HDAC4
-
Official Full Name
histone deacetylase 4 -
Overview
Histones play a critical role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Histone acetylation/deacetylation alters chromosome structure and affects transcription factor access to DNA. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to class II of the histone deacetylase/acuc/apha family. It possesses histone deacetylase activity and represses transcription when tethered to a promoter. This protein does not bind DNA directly, but through transcription factors MEF2C and MEF2D. It seems to interact in a multiprotein complex with RbAp48 and HDAC3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
HDAC4;histone deacetylase 4;HD4;AHO3;BDMR;HDACA;HA6116;HDAC-4;HDAC-A;histone deacetylase A
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Insect Cell
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- Insect cell
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&GST
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
Background
What is HDAC4 protein?
HDAC4 (histone deacetylase 4) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q37. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to class II of the histone deacetylase/acuc/apha family. It possesses histone deacetylase activity and represses transcription when tethered to a promoter. This protein does not bind DNA directly, but through transcription factors MEF2C and MEF2D. It seems to interact in a multiprotein complex with RbAp48 and HDAC3. The HDAC4 protein is consisted of 1084 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 119.0 kDa.
What is the function of HDAC4 protein?
HDAC4 can affect the structure of chromatin and transcriptional regulation of genes by deacetylating histones, and thus participate in biological processes such as cell differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis. HDAC4 plays an important role in the nervous system, especially in the development and functional maintenance of neurons. It can regulate the synaptic formation, excitatory transmission, learning and memory of neurons.
HDAC4 Related Signaling Pathway
HDAC4 inhibits gene expression by removing the acetyl group from the histone tail. This deacetylation causes chromatin structure to tighten, which restricts access to transcription factors and other transcriptional regulatory proteins, thereby reducing the transcriptional activity of specific genes. HDAC4 also interacts with a variety of non-histone substrates, including transcription factors, nuclear hormone receptors, and signaling pathway molecules, thereby indirectly affecting gene expression.
HDAC4 Related Diseases
HDAC4 is abnormally expressed or has altered activity in a variety of cancers, such as breast cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, etc. HDAC4 is also expressed in the nervous system, and its abnormality may be related to the occurrence and development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Huntington's disease (HD). HDAC4 plays an important role in cardiac development and cardiomyocyte function, and its abnormality may be related to cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial hypertrophy and heart failure.

Fig1. Potential of HDAC4-based therapy for ischemic stroke. (Qingsheng Kong, 2018)
Bioapplications of HDAC4
HDAC4 is a potential drug target, especially in certain types of cancer where abnormal HDAC4 activity may lead to tumor formation or progression. Inhibitors of HDAC4 are being investigated as potential treatments for some cancers.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Li-Si Zeng, 2016
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) mediate histone deacetylation, leading to transcriptional repression, which is involved in many diseases, including age-related tissue degeneration, heart failure and cancer. In this study, the researchers were aimed to investigate the expression, clinical significance and biological function of HDAC4 in esophageal carcinoma (EC). They found that HDAC4 mRNA and protein are overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tissues and cell lines. HDAC4 overexpression is associated with higher tumor grade, advanced clinical stage and poor survival. Mechanistically, HDAC4 promotes proliferation and G1/S cell cycle progression in EC cells by inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors p21 and p27 and up-regulating CDK2/4 and CDK-dependent Rb phosphorylation. HDAC4 also enhances ESCC cell migration. Furthermore, HDAC4 positively regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by increasing the expression of Vimentin and decreasing the expression of E-Cadherin/α-Catenin.

Fig1. Western blot analysis of HDAC4 protein expression in eight ESCC tissues and paired normal tissues.

Case Study 2: Ke Hu, 2023
Long noncoding RNAs (LncRNAs) are essential to regulate the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease (CAD). This study was conducted to analyze the functionality of long noncoding RNA cancer susceptibility candidate 11 (lncRNA CASC11) in oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced injury of cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (CMECs). CMECs were treated with ox-LDL to induce the CAD cell model. The cellular expression levels of CASC11 and histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) were determined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction or Western blot assay. Cell absorbance, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and inflammation were evaluated by cell counting kit-8, flow cytometry, tube formation, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. The binding of human antigen R (HuR) to CASC11 and HDAC4 was analyzed by RNA immunoprecipitation. HDAC4 stability was determined after actinomycin D treatment. CASC11 bound to HuR and improved HDAC4 expression. HDAC4 downregulation counteracted the protective role of CASC11 overexpression in CMECs.

Fig3. HDAC4 expression levels were determined by RT-qPCR and Western blot assay.

Quality Guarantee
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (HDAC4-4645H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
High Bioactivity

Fig2. Activity Data. (HDAC4-022H)
Involved Pathway
HDAC4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways HDAC4 participated on our site, such as Alcoholism,Epstein-Barr virus infection,Viral carcinogenesis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with HDAC4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MicroRNAs in cancer | PDGFA,ITGB3,HDAC1,APC,SLC45A3,PIK3CA,TTC6,PRKCE,PRKCG,PRKCA |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | HSPB2,PIK3R2,YWHAH,HSPA1L,PRKACB,YWHAG,TNFAIP3,NFKBIB,ITGAL,CCNA2 |
| Alcoholism | GNG13,H3F3A,MAP2K1,HDAC10,SHC4,HDAC7,GNB5,GNG4,BDNF,HIST1H2AN |
| Viral carcinogenesis | NFKB1,RB1,GTF2A1L,H2-Q10,HDAC7,HIST1H4B,CCNE1,EGR3,GTF2H2,PKM2 |

Fig1. The role of HDAC4 in ischemic stroke and underlying mechanisms. (Qingsheng Kong, 2018)

Fig2. The illustration of the explained mechanisms for miR-200b-3p in endothelial apoptosis. (Fan Zhang, 2021)
Protein Function
HDAC4 has several biochemical functions, for example, NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity (H3-K14 specific),RNA polymerase III transcription factor binding,activating transcription factor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by HDAC4 itself. We selected most functions HDAC4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with HDAC4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| activating transcription factor binding | EP300,GATA4,ZFP516,SMAD2,HDAC7A,MEF2C,EEF1D,PPARG,HDAC1,ATOH8 |
| chromatin binding | ZFP143,ATF5,DNMT1,KDM1A,RING1,KLHDC3,GLI2,BAHCC1,HMGN5,SHMT2 |
| core promoter binding | IFI203,NKX2-1,SAFB,E2F3,AGO2,HDAC5,CCAR1,INSM1B,NPAS2,ARNTL |
| contributes_to transcription regulatory region DNA binding | HDAC5,RXRA,TCF3,NFYB,NFYC,HAND1,NR1H3,NFYA,TCF12,ATF4 |
| transcription corepressor activity | SKIL,THRB,ENO1,ASXL1,CITED2,SKOR1,RYBP,E2F8,HSBP1,CSDA |
| zinc ion binding | SETDB1A,CA9,ZDHHC15A,PHF11,NBR1,TRIM22,PCGF5A,ACE2,MMP28,CPA1 |
| protein deacetylase activity | HDAC1,HDAC5,SIN3A,HDAC3,SIRT2,HDAC2,HDAC9,HDAC10,SIRT1 |
| RNA polymerase III transcription factor binding | HDAC5 |
| protein binding | IL7R,SNW1,SZL,NUP62L,CCBL1,SUPT5H,ANKHD1,FAM81B,PIBF1,RTN4 |
Interacting Protein
HDAC4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with HDAC4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of HDAC4.
YWHAG;YWHAZ;YWHAE;YWHAH
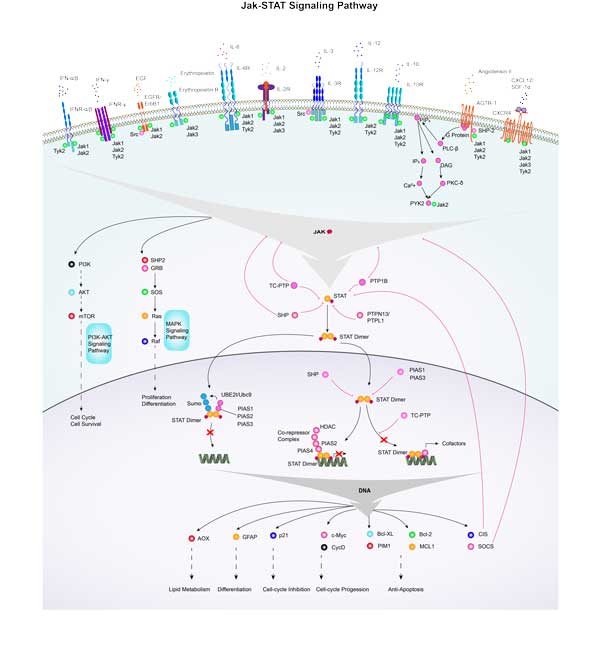
HDAC4 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wild, EJ; Tabrizi, SJ; et al. Targets for Future Clinical Trials in Huntington's Disease: What's in the Pipeline?. MOVEMENT DISORDERS 29:1434-1445(2014).
- Hannan, JL; Kutlu, O; et al. Valproic Acid Prevents Penile Fibrosis and Erectile Dysfunction in Cavernous Nerve-Injured Rats. JOURNAL OF SEXUAL MEDICINE 11:1442-1451(2014).