DHRS9
-
Official Full Name
dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 9 -
Overview
3-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase that converts 3-alpha-tetrahydroprogesterone (allopregnanolone) to dihydroxyprogesterone and 3-alpha-androstanediol to dihydroxyprogesterone. May play a role in the biosynthesis of retinoic acid from retinaldehyde, but seems to have low activity with retinoids. Can utilize both NADH and NADPH. -
Synonyms
DHRS9;dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 9;dehydrogenase/reductase SDR family member 9;3 alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase;3alpha HSD;NADP dependent retinol dehydrogenase/reductase;RDH15;RDHL;retinol dehydrogenase homolog;RETSDR8;SDR9C4;short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 9C;member 4;3-@alpha-HSD;3-@alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase;3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase;3-alpha-HSD;DHRS9_HUMAN;NADP-dependent retinol dehydrogenase/reductase;RDH-E2;RDHE2;RDHTBE;Retinol dehydrogenase, tracheobronchiol epithelail cell-specific;SDR family, member 9;short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 9;short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 9C, member 4;Short chain dehydrogenase/reductase retSDR8;Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase retSDR8;OTTHUMP00000163043;OTTHUMP00000204923;OTTHUMP00000204925;OTTHUMP00000204926;OTTHUMP00000205057;3ALPHA-HSD
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is DHRS9 protein?
DHRS9 gene (dehydrogenase/reductase 9) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q31. This gene encodes a member of the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) family. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. This protein demonstrates oxidoreductase activity toward hydroxysteroids and is able to convert 3-alpha-tetrahydroprogesterone to dihydroxyprogesterone and 3-alpha-androstanediol to dihydroxyprogesterone in the cytoplasm, and may additionally function as a transcriptional repressor in the nucleus. The DHRS9 protein is consisted of 319 amino acids and DHRS9 molecular weight is approximately 35.2 kDa.
What is the function of DHRS9 protein?
DHRS9 protein, also known as short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase 9 (SDR9C4), is a member of the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) family. It has been identified as a moonlighting protein, meaning it can perform multiple functions within the cell. The primary function of DHRS9 is its oxidoreductase activity towards hydroxysteroids, where it catalyzes the conversion of 3-alpha-tetrahydroprogesterone to dihydroxyprogesterone and 3-alpha-androstanediol to dihydroxyprogesterone in the cytoplasm. Additionally, it is involved in the biosynthesis of retinoic acid from retinaldehyde. DHRS9 can utilize both NADH and NADPH as cofactors and may also function as a transcriptional repressor in the nucleus.
DHRS9 Related Signaling Pathway
DHRS9 is involved in the synthesis of retinoic acid from retinaldehyde, an important signaling molecule that influences cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. In the context of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), DHRS9 may be associated with the NF-kappaB signaling pathway, which plays a key role in regulating immune response and inflammation. DHRS9 may play a role in the synthesis and metabolism of neurotransmitters, affecting the function of the nervous system. As a oxidoreductase, DHRS9 may play a role in maintaining intracellular REDOX balance and influence cellular response to oxidative stress.
DHRS9 Related Diseases
The DHRS9 protein has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including prostate cancer, glioma, and systemic lupus erythematosus. In prostate cancer, DHRS9 may be involved in the development and progression of the disease. Glioma is a brain tumor in which DHRS9 may affect the proliferation and survival of tumor cells. In addition, as systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease, DHRS9 may be related to the immune response and inflammatory processes of the disease.
Bioapplications of DHRS9
DHRS9 protein has many uses in scientific research and clinical applications. In the field of scientific research, DHRS9 protein is often used in experimental studies, such as protein expression and function analysis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), antibody binding assay (AbP), immunoprecipitation (STD) and Western Western blot (WB). In addition, DHRS9 has also been used as a stable marker of human regulatory macrophages (Mreg), contributing to the study of cell based adjuvant immunosuppressive therapy in organ transplant recipients. In terms of drug development, functional studies of DHRS9 contribute to the development of therapeutic strategies for specific diseases, such as in colon cancer, studying the molecular mechanism by which the transcription factor FXR activates DHRS9 to inhibit cellular oxidative phosphorylation and inhibit colon cancer progression.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jinlai Zhao, 2022
Colon cancer is a common gastrointestinal malignancy. It has been discovered that Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) plays an imperative regulatory role in multitype cancers in recent years. However, its regulatory mechanism in colon cancer has not been clearly explored. This study intended to explore the molecular regulatory mechanism of FXR and its downstream genes on the malignant progression of colon cancer. The binding relationship between FXR and its downstream gene dehydrogenase/reductase member 9 (DHRS9) was verified through luciferase reporter assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. The changes of oxidative phosphorylation were detected by Western blot and oxygen consumption rate determination. The effect of FXR/DHRS9 axis on the malignant progression of colon cancer cells was further confirmed by rescue experiments. The results showed that DHRS9 was a downstream gene of FXR, and FXR/DHRS9 inhibited the deterioration of colon cancer through inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation. Moreover, promoting FXR expression in colon cancer cells could partially reverse the biological function changes caused by silencing DHRS9 expression.
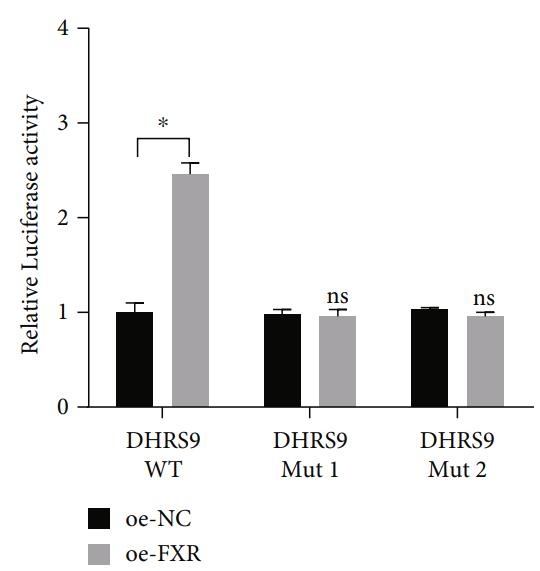
Fig1. Binding between FXR and DHRS9 promoter region demonstrated by dual-luciferase assays.

Fig2. The enrichment diagram of the KEGG pathway analysis on DHRS9 gene.
Case Study 2: Paloma Riquelme, 2017
The human regulatory macrophage (Mreg) has emerged as a promising cell type for use as a cell-based adjunct immunosuppressive therapy in solid organ transplant recipients. In this brief report, dehydrogenase/reductase 9 (DHRS9) is identified as a robust marker of human Mregs. The cognate antigen of a mouse monoclonal antibody raised against human Mregs was identified as DHRS9 by immunoprecipitation and MALDI-MS sequencing. Expression of DHRS9 within a panel of monocyte-derived macrophages was investigated by quantitative PCR, immunoblotting and flow cytometry. The results showed that a subpopulation of DHRS9-expressing human splenic macrophages was identified by immunohistochemistry. Expression of DHRS9 was acquired gradually during in vitro development of human Mregs from CD14 monocytes and was further enhanced by IFN-γ treatment on day 6 of culture. Stimulating Mregs with 100 ng/mL lipopolysaccharide for 24 hours did not extinguish DHRS9 expression. Dhrs9 was not an informative marker of mouse Mregs.

Fig3. DHRS9 protein was detected in human Mregs but not other tolerogenic monocyte-derived therapeutic cell products.
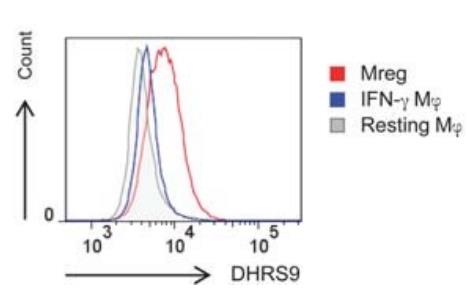
Fig4. Quantification of DHRS9 expression by flow cytometry.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DHRS9-2603H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DHRS9-1997H)
Involved Pathway
DHRS9 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DHRS9 participated on our site, such as Metabolic pathways,RA biosynthesis pathway,Retinol metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DHRS9 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| The canonical retinoid cycle in rods (twilight vision) | RBP3,RLBP1,RPE65B,STRA6,RBP4,ABCA4A,RLBP1B,MYO7A,MYO7AA,SDR9C7 |
| retinol biosynthesis | RBP5,DHRS4,CES5A |
| Visual phototransduction | RPE65B,APOA4A,RLBP1B,RLBP1A,PPEF1,ABCA4A,LRP12,NMT1A,METAP1,BCO2A |
| Signal Transduction | PDK2,IQGAP3,ARAP1,GPR132,ZNRF3,NRP2A,PROKR1A,DEPDC7,ABI1A,ARHGAP24 |
| RA biosynthesis pathway | DHRS3,RDH7,ADH8A,ADH8B,SDR16C5,DHRS4,RDH13,CYP26A1,CRABP1A,RDH10 |
| Metabolic pathways | COX4I1,RIMKLA,PIGH,ST6GALNAC5,GCNT3,DNMT3A,G6PC2,GMPS,AGXT2L2,LIPCA |
| Signaling by Retinoic Acid | RDH10,CRABP2A,PDK3,DHRS3,PDK4,FABP11B,CRABP1B,RDH7,CRABP1,RDH13 |
| Retinol metabolism | DHRS3B,CYP1A,UGT2A3,UGT1A7C,BCO1L,RDH10,DHRS4L2,AOX1,RPE65,UGT1A3 |
Protein Function
DHRS9 has several biochemical functions, for example, alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) activity,racemase and epimerase activity,retinol dehydrogenase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DHRS9 itself. We selected most functions DHRS9 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DHRS9. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| retinol dehydrogenase activity | DHRS3,RDH11,RDH7,RDH10,RDH1,RDH5,RDH12,ADH4,ADH7,BMP2 |
| alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) activity | ADH5,ADH8A,ADH1C,ADH1A,ADH1,ADH6,ADH8B,ADH7,ADH4 |
| testosterone dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity | HSD17B1,HSD17B6,H2-KE6,HSD17B2,HSD17B8,AKR1C3 |
Interacting Protein
DHRS9 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DHRS9 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DHRS9.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zubair, N; Kooperberg, C; et al. Genetic Variation Predicts Serum Lycopene Concentrations in a Multiethnic Population of Postmenopausal Women. JOURNAL OF NUTRITION 145:187-192(2015).
- Lord, DM; Baran, AU; et al. BdcA, a Protein Important for Escherichia coli Biofilm Dispersal, Is a Short-Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductase that Binds Specifically to NADPH. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).


