CLK1
-
Official Full Name
CDC-like kinase 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the CDC2-like (or LAMMER) family of dual specificity protein kinases. In the nucleus, the encoded protein phosphorylates serine/arginine-rich proteins involved in pre-mRNA processing, releasing them into the nucleoplasm. The choice of splice sites during pre-mRNA processing may be regulated by the concentration of transacting factors, including serine/arginine rich proteins. Therefore, the encoded protein may play an indirect role in governing splice site selection. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
CLK1;CDC-like kinase 1;dual specificity protein kinase CLK1;STY;CDC like kinase 1;CLK;CLK/STY;CLK1_HUMAN;OTTHUMP00000163673;OTTHUMP00000206165;OTTHUMP00000206166;CDC28/CDC2-like kinase;protein tyrosine kinase STY
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Insect Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His&GST
- GST
- Non
- His
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
What is CLK1 protein?
CLK1 gene (CDC like kinase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q33. This gene encodes a member of the CDC2-like (or LAMMER) family of dual specificity protein kinases. In the nucleus, the encoded protein phosphorylates serine/arginine-rich proteins involved in pre-mRNA processing, releasing them into the nucleoplasm. The choice of splice sites during pre-mRNA processing may be regulated by the concentration of transacting factors, including serine/arginine rich proteins. Therefore, the encoded protein may play an indirect role in governing splice site selection. The CLK1 protein is consisted of 192 amino acids and CLK1 molecular weight is approximately 21.5 kDa.
What is the function of CLK1 protein?
CLK1 is a bispecific protein kinase that plays an important role in many biological processes of cells. CLK1 is particularly critical in regulating RNA splicing, mRNA processing, and cell cycle regulation. It affects alternative splicing by phosphorylating members of the SR protein family, which in turn affects gene expression. In addition, CLK1 is involved in cellular stress response, cell proliferation and differentiation, and cellular senescence processes. Abnormal activity of CLK1 has been associated with a variety of diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, certain types of cancer, and viral infections. Therefore, CLK1 is a potential target in drug development, especially in the treatment of diseases caused by abnormal splicing.
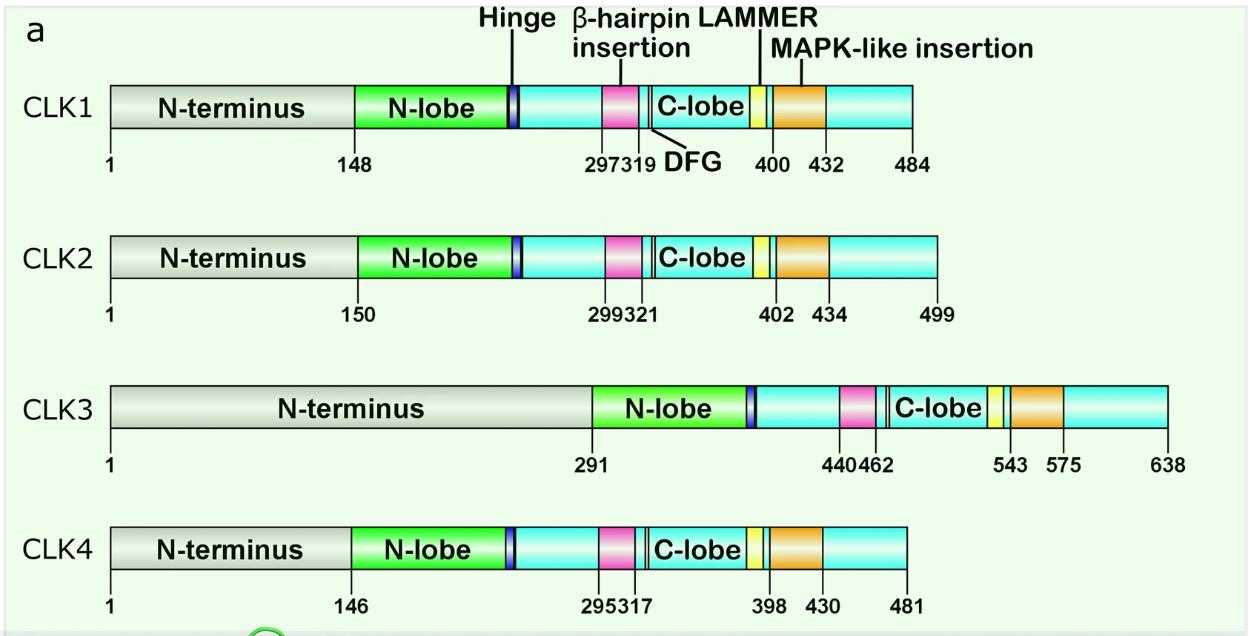
Fig1. Domain structures of human CLK1, -2, -3, and -4. (Mengqiu Song, 2023)
CLK1 related signaling pathway
CLK1 protein is a bi-specific kinase that mainly plays a role in the nucleus, influencing pre-mrna splicing through phosphorylation of Ser/ ARG-rich splicing factors to produce different protein isomers. CLK1 plays a key role in regulating cell growth, survival, cell cycle progression, and response to cellular stress. In addition, CLK1 is involved in a variety of biological processes, including cell differentiation, migration, tumorigenesis, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain viral infections. The abnormal activity of CLK1 has been associated with a variety of diseases, making it a potential target for drug development, especially in therapies targeting diseases caused by abnormal splicing.
CLK1 related diseases
The CLK1 protein plays a role in a variety of diseases, including but not limited to cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, viral infections, and cardiovascular disease. In cancer therapy, inhibitors of CLK1 are being tested in clinical trials to treat solid cancers because it can reduce the production of cancer-causing protein variants that promote tumor progression through alternative splicing. In addition, CLK1 also plays a role in regulating alternative splicing in viral infections such as HIV-1, influenza A virus, and Trypanosoma infections, suggesting that it may have potential in antiviral infection treatment. In neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, CLK1 may contribute to disease progression by affecting the alternative splicing of tau proteins. In addition, inhibitors of CLK1 have shown promise in the treatment of cardiovascular disease, for example by reducing pathological cardiac hypertrophy to protect heart function.
Bioapplications of CLK1
As a bispecific kinase, CLK1 plays an important role in RNA splicing regulation through phosphorylation of SR protein. Inhibitors of CLK1 are being investigated for the treatment of a variety of diseases, including cancer, viral infections, Alzheimer's disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and diabetes. In cancer therapy, inhibitors of CLK1 are able to reduce the production of cancer-causing protein variants that promote tumor progression through alternative splicing. In addition, CLK1 also plays a role in regulating viral infections such as HIV-1, influenza viruses, and trypanosoma infections, and its inhibitors may help inhibit replication of these pathogens. In the field of neurodegenerative diseases, CLK1 has been associated with the progression of Alzheimer's disease by influencing alternative splicing of tau proteins. In addition, inhibitors of CLK1 have shown potential in improving pathological splicing in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Studies have also shown that CLK1 may play a role in diabetes treatment by affecting the liver's gluconeogenesis process.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Noa Dekel, 2020
CLK1 is a kinase that can phosphorylate tyrosine and Ser/Thr residues, regulating splicing by targeting SR proteins. It's significant for the life cycle of several viruses, including influenza A, chikungunya, HIV-1, and West Nile, suggesting its potential in antiviral therapy. Researchers successfully produced recombinant CLK1 for crystallization using a method that involves co-expressing it with λ-phosphatase, which helps in obtaining uniform, unphosphorylated protein. This approach could be a general strategy for preparing other kinases for structural and biochemical studies, aiding in the development of new inhibitors.
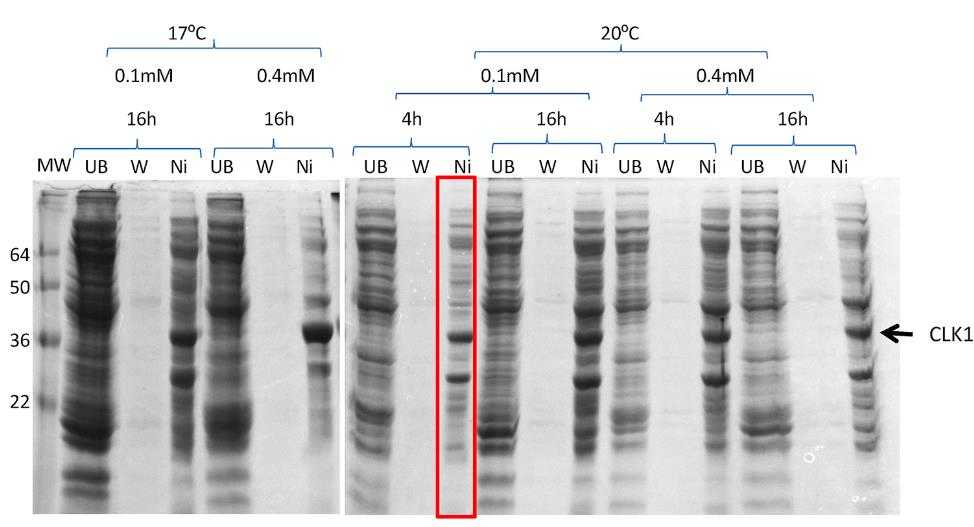
Fig1. Screening conditions for co-expression of CLK1 with λ-phosphatase in BL21 (DE3).
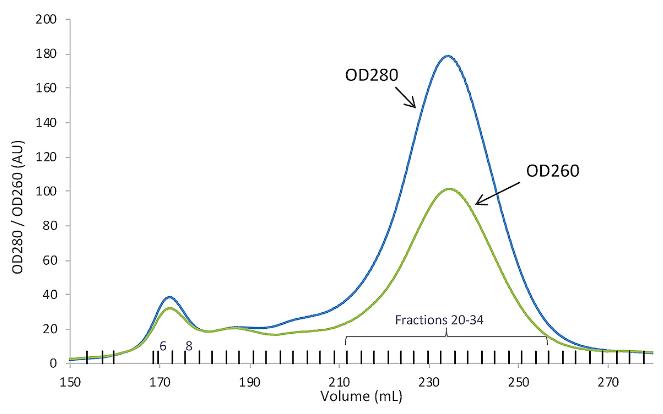
Fig2. Gel filtration chromatogram where CLK1 is eluted in the second peak.
Case Study 2: Brandon E Aubol, 2014
SR proteins, crucial for splicing, are regulated by phosphorylation by kinase families SRPKs and CLKs. While SRPKs target arginine/serine dipeptides, CLKs phosphorylate both these and serine-proline sites, promoting a hyperphosphorylated state that's key for SR protein function. CLK1's flexible N-terminal extension interacts with both its kinase domain and the RS domain of SR protein SRSF1, which is vital for hyperphosphorylation and enhances the binding of SRSF1 to RNA. This N-terminal region of CLK1 also significantly increases the phosphorylation of several SR proteins.
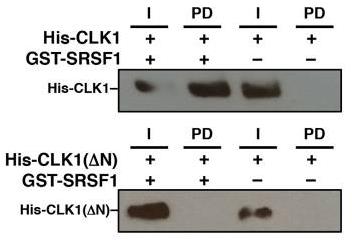
Fig3. The interaction of His-tagged CLK1 and CLK1(ΔN) with GST-SRSF1 is monitored on g-agarose beads using an anti-His antibody in pull-down assays.
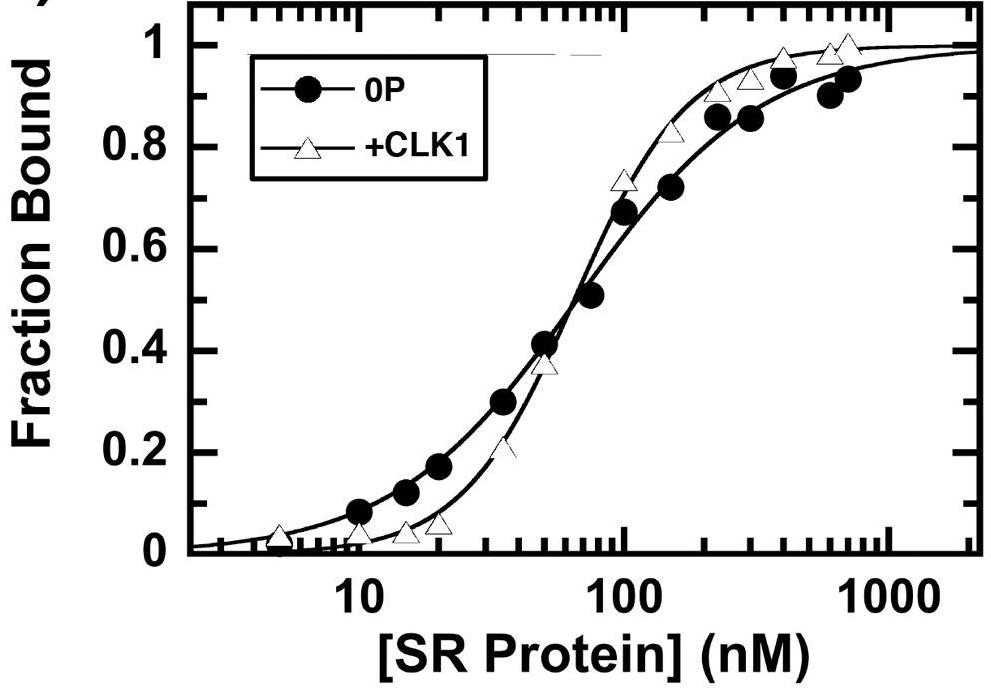
Fig4. CLK1 phosphorylation induces cooperative binding of SRSF1 to the Ron ESE.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CLK1-1491H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CLK1-1490H)
Involved Pathway
CLK1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CLK1 participated on our site, such as Legionellosis,mRNA processing, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CLK1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| mRNA processing | DHX8,SREK1,CLK2,RBM39,CELF1,DHX15,SF3B4,PRPF8,PSKH1,PTBP1 |
| Legionellosis | BNIP3,SAR1A,CR1,IL12A,RELA,HSPA2,NFKB1,EEF1A2,NAIP1,SAR1B |
Protein Function
CLK1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CLK1 itself. We selected most functions CLK1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CLK1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | ITM2A,SYNE3,TMEM231,ARL6IP4,PSMD11,ITGA1,CEP57L1,RAD51L3,SIX1,DDX58 |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | TEC,FES,STK16,FER,TXK,PTK2BB,SRMS,FGR,PRKCD,PTK6 |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | TESK1,AURKC,CLK4,AKT1,DYRK3,DSTYK,RPS6KA1,DYRK4,PRKAA2,MAP2K1 |
| ATP binding | PRKACA,HIPK1,EIF2B2,BSK146,PSMC1B,TK2,CCT5,CLCN6,EARS2,MYHC4 |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | NIM1K,TESK1,DCKL1B,PRKG1A,PRKCHA,CSNK1G2A,RIOK3,MAP3K8,PAK6,RPS6KA2 |
Interacting Protein
CLK1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CLK1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CLK1.
PDE9A;KRTAP10-7;PTPN1;N/A;SRPK2;SRPK1;PSEN2;YWHAG;PRMT5;ltp_ebvg;ezrA;PIAS4;GOLM1;q8xa11_eco57;DOCK9
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


