EPHX1
-
Official Full Name
epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal (xenobiotic) -
Overview
Epoxide hydrolase is a critical biotransformation enzyme that converts epoxides from the degradation of aromatic compounds to trans-dihydrodiols which can be conjugated and excreted from the body. Epoxide hydrolase functions in both the activation and detoxification of epoxides. Mutations in this gene cause preeclampsia, epoxide hydrolase deficiency or increased epoxide hydrolase activity. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
EPHX1;epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal (xenobiotic);EPHX;epoxide hydrolase 1;epoxide hydratase;MEH;EPOX;HYL1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Sus scrofa (Pig)
- Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
- Rat
- Insect cell
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- E.coli
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293T
- Mamanlian cells
- E.coli expression system
- His
- Non
- GST
- T7
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&SUMO
- Myc&DDK
- Flag
Background

Fig1. The schematic diagram of the CpG sites in the EPHX1 promoter. (Qing Sang, 2014)
What is EPHX1 protein?
EPHX1 (epoxide hydrolase 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q42. EPHX1 is an important bioconvertase that acts as an antidote in the human body. The enzyme EPHX1 catalyzes the hydrolysis of aromatic and aliphatic epoxides, converting these active metabolic intermediates into less active, more water-soluble substances. EPHX1 protein is expressed in a variety of tissues, but the level of expression may vary in different tissues. EPHX1 plays a role in drug metabolism, hormone biosynthesis, and detoxification of environmental toxins. The EPHX1 protein is consisted of 455 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 52.9 kDa.
What is the function of EPHX1 protein?
EPHX1 is a catalytic enzyme that is primarily responsible for converting epoxides produced during metabolic processes in the body into diols, a process that is essential for maintaining chemical balance and detoxification mechanisms in living organisms. Through its biotransforming role, EPHX1 is involved in drug metabolism, hormone synthesis, and neutralization of environmental toxins, playing an important role in reducing the harmful effects of active metabolites and protecting cells from damage. In addition, the activity and expression levels of EPHX1 are influenced by genetic polymorphisms, which may be related to individual susceptibility to certain diseases and differences in response to drugs.
EPHX1 Related Signaling Pathway
EPHX1 protein is an important enzyme involved in the signaling pathway of lipid metabolism and REDOX reaction. Specifically, EPHX1 is involved in the regulation of intracellular lipid metabolism by catalyzing the hydrolysis of epoxides and converting them into corresponding diols. In addition, EPHX1 can also regulate the REDOX state of cells and affect many biological processes, such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, and immune response.
EPHX1 Related Diseases
EPHX1 is associated with the occurrence and development of a variety of diseases, and changes in its gene polymorphism and enzyme activity may affect an individual's ability to metabolize certain compounds, which is associated with disease risk. For example, certain genetic variants of EPHX1 have been linked to the risk of alcoholic liver disease, while low activity alleles of EPHX1 have been linked to the onset of chronic hepatitis C and HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. In addition, the dysregulation of EPHX1 expression is associated with the occurrence and development of various cancers such as breast cancer, and some gene polymorphisms of EPHX1 are also associated with the antioxidant capacity of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Bioapplications of EPHX1
In the study of drug metabolism, the activity and genetic polymorphism of EPHX1 have important effects on the efficacy and toxicity of drugs, so it is used for personalized drug therapy and drug dose optimization. EPHX1 is also important in the field of environmental health, where it is involved in detoxification processes that help assess the toxicity and carcinogenic potential of chemicals. In disease research, the expression and activity of EPHX1 has been associated with multiple pathologic states, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, making it a potential biomarker and therapeutic target.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Matthew L Edin, 2018
Stimuli such as inflammation or hypoxia induce cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-mediated production of arachidonic acid-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). Previous in vitro assays have suggested that epoxide hydrolase 2 (EPHX2) is responsible for nearly all EET hydrolysis. EPHX1, which exhibits slow EET hydrolysis in vitro, is thought to contribute only marginally to EET hydrolysis. Using Ephx1-/-, Ephx2-/-, and Ephx1-/-Ephx2-/- mice, the researchers show here that EPHX1 significantly contributes to EET hydrolysis in vivo Disruption of Ephx1 and/or Ephx2 genes did not induce compensatory changes in expression of other Ephx genes or CYP2 family epoxygenases. Plasma levels of 8,9-, 11,12-, and 14,15-DHET were reduced by 38, 44, and 67% in Ephx2-/- mice compared with wildtype (WT) mice, respectively; however, plasma from Ephx1-/-Ephx2-/- mice exhibited significantly greater reduction (100, 99, and 96%) of those respective DHETs. Kinetic assays and FRET experiments indicated that EPHX1 is a slow EET scavenger, but hydrolyzes EETs in a coupled reaction with cytochrome P450 to limit basal EET levels.

Fig1. Expression of EPHX1, EPHX2, and β-actin proteins in liver S9 and microsomal fractions.

Fig2. Relative contribution of EPHX1 and EPHX2 to EET hydrolysis in liver S9 fractions.
Case Study 2: Ji Eun Lee, 2021
The researchers discovered that a previously unrecognized and primate-specific EPHX1 transcript, termed E1-b, was actually the predominant driver of EPHX1 expression in all human tissues. This study identifies another human EPHX1 transcript, designated as E1-b'. Unusually, both the E1-b and E1-b' mRNA transcripts are generated from the use of a far upstream gene promoter, localized ∼18.5 kb 5'-upstream of the EPHX1 protein-coding region. Although expressed at comparatively lower levels than E1-b, the novel E1-b' transcript is readily detected in all tissues examined, with highest levels maintained in human ovary. The E1-b' mRNA possesses unusual functional features in its 5'-untranslated region, including a GC-rich leader sequence and two upstream AUGs that encode for short peptides of 26 and 17 amino acids in length, respectively. Results from in vitro transcription/translation assays and direct transfection in mammalian cells of either the E1-b' transcript or the encoded peptides demonstrated that the E1-b' upstream open reading frames (uORFs) are functional, with their presence markedly inhibiting the translation of EPHX1 protein, both in cis and in trans configurations.
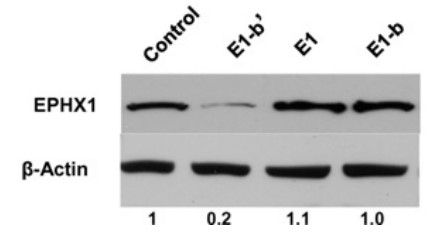
Fig3. Two micrograms of each of the constructs used in panel A was transfected into 293A cells.
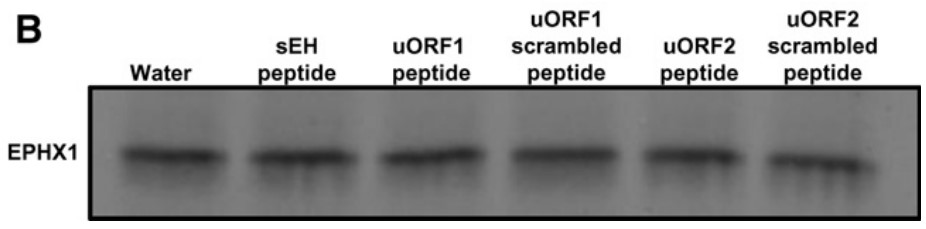
Fig4. uORF peptides do not induce nascent protein degradation.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (EPHX1-3407H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (EPHX1-5311H)
Involved Pathway
EPHX1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways EPHX1 participated on our site, such as Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P,Bile secretion,Chemical carcinogenesis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with EPHX1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Bile secretion | SLCO1B1,CYP3A4,SLCO1B2,Abcb1b,SLC22A1,SLC27A5,SLC51B,ADCY7,SLC4A4,ABCG8 |
| Chemical carcinogenesis | ALDH3B1,ADH7,HSD11B1,ALDH3B2,CYP2C54,CYP3A25,CYP3A7-CYP3AP1,NAT2,NAT1,UGT1A6B |
| Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P | SULT2A1,GSTT2B,UGT1A6A,GSTM6,GSTA,CYP2F2,UGT1A6B,UGT1AB,GSTM1,UGT2A1 |
Protein Function
EPHX1 has several biochemical functions, for example, cis-stilbene-oxide hydrolase activity,epoxide hydrolase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by EPHX1 itself. We selected most functions EPHX1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with EPHX1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| epoxide hydrolase activity | EPHX3,EPHX2,Npepo,RNPEP,EPHX4,LTA4H |
Interacting Protein
EPHX1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with EPHX1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of EPHX1.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


