Gpt
-
Official Full Name
glutamic-pyruvate transaminase (alanine aminotransferase) -
Overview
This gene encodes cytosolic alanine aminotransaminase 1 (ALT1); also known as glutamate-pyruvate transaminase 1. This enzyme catalyzes the reversible transamination between alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to generate pyruvate and glutamate and, therefore, plays a key role in the intermediary metabolism of glucose and amino acids. Serum activity levels of this enzyme are routinely used as a biomarker of liver injury caused by drug toxicity, infection, alcohol, and steatosis. A related gene on chromosome 16 encodes a putative mitochondrial alanine aminotransaminase. -
Synonyms
GPT;glutamic-pyruvate transaminase (alanine aminotransferase);alanine aminotransferase 1;ALT1;GPT1;AAT1;Alanine aminotransferase;ALAT1_HUMAN;Glutamate pyruvate transaminase 1;Glutamic alanine transaminase 1;Glutamic pyruvic transaminase 1;Glutamic--alanine transaminase 1;Glutamic--pyruvic transaminase 1;GPT 1;OTTHUMP00000228783;glutamic-alanine transaminase 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Human
- Mouse
- Pig
- Porcine
- Rhesus macaque
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- Human Liver
- Human Heart
- Porcine Heart
- Human
- Mammalian Cell
- Insect Cell
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293T
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- His&GST
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
- Myc&DDK
- GST
Background
What is GPT protein?
GPT gene (glutamic--pyruvic transaminase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8q24. This gene encodes cytosolic alanine aminotransaminase 1 (ALT1); also known as glutamate-pyruvate transaminase 1. This enzyme catalyzes the reversible transamination between alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to generate pyruvate and glutamate and, therefore, plays a key role in the intermediary metabolism of glucose and amino acids. Serum activity levels of this enzyme are routinely used as a biomarker of liver injury caused by drug toxicity, infection, alcohol, and steatosis. The GPT protein is consisted of 496 amino acids and GPT molecular weight is approximately 54.6 kDa.
What is the function of GPT protein?
The GPT protein is a pyruvase that catalyzes reversible ammonia interaction between alanine and 2-oxoglutaric acid to produce pyruvate and glutamic acid. GPT is an important indicator of liver function. When liver cells undergo damage such as inflammation, necrosis, or poisoning, GPT is released from liver cells into the blood, resulting in elevated serum GPT levels. Certain drugs and chemicals may cause liver cell damage, which can lead to increased GPT levels. For example, erythromycin, tetracycline, sleeping pills, antipyretic analgesics and other drugs. Changes in pregnancy and alcohol influence can also cause changes in GPT levels.
GPT Related Signaling Pathway
GPT is connected to the Rho GTPase signaling pathway, which controls various cellular processes such as cell shape, motility, and adhesion. Rho GTPases are molecular switches that cycle between an inactive GDP-bound state and an active GTP-bound state, interacting with multiple proteins to regulate signaling pathways. GPT may also be involved in signaling pathways mediated by GPCRs. GPCRs are a large family of cell surface receptors that transduce extracellular signals into intracellular responses, affecting a wide range of physiological functions. GPT is also involved in immune cell function, particularly in T cell activation and migration.
GPT Related Diseases
All kinds of acute and chronic viral hepatitis can lead to increased GPT. When cirrhosis is active, GPT is usually elevated, reflecting liver cell damage. Liver cancer tissue can damage liver cells, resulting in the release of GPT into the blood, resulting in elevated GPT. Many other diseases can also cause increased GPT, such as cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, acute myocardial infarction, myocarditis, and heart failure. Some drug-induced hepatitis can also cause an increase in GPT.
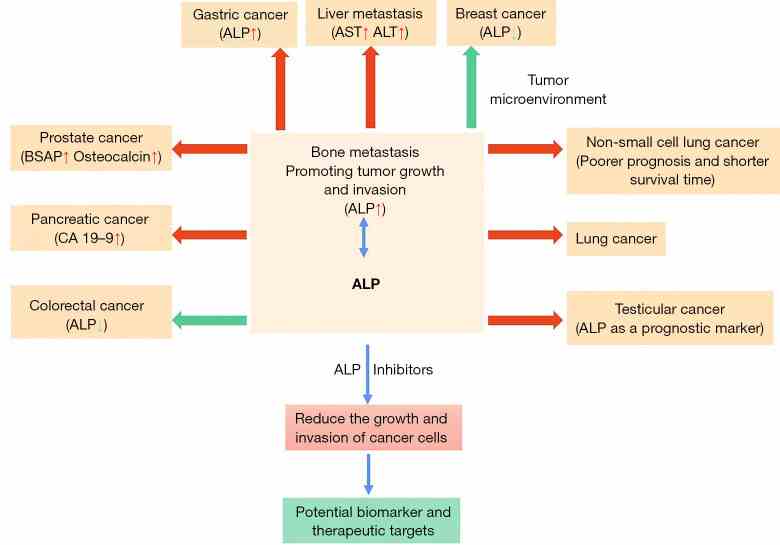
Fig1. Abnormalities in ALP expression and activity have been observed in certain types of cancer. (Tingting Jiang, 2023)
Bioapplications of GPT
Glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (GPT), also known as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), is an enzyme primarily found in the liver, and its changes in blood levels are commonly used to screen and monitor liver disease. Monitoring of GPT levels during or after treatment helps to assess liver status; The De Ritis ratio of GPT to aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is used to evaluate alcoholic liver disease. They can also assess other diseases or damage to other organs.
Case Study
Case Study 1: François Pognan, 2022
Sotuletinib (BLZ945), a CSF1-R specific kinase inhibitor developed for the treatment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, induced liver enzyme elevation in absence of hepatocellular lesions in preclinical rat and monkey studies. The monocytic cell family, including Kupffer cells, e.g., the liver-resident macrophages, are dependent upon CSF1 pathway activation for their survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Kupffer cells act as the main body compartment responsible for elimination of some blood-borne proteins, like ALT, AST, and few others. The depletion of Kupffer cells through CSF1 pathway inhibition has already been hypothesized as responsible for apparent liver enzyme elevation without detectable corresponding liver damage. However, a release of these biomarkers from unseen hepatic lesions or from other organs cannot be excluded. In order to eliminate a potential contribution of ALT elevation from an internal organ source, researchers injected recombinant his-Tagged ALT1 into rats pretreated with Sotuletinib. The elimination rate of the exogenous ALT1 was significantly lower in treated animals, demonstrating a delayed clearance independently of any potential organ lesions.

Fig1. Kinetic of ALT elevation upon Sotuletinib treatment and reversibility upon compound withdrawal.

Fig2. Plasma His-ALT1 activities of vehicle control and Sotuletinib-treated rats.
Case Study 2: Xiao Fu, 2022
To investigate the mechanism of alanine aminotransferase 1 (ALT1) in the progression of HCC, the differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) in the ALT1 interaction network were identified by targeted proteomic analysis. Wound healing and transwell assays were conducted to assess the effect of ALT1 on cellular migration and invasion. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), colony formation, and flow cytometry assays were performed to identify alterations in proliferation and apoptosis. The results showed that ALT1 knockdown inhibits the migration, invasion, proliferation of HepG2 cells, and promotes apoptosis. Knockdown of ALT1 in HepG2 cells reduced the expression of Ki67 and epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EP-CAM). Suppression of the ALT1 and EP-CAM expression contributed to alterations in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) -associated markers and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Additionally, inhibition of ALT1 and Ki67 also decreased the expression of apoptosis and proliferation factors. Furthermore, inhibition of ALT1 and ASPP2 also changed the expression of P53, which may be the signaling pathway by which ALT regulates these biological behaviors.

Fig3. Quantitative analysis results and representative images of the Western blot results for ALT1.

Fig4. Flow cytometry images of the cell cycle distribution in the negative control and ALT1 knockdown cells.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GPT-5304H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GPT-5420H)
Involved Pathway
Gpt involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Gpt participated on our site, such as Arginine biosynthesis,Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Gpt were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Carbon metabolism | FBP1A,GOT1,TPI1B,GPI,ALDOB,PKMB,OGDHA,OGDH,PDHA1A,PRPS1A |
| -Oxocarboxylic acid metabolism | AADAT,GOT2A,IDH3A,IDH3B,GPT2,ACY1,IDH2,GOT2B,GPT2L,GOT2 |
| Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | GOT2,RIMKLB,GAD1,GLUL,ADSL,AGXTB,GLUD2,CAD,ASPA,NIT2 |
| Metabolic pathways | ACSS1,BST1,GMDS,NDUFB1,ACSM4,ACAD8,MINPP1A,CEPT1,CERS5,PON2 |
| Arginine biosynthesis | GLUL,NOS2B,ASL2,GLS,NOS3,NAGS,GLUD2,GOT2A,NOS1,GOT1 |
| Biosynthesis of amino acids | PGK1,PGAM1A,ENO1B,PHGDH,pykF,GOT1,GOT2A,ARG2,PKLR,RPE |
Protein Function
Gpt has several biochemical functions, for example, L-alanine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity,pyridoxal phosphate binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Gpt itself. We selected most functions Gpt had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Gpt. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| L-alanine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity | GPT2L,GPT2 |
| pyridoxal phosphate binding | ABAT,PYGL,SGPL1,CTH,PHYKPL,HINT2,CCBL2,GOT1,GOT2B,PYGMB |
Interacting Protein
Gpt has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Gpt here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Gpt.
CDC7;RALA;SASS6
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Selleng, S; Selleng, K; et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of anti-PF4/heparin antibodies in intensive care patients: a prospective observational study. JOURNAL OF THROMBOSIS AND THROMBOLYSIS 39:60-67(2015).
- Zhang, FS; Chen, WQ; et al. Transcriptional activity comparison of different sites in recombinant Marek's disease virus for the expression of the H9N2 avian influenza virus hemagglutinin gene. JOURNAL OF VIROLOGICAL METHODS 207:138-145(2014).



