What is HSPA5 Protein?
The HSPA5 protein, more commonly known as 78kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78), is a multifaceted biomolecule that has remained under the scientific microscope for its distinctive role in cellular functionality and human diseases. Discovered in the late 1970s, this protein was initially identified as a biochemical agent linked to glucose metabolism. However, subsequent research has unearthed extensive insights into its role, unraveling its crucialness in significant biological operations.
Structured as part of the Heat Shock Protein (HSP) family, HSPA5 is encoded by the HSPA5 gene located on the ninth chromosome of the human genome (9q33.3). The protein comprises approximately 654 amino acids, forming a bulky structure with a molecular mass around 78kDa. Unraveling its conformational design, the presence of two ATPase domains and a protein-binding domain is prominent. Additionally, its bipartite signal sequence allows it to extensively interact with other proteins, thus playing significant roles in a variety of intracellular pathways.
Function of HSPA5 protein
HSPA5 plays a prime role in protein synthesis, folding, intracellular calcium homeostasis, and apoptosis regulation. As an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone, it facilitates the correct folding of newly synthesized proteins, preventing aggregation and premature degradation. Additionally, the protein also functions as a stress sensor in the ER. When the ER encounters stress, such as an accumulation of unfolded proteins, the transcription of HSPA5 is up-regulated to restore cellular homeostasis.
Furthermore, research across the years has illuminated the indispensable role of HSPA5 protein in signal pathways. For instance, HSPA5-IRE1a, a signal pathway, enables cells to detect any distortion in protein homeostasis in the ER, thus initiating the unfolded protein response (UPR). In another example, HSPA5 is critically involved in the mTOR signaling pathway which regulates cell growth and metabolism in response to environmental cues such as nutrients and growth factors.
HSPA5 protein related diseases
The role of HSPA5 protein extends further into the realm of human diseases, specifically cancer. Overexpression of HSPA5 has been detected in various cancers, including liver, lung, colon, and breast cancers. The enhanced ER stress response might provide cancer cells with a survival advantage, enabling them to resist conditions that would otherwise induce cell death. Moreover, HSPA5 is implicated in other diseases associated with protein misfolding and aggregation, such as neurodegenerative disorders (Alzheimer's, Parkinson's) and diabetes.
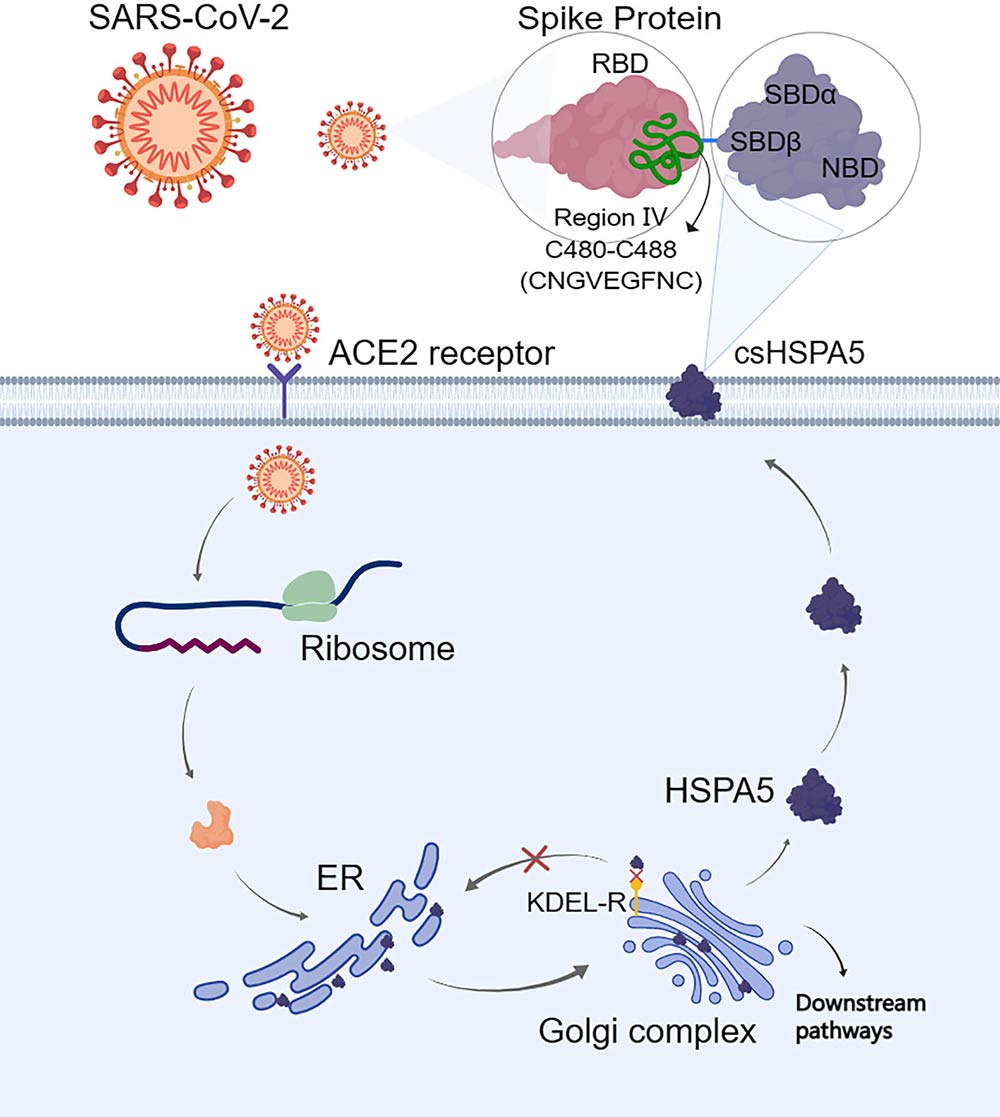
Recent scientific strides have also made us realize the potential role of HSPA5 in virology. This protein assists in the translocation of the viral proteins in the host ER, a critical step for the assembly and release of infectious virions. Consequently, HSPA5 has become a potential therapeutic target for many viral infections, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
HSPA5 protein's applications in biomedical
In biomedical applications, HSPA5 protein takes center stage for its potential as a therapeutic target and biomarker. Its overexpression in tumors and subsequent protective role against various cellular stresses make it a viable target for adjuvant therapies. In addition to anti-cancer drugs, HSPA5 inhibitors are being developed to suppress the protective ER stress response in cancer cells. Its role is also under investigation in treatments of neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic disorders, given its involvement in protein misfolding.
As a biomarker, HSPA5 can have enormous potential. Its activity levels could provide insights into cell health, response to stress, and disease progression. Moreover, the presence of HSPA5 at the cell surface, particularly in cancer cells, offers a unique target for the development of selective therapeutic antibodies.
The HSPA5 protein's undeniably intricate mapping in cellular functionality and its linkages to various human diseases underline its importance. It serves as a pivotal platform connecting genotype and phenotype, aberrations in which may cause human disease. Moreover, its role as a potential therapeutic target adds an additional layer of significance, attracting the focus of researchers globally. Thus, HSPA5 protein is a substantial contributor to the understanding and advancement of cellular biology and clinical medicine.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSPA5-1551H | Active Recombinant Human HSPA5 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| HSPA5-5107H | Recombinant Human HSPA5 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| HSPA5-3897HF | Recombinant Full Length Human HSPA5 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| HSPA5-52HFL | Active Recombinant Full Length Human HSPA5 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| HSPA5-1119H | Recombinant Human HSPA5 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Hspa5-2071M | Recombinant Mouse Heat Shock Protein 5 | Mouse | E.coli | N/A |
| Hspa5-238M | Recombinant Mouse Hspa5 Protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| HSPA5-3232M | Recombinant Mouse HSPA5 protein, His-GST-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His/GST |
| HSPA5-2165R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey HSPA5 Protein, His-tagged | Rhesus Macaque | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Li, T., Fu, J., Cheng, J., Elfiky, A. A., Wei, C., & Fu, J. (2023). New progresses on cell surface protein HSPA5/BiP/GRP78 in cancers and COVID-19. Frontiers in Immunology, 14, 1166680. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1166680
