HFE2
-
Official Full Name
hemochromatosis type 2 (juvenile) -
Overview
The product of this gene is involved in iron metabolism. It may be a component of the signaling pathway which activates hepcidin or it may act as a modulator of hepcidin expression. It could also represent the cellular receptor for hepcidin. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. Defects in this gene are the cause of hemochromatosis type 2A, also called juvenile hemochromatosis (JH). JH is an early-onset autosomal recessive disorder due to severe iron overload resulting in hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism, hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis and cardiomyopathy, occurring typically before age of 30. -
Synonyms
HFE2;hemochromatosis type 2 (juvenile);hemojuvelin;haemojuvelin;HFE2A;HJV;JH;repulsive guidance molecule c;RGMC;RGM domain family member C;hemochromatosis type 2 protein;MGC23953
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Insect Cells
- Insect Cell
- E.coli
- Human Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293F
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- His
- His&T7
- His&GST
- Flag
- His&Fc
- GST
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFE2-7288H | Recombinant Human HFE2 protein(Met1-Ser399), His-tagged | Insect Cells | Human | His | Met1-Ser399 | |
| HFE2-205C | Recombinant Cynomolgus HFE2, His-tagged | Insect Cell | Cynomolgus | His | Met1-Ser400 |
|
| HFE2-2082H | Recombinant Human HFE2 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Lys234~Ser416 |
|
| HFE2-2083H | Recombinant Human HFE2 protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&T7 | Leu29~Ala401 |
|
| HFE2-2084H | Recombinant Human HFE2 protein, His & GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&GST | Gln36~Phe200 |
|
| HFE2-2419H | Recombinant Human Hemochromatosis Type 2 (Juvenile), FLAG-tagged | Human Cell | Human | Flag | 36-398 a.a. |
|
| HFE2-4276Z | Recombinant Zebrafish HFE2 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| HFE2-469H | Recombinant Human HFE2 protein, His & Fc-tagged | HEK293F | Human | His&Fc | Gln36~Asp400 |
|
| HFE2-4722H | Recombinant Human HFE2 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| HFE2-7602M | Recombinant Mouse HFE2 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| HFE2-001CCL | Recombinant Cynomolgus HFE2 cell lysate | Insect Cell | Cynomolgus | Non |
|
|
| HFE2-423HCL | Recombinant Human HFE2 cell lysate | Insect Cell | Human | Non |
|
|
| HFE2-4145M | Recombinant Mouse HFE2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| HFE2-4145M-B | Recombinant Mouse HFE2 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is HFE2 protein?
HFE2 is also called HJV. HJV (hemojuvelin BMP co-receptor) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q21. The product of this gene is involved in iron metabolism. It may be a component of the signaling pathway which activates hepcidin or it may act as a modulator of hepcidin expression. It could also represent the cellular receptor for hepcidin. Two uORFs in the 5' UTR negatively regulate the expression and activity of the encoded protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. The HFE2 protein is consisted of 426 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 45.1 kDa.
What is the function of HFE2 protein?
The HFE2 protein, also known as hemochromatosis protein 2, is involved in the regulation of iron homeostasis in the body. It is secreted by the liver and muscle and plays a role in maintaining the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). According to the provided references, HFE2 administration in an animal model of multiple sclerosis, which is a condition that involves immune cell infiltration and disruption of the BBB, has been shown to prevent paralysis and immune cell infiltration by inhibiting RGMa-mediated BBB alteration.
This suggests that HFE2 protein has a protective function against neurological damage associated with autoimmune diseases by preserving the integrity of the BBB and potentially modulating immune cell activity. However, it's important to note that the exact mechanisms of HFE2 are still under investigation, and further research is needed to fully understand its roles and potential therapeutic applications.

Fig1. Complex pathways of iron transport regulation in hepatocytes. (Alla Turshudzhyan, 2023)
HFE2 Related Signaling Pathway
HFE2 has been shown to have neuroprotective effects in models of neurological disorders, potentially through its involvement in pathways that maintain the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and modulate immune cell infiltration. This suggests a role for HFE2 in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative processes. There is evidence suggesting that HFE2 may interact with GPCR pathways, which are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including sensory perception, immune system modulation, and metabolic regulation.
HFE2 Related Diseases
Juvenile Hemochromatosis is a form of hereditary hemochromatosis that is caused by mutations in the HFE2 gene. The disease is associated with diabetes and sexual development issues due to iron deposition in various organs. HFE2 mutations can lead to the accumulation of iron in vital organs such as the liver, heart, endocrine glands, joints, and skin, causing a range of symptoms and potential organ damage. Iron deposition in endocrine glands can lead to disorders such as diabetes mellitus due to damage to the pancreas and impaired insulin production. Additionally, gonadal function can be affected, leading to hypogonadism.
Hereditary Hemochromatosis (HH): HFE2 mutations are linked to type 2 HH, which is a rare form of the disease. Unlike the more common HFE-related HH (type 1), type 2 HH is caused by mutations in the HJV or HAMP genes, with HJV gene mutations accounting for the majority of cases.
Bioapplications of HFE2
Mutations in the HFE2 gene are linked to specific types of hereditary hemochromatosis. Genetic testing for HFE2 can be used as a diagnostic tool to identify individuals at risk for developing iron overload conditions. Given its role in iron regulation, HFE2 could be a potential therapeutic target for conditions characterized by iron dysregulation, such as anemia, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain cancers.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xue Fan Wang, 2024
Liver failure causes breakdown of the Blood CNS Barrier (BCB) leading to damages of the Central-Nervous-System (CNS), however the mechanisms whereby the liver influences BCB-integrity remain elusive. One possibility is that the liver secretes an as-yet to be identified molecule(s) that circulate in the serum to directly promote BCB-integrity. To study BCB-integrity, the researchers developed light-sheet imaging for three-dimensional analysis. They show that liver- or muscle-specific knockout of Hfe2/Rgmc induces BCB-breakdown, leading to accumulation of toxic-blood-derived fibrinogen in the brain, lower cortical neuron numbers, and behavioral deficits in mice. Soluble HFE2 competes with its homologue RGMa for binding to Neogenin, thereby blocking RGMa-induced downregulation of PDGF-B and Claudin-5 in endothelial cells, triggering BCB-disruption. HFE2 administration in female mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a model for multiple sclerosis, prevented paralysis and immune cell infiltration by inhibiting RGMa-mediated BCB alteration.

Fig1. Immunocytochemistry of claudin-5 in human primary endothelial cell monolayer after PBS, HFE2, RGMa, and RGMa&HFE2 treatments and quantification.
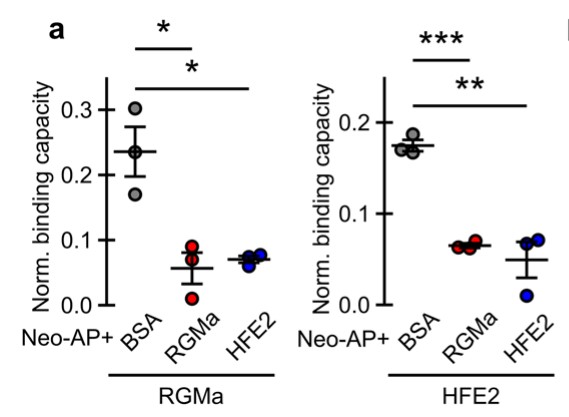
Fig2. HFE2 blocks RGMa-interaction with Neogenin.
Case Study 2: Carine Fillebeen, 2018
Systemic iron balance is controlled by hepcidin, a liver hormone that limits iron efflux to the bloodstream by promoting degradation of the iron exporter ferroportin in target cells. Iron-dependent hepcidin induction requires hemojuvelin (HJV), a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) coreceptor that is disrupted in juvenile hemochromatosis, causing dramatic hepcidin deficiency and tissue iron overload. Hjv-/- mice recapitulate phenotypic hallmarks of hemochromatosis but exhibit blunted hepcidin induction following lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration. The researchers show that Hjv-/- mice fail to mount an appropriate hypoferremic response to acute inflammation caused by LPS, the lipopeptide FSL1, or Escherichia coli infection because residual hepcidin does not suffice to drastically decrease macrophage ferroportin levels. Hfe-/- mice, a model of milder hemochromatosis, exhibit almost wild-type inflammatory hepcidin expression and associated effects, whereas double Hjv-/-Hfe-/- mice phenocopy single Hjv-/- counterparts. In primary murine hepatocytes, Hjv deficiency does not affect interleukin-6 (IL-6)/Stat, and only slightly inhibits BMP2/Smad signaling to hepcidin; however, it severely impairs BMP6/Smad signaling and thereby abolishes synergism with the IL-6/Stat pathway. Inflammatory induction of hepcidin is suppressed in iron-deficient wild-type mice and recovers after the animals are provided overnight access to an iron-rich diet.

Fig3. Livers of Hjv-deficient mice retain inflammatory Smad signaling, presumably via activin B.

Fig4. Hjv-/- hepatocytes exhibit impaired Smad signaling in response to BMP6.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (HFE2-4722H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (HFE2-2082H)
Involved Pathway
HFE2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways HFE2 participated on our site, such as Axon guidance,BMP receptor signaling,Developmental Biology, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with HFE2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Netrin-1 signaling | NTN1A,TRPC5,SIAH2,UNC5D,RNF8,PITPNA,RGMA,EZRA,NTN1B,TRPC4 |
| Developmental Biology | IL17RD,CACNG8A,FGF8B,DOCK1,NRTN,COL6A1,CLASP1,NRP1A,NR6A1,EFNA1B |
| Axon guidance | DAB2IPB,SEMA4B,COL6A2,GSK3B,ARPC2,DPYSL3,CSNK2B,UNC5D,AP2A2,DUSP1 |
| BMP receptor signaling | RGMA,CHRDL1,CTDSP2,NOG,GREM1,CTDSPL,FST,RGMB,SKI,CTDSP1 |
Protein Function
HFE2 has several biochemical functions, for example, BMP binding,contributes_to BMP receptor activity,coreceptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by HFE2 itself. We selected most functions HFE2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with HFE2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| glycoprotein binding | APOH,RGMA,SHB,EDEM1,CANX,HSPA5,SERPINA1D,BMPR1A,PIP,FOXRED2 |
| BMP binding | GREM2,GDF5,GREM1,CER1,TCAP,NBL1,BMPR2 |
| coreceptor activity | TMIGD2,PVRL1,RGMB,CD86,CD4,CCR8,CD8A,PVRL2,RGMA,CXCR7B |
| protein binding | OTULIN,EFNB2,LRCH3,LAMTOR2,FBXW5,BRSK1,MAPT,RAB7A,PPP4C,NHP2 |
| transferrin receptor binding | RGMA,Trf,SNX4,CD81,TF,SNX2,HFE,SNX1 |
| receptor binding | DDX54,SMAGP,NCK1,EPHX2,ITGA1,NPFFL,CRAT,FGF13B,LYN,PVRL1A |
Interacting Protein
HFE2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with HFE2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of HFE2.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


