CYC1
-
Official Full Name
cytochrome c-1 -
Overview
This is the heme-containing component of the cytochrome b-c1 complex, which accepts electrons from Rieske protein and transfers electrons to cytochrome c in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. -
Synonyms
CYC1;cytochrome c-1;cytochrome c1, heme protein, mitochondrial;UQCR4;heme protein;mitochondrial;Complex III subunit 4;Complex III subunit IV;CY1_HUMAN;Cytochrome b c1 complex subunit 4;Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 4;Cytochrome bc1 complex subunit 4;Cytochrome c 1;Cytochrome c1;Ubiquinol cytochrome c reductase complex cytochrome c1 subunit;Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase complex cytochrome c1 subunit
Recombinant Proteins
- Rhesus macaque
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Yeast
- Bovine
- Dictyostelium Discoideum
- Mus musculus
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- HEK293
- E.coli
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- E.coli expression system
- His
- GST
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYC1-1130R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey CYC1 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cell | Rhesus macaque | His |
|
|
| CYC1-2224H | Recombinant Human CYC1 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| CYC1-3518Z | Recombinant Zebrafish CYC1 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| CYC1-4134M | Recombinant Mouse CYC1 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| CYC1-467Y | Recombinant Yeast Cyc1p | Yeast | Yeast | Non | Full L. 1-108 a.a. |
|
| CYC1-7136HCL | Recombinant Human CYC1 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| CYC1-20H | Recombinant Human CYC1 protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 85-325aa |
|
| CYC1-2119M | Recombinant Mouse CYC1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| CYC1-2119M-B | Recombinant Mouse CYC1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| CYC1-2390HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CYC1 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 325 amino acids |
|
| CYC1-955R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque CYC1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| CYC1-955R-B | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque CYC1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque |
|
||
| RFL12697HF | Recombinant Full Length Human Cytochrome C1, Heme Protein, Mitochondrial(Cyc1) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli expression system | Human | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (85-325) |
|
| RFL28798BF | Recombinant Full Length Bovine Cytochrome C1, Heme Protein, Mitochondrial(Cyc1) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli expression system | Bovine | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (85-325) |
|
| RFL29898DF | Recombinant Full Length Dictyostelium Discoideum Cytochrome C1, Heme Protein, Mitochondrial(Cyc1) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli expression system | Dictyostelium Discoideum | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (29-275) |
|
| RFL35976MF | Recombinant Full Length Mouse Cytochrome C1, Heme Protein, Mitochondrial(Cyc1) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli expression system | Mus musculus | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (85-325) |
|
Background
What is cyc1 protein?
Cyc1 is a gene that encodes for Cytochrome c1, a major component of the cytochrome b-c1 complex, which is part of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. This chain is responsible for the final stages of cellular respiration, a fundamental metabolic process in the generation of ATP, the main molecule used by cells for storing and transferring energy.
Cytochrome c1 is involved in both the electron transport and proton pumping activities of the complex. It receives electrons from the cytochrome b subunit and transfers them to a soluble cytochrome c, which then carries the electrons to the cytochrome oxidase complex, the next step in the respiratory chain. This complex helps to accomplish ATP biosynthesis and associated energy production for cellular activities.
The cyc1 gene and its encoded protein were initially discovered through studies of yeast mitochondrial mutants in the late 1960s and early 1970s. These pioneers identified various cytochrome-deficient mutants, including those deficient in cytochrome c1, establishing the fundamental role of this protein in cellular respiration.
In terms of protein structure, cytochrome c1 is a heme protein, which means it has a prosthetic group (a non-protein component required for the protein's biological activity) called a heme group. This heme group allows the protein to carry out its redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions, accepting and donating electrons. The protein chain of cytochrome c1 is anchored to the inner mitochondrial membrane via a transmembrane helix, and its electron transferring domain is placed in the intermembrane space.
In eukaryotes, including humans, the mature cytochrome c1 protein is made up of 244 amino acids and has a molecular mass of about 27 kDa. Mutations in the gene coding for cytochrome c1 can result in a spectrum of mitochondrial disorders, which can impact a broad range of biological processes and physiological functions. Therefore, the CYC1 gene and cytochrome c1 protein are quite important in the field of medical research.
What is the function of cyc1 protein?
Cyc1 (Cytochrome C1) protein is an integral part of the respiratory chain in mitochondria that plays a crucial role in oxidative phosphorylation. Here are some specific functions of Cyc1 protein:
Energy Production: The most important function of Cyc1 is to assist in the production of energy within the mitochondria. It plays an integral role in electron transport chain where it transports electrons and helps in creating a proton gradient for the production of ATP, the molecular unit of energy.
Apoptosis: Cytochrome c1 is also involved in initiating apoptosis, or programmed cell death. When a cell is subjected to stress or damage, cytochrome c1 can be released from the mitochondria and trigger a series of events that lead to cell death. This helps in maintaining the health of an organism by eliminating damaged or unwanted cells.
Reactive Oxygen Species Detection: Studies have also suggested that Cytochrome C1 might play a role in maintaining the mitochondrial membrane potential and in the detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can cause damage to cells.
Reducing Coenzyme Q: It is a part of the complex III (cytochrome bc1 complex) where it helps in the reduction of coenzyme Q10.
Cardiovascular Function: Although not fully understood, mutations in the CYC1 gene have been associated with various cardiovascular anomalies, indicating a potential role in maintaining cardiovascular function.
Cyc1 related signaling pathway
Retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway: CYC1 promotes G1/S transition by stimulating E2F transcription factors that activate S-phase genes. Hyperphosphorylated Rb releases E2Fs for CYC1 to activate.
Cyclin-CDK pathway: CYC1 drives expression of D-type cyclins and CDK4/6 to phosphorylate Rb. It also induces cyclin E expression to activate CDK2 for S-phase entry.
Wnt/β-catenin pathway: CYC1 transcriptionally activates Wnt target genes through β-catenin. Wnt signaling cooperates with CYC1 to enhance cell cycle progression.
Hedgehog pathway: CYC1 interacts with GLI transcription factors downstream of Hedgehog, stimulating their pro-proliferative effects in cancer.
CYC1 Related Diseases
- Cancer: Abnormal upregulation or hyperactivation of CYC1 has been observed in several cancer types, promoting uncontrolled cell proliferation. This includes breast, lung, colorectal cancers.
- Colorectal cancer: Higher CYC1 expression correlates with advanced stage and poorer prognosis in colon cancer patients. It may contribute to tumorigenesis.
- Breast cancer: Elevated CYC1 levels are associated with tumor growth and progression. Its knockdown can suppress breast cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo.
- Cancer therapy - Developing CYC1 inhibitors as anticancer drugs to block uncontrolled proliferation in CYC1-dependent tumors.
- Biomarker - Investigating CYC1 expression levels as a biomarker to predict cancer progression, recurrence, or response to specific treatments.
- Drug targets - Identifying CYC1 interactors and downstream effectors as new druggable targets for cancer therapies.
- Cancer therapy - Developing CYC1 inhibitors as anticancer drugs to block uncontrolled proliferation in CYC1-dependent tumors.
- Biomarker - Investigating CYC1 expression levels as a biomarker to predict cancer progression, recurrence, or response to specific treatments.
- Drug targets - Identifying CYC1 interactors and downstream effectors as new druggable targets for cancer therapies.
Case Study
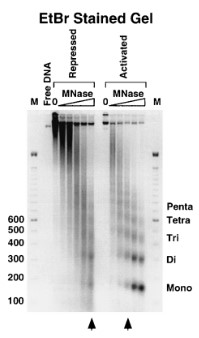
(Craig Martens, 2001)
Fig2. Ethidium bromide-stained gel. The nuclei were digested with micrococcal nuclease in order to produce a significant degree of cleavage. The DNA was purified and resolved on an agarose gel. The result is a 'nucleosome ladder' with steps of ≈ 165 bp for the total yeast DNA.

(ZIJIAN GUO, 1995)
Fig3. Northern blot analysis of the 630-nt CYCI mRNA. Total yeast RNA, transferred to a nitrocellulose filter, was first hybridized to a URA3 probe. The full-length URA3 mRNA from the wild-type URA3 gene on the plasmids is indicated. Some truncated URA3 transcripts from the chromosomal ura3-52 allele were also observed but are not shown. After autoradiographs were obtained, the URA3 probe was removed by washing and a CYCI probe was hybridized to the same filter. The 630-nt CYC1 mRNA was quantitated by densitometry using the full-length URA3 mRNA as an internal standard.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
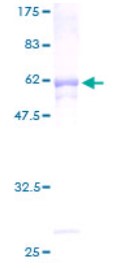
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cat. No.: CYC1-2224H)
Involved Pathway
CYC1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CYC1 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CYC1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
CYC1 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CYC1 itself. We selected most functions CYC1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CYC1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | GATSL3,SLC16A3,EYA3,HSPA4,USP2,BTK,HIST1H4B,PIK3C3,VPS26A,RBM14 |
Interacting Protein
CYC1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CYC1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CYC1.
Tubb4b;CLN3;Haus1;FLOT1;MYC;ATF2;HTT;FLOT2;GOLT1B
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Lin, J; Diamanduros, A; et al. Specific electron transport chain abnormalities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY 256:774-782(2009).
- Ivanov, PA; Lewitin, EI; et al. Sup35p yeast prion-like protein as an adapter for production of the Gag-p55 antigen of HIV-1 and the L-chain of botulinum neurotoxin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RESEARCH IN MICROBIOLOGY 152:27-35(2001).


