity | KAT6A,NCOA1,KAT7B,HAT1,GTF3C4,TAF1,KAT2A,TAF1L,KAT8,MED24 |
| androgen receptor binding | CTNNB1,CALR,DAXX,KDM3A,NCOA1,NCOA3,KDM4C,NRIP1,RNF14,NSD1 |
| acetyltransferase activity | MBOAT7,MBOAT1,KAT8,KAT2B,CML5,AANAT1,MBOAT4,KAT6B,LPCAT3,NAT14 |
| transcription coactivator activity | ASXL1,POU2AF1,RUNX1,SERTAD2,TRIM32,ECD,MTDH,TRIP4,CDK7,TAF9 |
| repressing transcription factor binding | SRI,HDAC7,CTBP1,PARK7,CTNNB1,HDAC7A,PRDM5,DDX20,CBX5,HHEX |
| contributes_to histone acetyltransferase activity | TADA2B,SUPT7L,TAF9,TAF10,ELP4,EPC1,TAF5L,TADA1,TEX30,KAT2A |
Interacting Protein
KAT5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with KAT5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of KAT5.
MRGBP;ZBTB8A;RUVBL1;Myod1;CBX8
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



