GBA
-
Official Full Name
glucosidase, beta, acid -
Overview
This gene encodes a lysosomal membrane protein that cleaves the beta-glucosidic linkage of glycosylceramide, an intermediate in glycolipid metabolism. Mutations in this gene cause Gaucher disease, a lysosomal storage disease characterized by an accumulation of glucocerebrosides. A related pseudogene is approximately 12 kb downstream of this gene on chromosome 1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. -
Synonyms
GBA;glucosidase, beta, acid;GLUC, glucosidase, beta;acid (includes glucosylceramidase) , glucosylceramidase;glucosylceramidase;GBA1;alglucerase;imiglucerase;acid beta-glucosidase;beta-glucocerebrosidase;lysosomal glucocerebrosidase;D-glucosyl
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Insect Cell
- E.coli
- HEK293
- CHO
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293T
- Mamanlian cells
- Yeast
- His
- His&Myc&SUMO
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- His&GST
- His&SUMO
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
- GST
Background
What is GBA protein?
GBA (GBA1, glucosylceramidase beta 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q22. GBA1, full name Glucosylceramidase Beta 1, also known as acidic beta-glucocerebrosidase (GCase), is a lysosomal enzyme, The main function is to catalyze the breakdown of a specific type of glycolipid, glucosylceramide. It consists of a 39-amino acid signaling peptide and a transmembrane region, as well as five glycosylation sites. GCase is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and transported by the Golgi to the lysosome, where it plays the role of breaking down glucocerebroside into glucose and ceramide. GBA protein is consisted of 536 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 59.7 kDa.
What is the function of GBA protein?
GBA is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and then transported to the Golgi apparatus. From the Golgi, GBA is directed to the lysosomes, which are the cellular organelles responsible for breaking down and recycling cellular waste and external materials. Within the lysosome, GBA catalyzes the hydrolysis of glucosylceramide into glucose and ceramide. This reaction is essential for the turnover of glycosphingolipids, which are a type of lipid found in the cell membrane. By breaking down glucosylceramide, GBA helps maintain cellular homeostasis and prevents the accumulation of this lipid, which can be toxic to cells if it builds up.
GBA Related Signaling Pathway
GBA plays a central role in the lysosome by breaking down glucosylceramide into glucose and ceramide. This process is crucial for the turnover of glycosphingolipids. Certain mutations in the GBA gene can cause GCase to be misfolded and retained in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), activating stress responses such as the UPR. Prolonged activation of the UPR can lead to cell death pathways, contributing to neurodegeneration. Accumulation of lipids or misfolded proteins due to GBA deficiency can activate microglia and contribute to neuroinflammation, another factor in the development of PD. There is a suggested link between GBA mutations, leading to a decrease in GCase activity, and the impaired metabolism of alpha-synuclein.
GBA Related Diseases
Mutations in the GBA gene that result in reduced or loss of GCase activity can lead to Gaucher disease, a lysosomal storage disorder characterized by the accumulation of glucosylceramide in cells, particularly macrophages. This accumulation leads to the formation of 'Gaucher cells' which can cause damage in various organs, including the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. In addition to its role in Gaucher disease, GBA mutations are also a significant genetic risk factor for Parkinson's disease. The exact mechanisms by which GBA mutations contribute to Parkinson's are still under investigation but may involve impaired alpha-synuclein metabolism and lysosomal dysfunction.

Fig1. Possible mechanisms underlying the link between GCase, alpha-synuclein and PD. (Laura Smith, 2022)
Bioapplications of GBA
During drug screening and development, purified GBA proteins can be used to test the efficacy of potential therapeutic drugs, assess their impact on GBA activity and potential for treatment of related diseases. Enzyme replacement therapy is a common treatment for patients with Gaucher's disease, which involves the application of GBA protein. Although modified GBA proteins are used in enzyme replacement therapy, purified GBA proteins are essential in the development and quality control process.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Zhidong Qiu, 2022
The influence of glucosylceramide (GlcCer) on liver cancer spread is not well understood. This research showed that the expression of GBA1, an enzyme that converts GlcCer to ceramide, was lower in liver cancer tissues. Clinical data analysis showed that reduced GBA1 expression was linked to liver cancer cells' ability to spread. Further experiments confirmed that low GBA1 expression increased liver cancer spread both in the lab and in living organisms. The underlying mechanism showed that low GBA1 expression boosted liver cancer spread by promoting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), with the involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway. On the plasma membrane (PM), the reprogramming of GlcCer by GBA1 increased the presence of LRP6 in the PM, leading to GlcCer and LRP6 interaction, which promoted LRP6 phosphorylation at Ser1490 and activated the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This is the first discovery that GlcCer interacts with a protein.

Fig1. ROC curve analyses show the diagnostic potential of GBA1 in liver cancer.
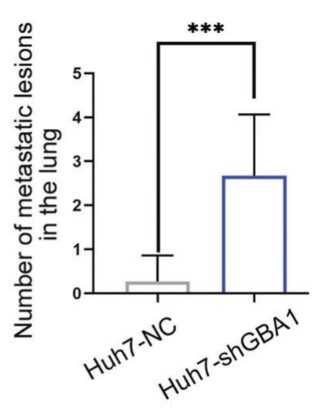
Fig2. The effect of GBA1 loss-of-function on spontaneous lung metastasis in the orthotopic xenograft model.
Case Study 2: Soojin Kim, 2021
Mitochondria-lysosome interactions at specific contact sites have been newly recognized for facilitating communication between these two cellular compartments. However, their function in healthy and pathological human neurons is not well understood. This research reveals that these contacts can dynamically assemble in various regions of human neurons, including the cell body, axons, and dendrites, facilitating reciprocal communication. In neurons derived from Parkinson's disease patients with GBA1 mutations, the researchers observed an abnormal prolongation of mitochondria-lysosome contacts. This was attributed to a malfunction in the regulation of the protein TBC1D15, which is crucial for the hydrolysis of Rab7 GTP, a process that helps to detach these contacts. The cause of this malfunction was a reduction in the activity of the lysosomal enzyme GBA1 (β-glucocerebrosidase or GCase) in neurons from affected individuals, and this could be corrected by enhancing the enzyme's activity using a GCase modulator. The observed defects led to disruptions in mitochondrial distribution and functionality. Furthermore, the issues could be rectified by restoring TBC1D15 function in neurons from Parkinson's patients with GBA1-linked mutations.
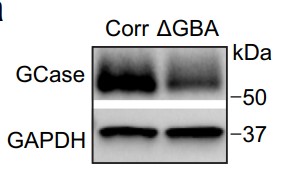
Fig3. Western blot analysis of PD patient-derived mutant GBA1 dopaminergic neurons.

Fig4. Fis1 levels in PD patient-derived mutant GBA1 dopaminergic neurons.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GBA-7841H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GBA-5174H)
Involved Pathway
GBA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GBA participated on our site, such as Other glycan degradation,Sphingolipid metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GBA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Other glycan degradation | AGA,NEU4,MAN2B1,MAN2C1,NEU1,ENGASE,FUCA1.2,GBA2,MANBA,FUCA2 |
| Metabolic pathways | NDUFV3,H2-KE6,EARS2,G6PCA.2,PKM,AKR1B1L,C1GALT1A,PTDSS1,SPS2,ARG1 |
| Lysosome | LAMP3,SMPD1,IGF2R,SUMF1,HGSNAT,CTSE,GGA3,ATP6V0A1,ACP2,HEXA |
| Sphingolipid metabolism | SGPP1,SPTLC2B,SERINC1,GALCA,ASAH1B,SMPD5,NEU1,ASAH1A,CERS2A,PPAP2C |
Protein Function
GBA has several biochemical functions, for example, glucosylceramidase activity,protein binding,receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GBA itself. We selected most functions GBA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GBA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| receptor binding | FGF12B,ECH1,POMC,FGF6A,CD86,DECR2,NPPA,LPL,HLA-E,GNB2L1 |
| glucosylceramidase activity | GBA2 |
| protein binding | MAGOH,RNF2,MC5R,CEP63,ECM1,VEGFB,ABCD1,INCENP,RNF113A,FOXO3B |
Interacting Protein
GBA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GBA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GBA.
Scarb2;pi3p;SCAMP3;TOP3B;A2M;cona_canen;HSPD1;HSP90B1;ATP5J;CANX;ATP6V1A;SKIV2L2;CCT3;CCT8;RPS6KA3;FMR1;ZMYND11;DHCR24;RNF20;ZCCHC8
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Sinclair, G; Pfeifer, TA; et al. Secretion of human glucocerebrosidase from stable transformed insect cells using native signal sequences. BIOCHEMISTRY AND CELL BIOLOGY-BIOCHIMIE ET BIOLOGIE CELLULAIRE 84:148-156(2006).
- Favalli, EG; Varenna, M; et al. Drug-induced agranulocytosis during treatment with infliximab in enteropathic spondyloarthropathy. CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL RHEUMATOLOGY 23:247-250(2005).


