HTT
-
Official Full Name
Htt huntingtin -
Synonyms
HTT;huntingtin;HD protein homolog;Huntington disease gene homolog;huntington disease protein homolog;Hd;Hdh;IT15;AI256365;C430023I11Rik
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Human
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293T
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- GST
- His
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&MBP
- His&GST
- Flag
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| htt-3808D | Recombinant ZHD, GST-tagged | E.coli | Zebrafish | GST | 494-604aa | |
| HTT-3873H | Recombinant Human HTT protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 2845-3000 aa | |
| HTT-28315TH | Recombinant Human HTT | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 110 amino acids |
|
| HTT-4637H | Recombinant Human HTT Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| HTT-8648Z | Recombinant Zebrafish HTT | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| Htt-1107M | Recombinant Mouse Htt Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Mouse | Myc&DDK |
|
|
| HTT-1126H | Recombinant Human HTT Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| HTT-1126H-B | Recombinant Human HTT Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Human |
|
||
| HTT-1313H | Recombinant Human HTT protein | E.coli | Human | Non | Met 1 - Glu 82 |
|
| HTT-1536H | Recombinant Human HTT protein, MBP-His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&MBP | 1-82 a.a. |
|
| Htt-1597M | Recombinant Mouse Htt protein, His & GST-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His&GST | Thr782~Phe920 |
|
| HTT-20HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human HTT Protein | Mammalian cells | Human | Flag | Full L. 1-3142 a.a. |
|
| HTT-2263H | Recombinant Human HTT Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Thr803-Phe941 |
|
| HTT-3829H | Recombinant Human HTT Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Human | Myc&DDK |
|
Background
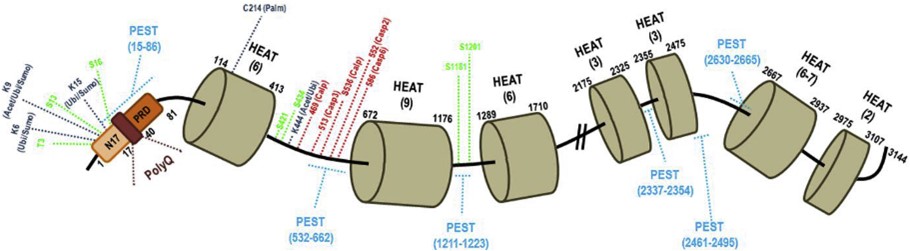
Fig1. Schematic representation of the human Huntingtin protein sequence. (Marco Caterino, 2018)
What is HTT protein?
HTT gene (huntingtin) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4p16. Huntingtin is a disease gene linked to Huntington's disease, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons. The huntingtin gene is widely expressed and is required for normal development. It is expressed as 2 alternatively polyadenylated forms displaying different relative abundance in various fetal and adult tissues. One candidate is the huntingtin-associated protein-1, highly expressed in brain, which has increased affinity for huntingtin protein with expanded polyglutamine repeats. This gene contains an upstream open reading frame in the 5' UTR that inhibits expression of the huntingtin gene product through translational repression. The HTT protein is consisted of 3142 amino acids and HTT molecular weight is approximately 347.6 kDa.
What is the function of HTT protein?
A significant number of HTT protein interactors are involved in this process, which is essential for the transport of materials within neurons. HTT is known to interact with various proteins, including Huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1) and HTT-interacting protein 1 (HIP1). These interactions are crucial for understanding the huntingtin function. HTT is associated with Huntington's disease, where a mutation in the HTT gene leads to the production of a toxic protein that affects neuronal function and survival. Certain kinases, such as MAPK11 and HIPK3, have been found to regulate the levels of mutant HTT protein, suggesting a role for these kinases in the pathogenesis of HD and as potential therapeutic targets.
HTT Related Signaling Pathway
Although the direct link between HTT protein and the Hedgehog signaling pathway is not clear, the Hedgehog signaling pathway plays a role in cell differentiation and proliferation, and is involved in the development of tumors. HTT protein may be indirectly associated with this pathway by influencing cell proliferation and differentiation. JAK-STAT signaling pathway is involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and immune regulation. The HTT protein may be associated with the JAK-STAT signaling pathway by influencing these basic cellular processes. They can also be participants in Ras, PI(3)K and mTOR signaling pathways, Wnt signaling pathways, and BMP signaling pathways.
HTT Related Diseases
HTT protein (Huntingtin protein) is mainly associated with Huntington's Disease (HD). Huntington's disease is a rare, familial, dominant neurodegenerative disorder characterized by abnormal autonomic movement, cognitive dysfunction, and psychiatric disorders. The disease usually begins between the ages of 35 and 50 and continues to progress for about 15 to 20 years, eventually leading to death. The main pathological features of Huntington's disease are a large number of deletion of striatal efferent spiny neurons in the basal ganglia, the formation of intranuclear inclusion bodies of neurons and the aggregation of misfolded mutant Huntington's proteins in the cytoplasm.
Bioapplications of HTT
The application of HTT protein (Huntingtin protein) is mainly focused on the research and treatment of Huntington's disease (HD). Because mutations in the HTT protein are the direct cause of HD, it has become a key target for disease research and intervention. Through high-throughput screening and other methods, researchers searched for genes that can inhibit the toxic effects of mutated HTT proteins, such as the discovery of the NUB1 gene, which reduces the amount of mHTT by promoting polyubiquitination and proteasome degradation of mHTT proteins. In addition, kinase genes such as MAPK11 and HIPK3 have been explored for their potential role in regulating levels of mutated HTT proteins. These findings not only improve the understanding of the pathogenesis of HD, but also provide the possibility for the development of new therapeutic strategies, including RNA interference, antisense oligonucleotides, small molecule drugs, and apoptosis intervention methods.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Nitin K Pandey, 2024
Fluorescent protein tags are convenient tools for tracking the aggregation states of amyloidogenic or phase separating proteins, but the effect of the tags is often not well understood. Here, researchers investigated the impact of a C-terminal red fluorescent protein (RFP) tag on the phase separation of huntingtin exon-1 (Httex1), an N-terminal portion of the huntingtin protein that aggregates in Huntington's disease. The results showed that the RFP-tagged Httex1 rapidly formed micron-sized, phase separated states in the presence of a crowding agent. The formed structures had a rounded appearance and were highly dynamic according to electron paramagnetic resonance and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching, suggesting that the phase separated state was largely liquid in nature. Remarkably, the untagged protein did not undergo any detectable liquid condensate formation under the same conditions. In addition to strongly promoting liquid-liquid phase separation, the RFP tag also facilitated fibril formation, as the tag-dependent liquid condensates rapidly underwent a liquid-to-solid transition. The rate of fibril formation under these conditions was significantly faster than that of the untagged protein. When expressed in cells, the RFP-tagged Httex1 formed larger aggregates with different antibody staining patterns compared to untagged Httex1.

Fig1. Phase separation of Httex1(Q25)-RFP is promoted by crowding agents.

Fig2. Freshly prepared Httex1(Q39)-RFP rapidly transitions into fibrils.
Case Study 2: Azza Ramadan, 2023
Huntington's disease is an inherited progressive neurodegenerative disorder caused by an expansion of the polyglutamine tract leading to malformation and aggregation of the mutant huntingtin protein in the cell cytoplasm and nucleus of affected brain regions. The development of neuroprotective agents from plants has received considerable research attention. This study aims to investigate the neuroprotective effects of luteolin and the mechanisms that underline its potential mediated protection in the mutant htt neuroblastoma cells. The mutant htt neuroblastoma cells were transfected with 160Q, and the control wild-type neuroblastoma cells were transfected with 20Q htt for 24 h and later treated with luteolin. Cell viability, aggregation formation and western blotting were performed. Luteolin presents a new potential therapeutic and protective agent for the treatment and decreasing the cytotoxicity in neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington's disease.
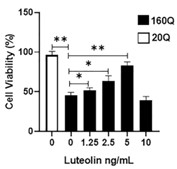
Fig3. Luteolin treatment protected the neuroblastoma cells against mutant htt cytotoxicity.
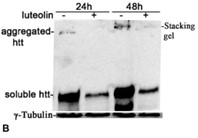
Fig4. Western blotting detection of the mutant Htt aggregates and soluble protein in the cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (HTT-4637H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (HTT-20HFL)
Involved Pathway
HTT involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways HTT participated on our site, such as Huntingtons disease, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with HTT were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Huntingtons disease | NDUFB8,NDUFS5,ATP5J,NDUFB3,ATP5A1,NDUFS8,HAP1,POLR2J,NDUFA12,SOD2 |
Protein Function
HTT has several biochemical functions, for example, beta-tubulin binding,dynactin binding,dynein intermediate chain binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by HTT itself. We selected most functions HTT had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with HTT. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | LCK,MLL1,SHANK3,AGER,DRG1,IGF2R,SMN1,SP100,PDCD6,SHMT2 |
| dynactin binding | BBS4,SNX6,CCDC64,PROL1,SNX5,BICD1 |
| dynein intermediate chain binding | PAFAH1B1,RAN,HEATR2 |
| p53 binding | TP53RK,AXIN1,AAAS,BRD7,PTTG1IP,TRP53,ZNF346,ZFP385C,RNF34,EP300 |
| transcription factor binding | PRICKLE1,HDAC4,TFDP1A,MED12,PPARG,PPARGC1B,SIRT1,CEBPA,NKX3-1,GPX3 |
| ion channel binding | GPD1L,KCNJ11,PKD2,HSP90AB1,CAV3,FHL1,PACS2,AASS,PIRT,KCNB2 |
| protein binding | AUNIP,FSTL3,PRTFDC1,RAB27A,SF3A1,ARF4,BCL2L16,TJP1,SNX3,TSR2 |
| receptor binding | TENM2,SERPINE2,PVRL3B,VTCN1,ABL1,P2RX4,LEPROT,AGXT,PLXNC1,ADCYAP1 |
| beta-tubulin binding | RGS2,GABARAP,ARL8A,VAPB,SPAST,PROL1,OST4,SNCA,MAP1S,FGF13 |
Interacting Protein
HTT has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with HTT here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of HTT.
PRPF40A;SH3GL3
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Yao, J; Ong, SE; et al. Huntingtin is associated with cytomatrix proteins at the presynaptic terminal. MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE 63:96-100(2014).
- Fodale, V; Kegulian, NC; et al. Polyglutamine- and Temperature-Dependent Conformational Rigidity in Mutant Huntingtin Revealed by Immunoassays and Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).


