GH
-
Official Full Name
Growth Hormone -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family of hormones which play an important role in growth control. The gene, along with four other related genes, is located at the growth hormone locus on chromosome 17 where they are interspersed in the same transcriptional orientation; an arrangement which is thought to have evolved by a series of gene duplications. The five genes share a remarkably high degree of sequence identity. Alternative splicing generates additional isoforms of each of the five growth hormones, leading to further diversity and potential for specialization. This particular family member is expressed in the pituitary but not in placental tissue as is the case for the other four genes in the growth hormone locus. Mutations in or deletions of the gene lead to growth hormone deficiency and short stature. -
Synonyms
GH;IGHD1B;GH-N;Somatotropin;GHN;Growth hormone;hGH-N;GH1;HGH
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Ovine
- Carp
- Denis
- EBV
- Mai Mai
- Pig
- Rabbit
- Chicken
- Bream
- Dog
- Cattle
- Human cytomegalovirus
- Human herpesvirus 4
- HHV3
- HHV5
- Human herpesvirus 3
- Elephantid herpesvirus 1 (isolate Asian elephant/Berlin/Kiba/1998) (EIHV-1) (Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus)
- Feline herpesvirus 1 (FeHV-1) (Feline viral rhinotracheitis virus)
- Human Herpesvirus 6A
- Suid herpesvirus 1
- Gallid herpesvirus 2
- Human herpesvirus 6B
- HHV4
- SaHV-2
- Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1
- MeHV-1
- GPCMV
- Human herpesvirus 7
- Psittacid herpesvirus 1 (isolate Amazon parrot/-/97-0001/1997) (PsHV-1) (Pacheco's disease virus)
- MuHV-1
- EHV2
- Nicotiana Benthamiana
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- Non
- His
- SUMO
- Myc
Background
What is GH protein?
GH is also known as GH1. GH1 gene (growth hormone 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q23. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family of hormones which play an important role in growth control. The gene, along with four other related genes, is located at the growth hormone locus on chromosome 17 where they are interspersed in the same transcriptional orientation; an arrangement which is thought to have evolved by a series of gene duplications. The five genes share a remarkably high degree of sequence identity. This particular family member is expressed in the pituitary but not in placental tissue as is the case for the other four genes in the growth hormone locus. The GH protein is consisted of 217 amino acids and GH molecular weight is approximately 24.8 kDa.
What is the function of GH protein?
GH stimulates the growth of bones, muscles, and other tissues by promoting the synthesis of proteins and the retention of nitrogen in tissues. In adults, GH helps regulate metabolism by stimulating the breakdown of fats to provide energy necessary for tissue growth. It also opposes the action of insulin, leading to increased fat breakdown and insulin resistance. GH affects body composition by promoting the growth of muscle mass and reducing the amount of adipose tissue. GH secretion is regulated by various factors including growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), somatostatin, ghrelin, and other physiological factors such as sleep, exercise, and nutrition. GH may possess immunomodulatory actions, as immune cells express receptors for GH and can respond to its stimulation, potentially affecting immune function.
GH Related Signaling Pathway
GH binds to its receptor to activate JAK2 (non-receptor tyrosine kinase 2), which in turn activates STAT (signal transduction and transcriptional activator) proteins, which migrate to the nucleus and activate or inhibit the expression of specific genes. GH signaling also acts through the PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase) and Akt (protein kinase B) pathways, which are involved in cell growth, differentiation, and survival. GH is also able to activate the ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) and MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) pathways, which are involved in cell proliferation and differentiation. GH promotes the production of IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) in the liver and other tissues, and IGF-1 activates PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways through its receptor IGF-1R to promote cell growth and metabolism.
GH Related Diseases
GH related diseases mainly involve abnormal GH secretion, including GH deficiency and GH excess. GH deficiency can lead to growth retardation, commonly seen in children, known as growth hormone deficiency (GHD). GH deficiency in adults may be associated with cardiovascular disease, muscle loss, osteoporosis, and cognitive decline. GH excess is often associated with pituitary adenomas and may lead to acromegaly or gigantism. In addition, GH, by affecting the GH/IGF-1 axis, may be associated with the aging process and age-related diseases, such as cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Mutations in the GH receptor (GHR) or GH-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR) may also lead to specific growth disorders or endocrine diseases.
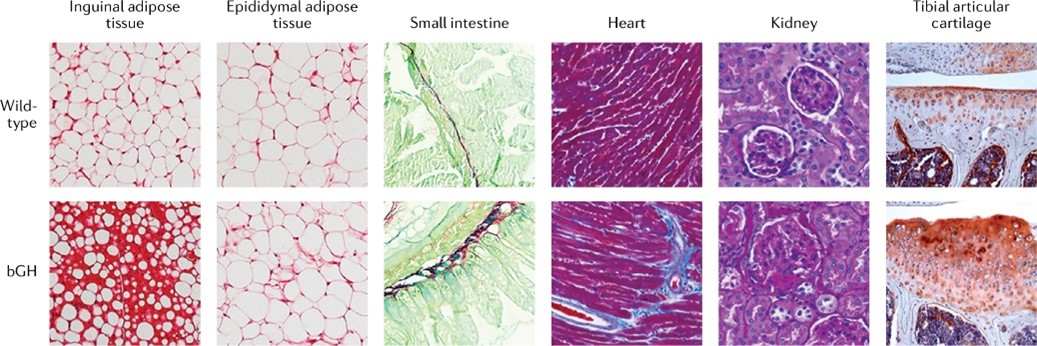
Fig1. GH overexpression in mice induces tissue fibrosis. (John J Kopchick, 2022)
Bioapplications of GH
Growth hormone replacement therapy: Used to treat growth hormone deficiency (GHD) and promote normal growth and development in children and adolescents.
Treatment of adult growth hormone deficiency: improvement of metabolic abnormalities, muscle loss, osteoporosis, and decreased quality of life caused by GH deficiency in adults.
Treatment of certain metabolic diseases: For example, GH may help improve certain types of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Burn and trauma recovery: GH helps in wound healing and tissue repair, and its use in burn and trauma recovery is being studied.
Athletic performance and body shaping: In some cases, athletes may use GH to improve athletic performance or change body composition, although this is illegal and unsafe.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Tim Hollstein, 2022
As ghrelin and the growth hormone (GH)/insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) axis are implicated in the regulation of energy intake and metabolism, researchers investigated whether ghrelin, GH, and IGF-1 concentrations mediate the fasting-induced decrease in 24hEE that characterizes thriftiness. Plasma total ghrelin, GH, and IGF-1 concentrations were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay after an overnight fast the morning before and after each 24-hour session. During 24-hour fasting, on average 24hEE decreased by 8.0%, GH increased by ~5-fold. Greater fasting-induced increase in ghrelin was associated with a greater decrease in 24hEE during 24-hour fasting.
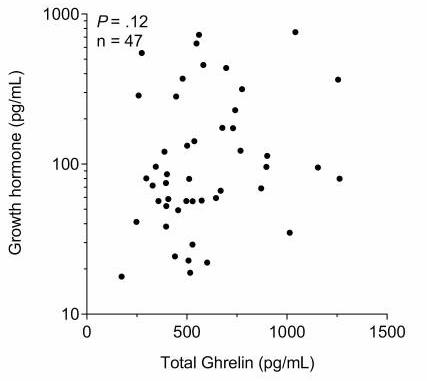
Fig1. Associations between fasting total ghrelin and growth hormone.
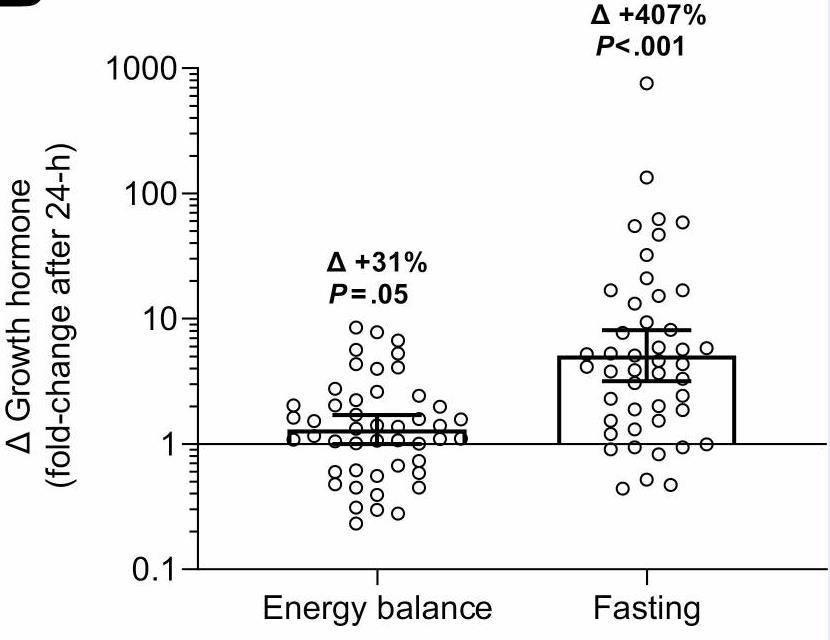
Fig2. Changes in growth hormone concentrations after 24-hour energy balance and fasting conditions.
Case Study 2: Alexandre Marchand, 2022
The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) prohibits athletes from using recombinant growth hormone (GH). The validated method used in antidoping laboratories for the direct detection of exogenous GH in serum requires two immunoluminometric assays (ILMAs): The first mainly measures the concentration of the full-length (22 kDa) form of GH (recGH), and the second measures concentrations of multiple GH fragments produced by the pituitary gland (22 kDa, 20 kDa and other forms) (pitGH). The tube-by-tube analysis is laborious. A recent development opened new possibilities to simplify the detection of recGH in serum: multiplexed immunoassays that detect multiple targets in a single well of a 96-well plate using an ELISA-like procedure with high sensitivity. This study aimed to evaluate this technology by developing a customized assay for GH detection. One pair of antibodies with specificities similar to those of the recGH assay and one pair of antibodies compatible with pitGH detection were selected for a single duplex assay. Forty-eight serum samples (negative athlete samples and positive samples following GH administration) were analyzed using the two methods. The microplate duplex assay discriminated between the negative athlete samples and the positive controls, although the rec/pit ratios from the duplex assay were lower than those obtained with the ILMAs.
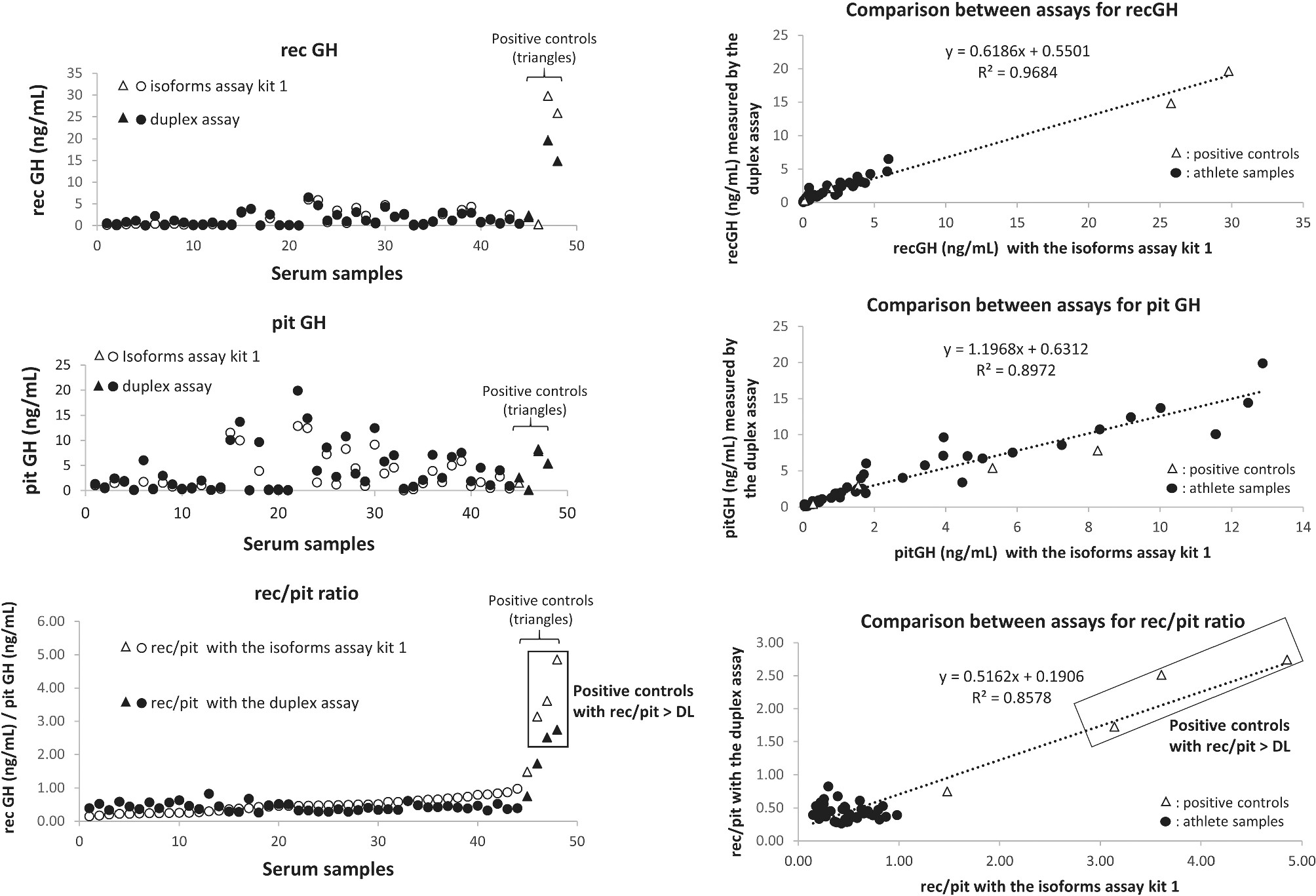
Fig3. recGH, pitGH, and rec/pit results obtained for 48 serum samples using GH isoforms assay kit 1 and the new duplex assay.
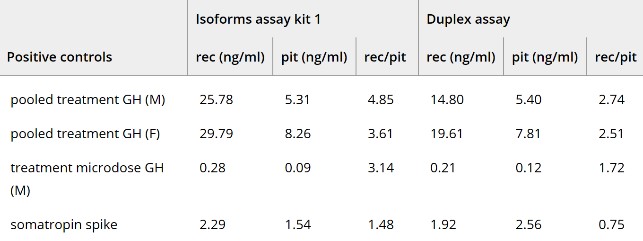
Fig4. Results obtained for the positive controls.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
GH involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GH participated on our site, such as Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction,PIK-Akt signaling pathway,Jak-STAT signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GH were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | GM13305,MPL,LEP,CRLF2,Ifna11,PIK3CA,Ifnlr1,Il23a,PRLRA,GRB2A |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | PPP2R3C,PDGFB,FGF12,PIK3R3,GNG12,GNB3,INS1,LAMA3,Il2,PDGFA |
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | GRIK4,RXFP4,TAAR7F,CHRNB3A,UTS2R,PTGER2,TAAR12H,RXFP1,CHRNA4,MC5RB |
Protein Function
GH has several biochemical functions, for example, growth hormone receptor binding,hormone activity,metal ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GH itself. We selected most functions GH had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GH. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | ADARB2,ADH1,ZNF729,MMP1A,HCCS,MYLIPB,NINL,TGM2,ADSSL,NME3 |
| growth hormone receptor binding | TYK2,JAK1,SOCS2,GH1,JAK2 |
| hormone activity | INHBAB,IAPP,EDN1,MLN,GIP,INHBB,CSH2,RLN3A,STC1,UTS2 |
Interacting Protein
GH has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GH here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GH.
Ywhae
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References

.jpg)
.jpg)

