IL-6 Family
Creative BioMart IL-6 Family Product List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CSF Receptor Research
Creative BioMart is the premier destination for all your research needs concerning CSF receptors. Our comprehensive selection of meticulously crafted products and tailored services is specially curated to assist you in exploring the intricate world of CSF receptors and their crucial involvement in multiple physiological processes.
- Our line of products features premium recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and more, all designed to meet your research requirements with optimum quality and precision.
- In addition, we provide a wealth of resources on CSF receptors, including detailed information on associated pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, relevant articles, and areas of ongoing research. Trust Creative BioMart to be your go-to source for all things related to CSF receptors.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSF1R-805H | Recombinant Human CSF1R protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CSF2RA-724H | Recombinant Human CSF2RA protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | human/IgG1/Fc |
| CSF2RB-3177H | Active Recombinant Human CSF2RB protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CSF3R-8526H | Recombinant Human CSF3R protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
About CSF Receptors
CSF receptors, also known as CSF receptor complexes, are cell surface proteins that bind to colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) and transmit signals into the cell upon ligand binding. These receptors are critical for mediating the biological effects of CSFs by initiating intracellular signaling pathways that regulate cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation.
CSF receptors are typically composed of multiple subunits that come together to form a functional receptor complex. The specific composition of the receptor complex depends on the type of CSF and the target cell type. Here are some examples of CSF receptors:
- Granulocyte-CSF receptor (G-CSFR): The G-CSFR is a receptor complex that binds to granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF). It consists of a ligand-binding subunit and a signal-transducing subunit. The ligand-binding subunit is specific to G-CSF and is responsible for high-affinity binding to the ligand, while the signal-transducing subunit is involved in transmitting intracellular signals upon ligand binding.
- Granulocyte-macrophage-CSF receptor (GM-CSFR): The GM-CSFR is a receptor complex that binds to granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). It also consists of a ligand-binding subunit and a signal-transducing subunit. The ligand-binding subunit recognizes GM-CSF, while the signal-transducing subunit activates intracellular signaling pathways upon ligand binding.
- Macrophage-CSF receptor (M-CSFR): The M-CSFR, also known as CD115, is the receptor for macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF). It is a single-chain receptor that binds to M-CSF and transduces signals into the cell to regulate macrophage differentiation, proliferation, and survival.
- Erythropoietin receptor (EPOR): The EPOR is the receptor for erythropoietin (EPO), a CSF that regulates the production of red blood cells. The EPOR is a single-chain receptor that binds to EPO and activates signaling pathways involved in erythroid cell development and survival.
Upon ligand binding, CSF receptors undergo conformational changes that lead to receptor dimerization or oligomerization. This clustering of receptors initiates intracellular signaling cascades, typically involving tyrosine kinase activation and subsequent phosphorylation of downstream signaling molecules. These signaling events regulate various cellular processes, such as gene expression, cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation.
CSF receptors are expressed on different types of hematopoietic cells, including hematopoietic stem cells, progenitor cells, and mature blood cells. Their activation by CSFs is essential for the regulation of hematopoiesis, immune responses, and tissue homeostasis.
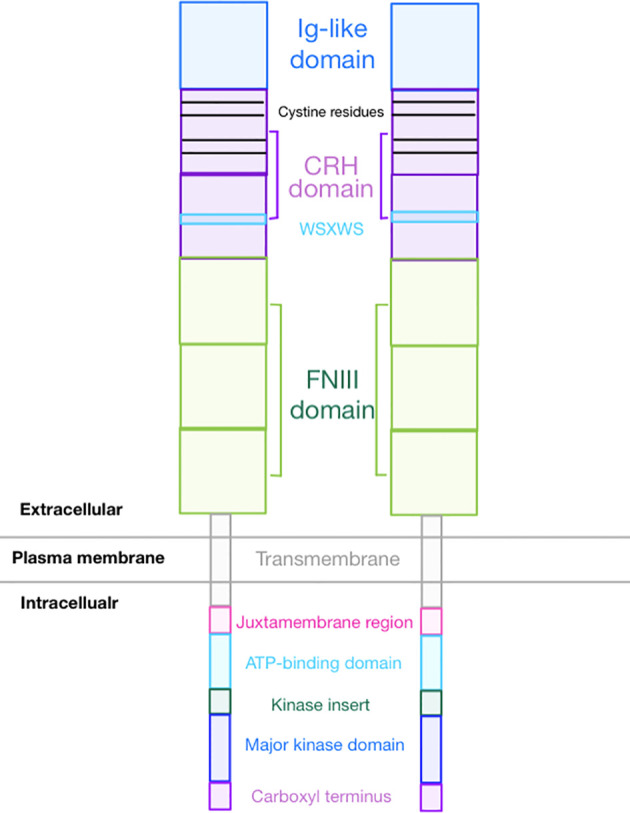 Fig.1 Overall GCSFR structure. (Park SD, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Overall GCSFR structure. (Park SD, et al., 2022)
CSF Receptor Signaling Pathways
CSF receptor signaling pathways are complex and diverse, as they involve the activation of various intracellular signaling molecules and cascades. The specific signaling pathways activated by CSF receptors may vary depending on the type of CSF and the cell type expressing the receptor. However, there are common signaling components and pathways that play essential roles in transmitting the signals initiated by CSF receptor activation. Here is an overview of some key signaling pathways associated with CSF receptor signaling:
- Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway: This is one of the major signaling pathways activated by CSF receptors. Upon ligand binding, CSF receptors induce the dimerization and activation of associated Janus kinases (JAKs). The activated JAKs phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor, providing docking sites for signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins. Once recruited, STAT proteins are phosphorylated by JAKs, leading to their dimerization, nuclear translocation, and subsequent modulation of gene expression. The JAK/STAT pathway is involved in regulating cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation.
- Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway: CSF receptor activation can also trigger the activation of PI3K. This enzyme phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol lipids, generating phosphoinositide 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3). PIP3 serves as a second messenger that recruits and activates Akt (also known as protein kinase B). Activated Akt phosphorylates multiple downstream targets involved in cell survival, growth, and metabolism. The PI3K/Akt pathway is crucial for mediating the anti-apoptotic and pro-survival effects of CSF receptors.
- Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway: CSF receptor activation can stimulate various MAPK cascades, including the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 MAPK pathways. These pathways involve sequential phosphorylation events, ultimately leading to the activation of specific transcription factors and modulation of gene expression. MAPK signaling is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival in response to CSF stimulation.
- Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway: CSF receptor activation can activate the NF-κB pathway, which plays a critical role in immune and inflammatory responses. Upon stimulation, CSF receptors can trigger the phosphorylation and degradation of the inhibitor of kappa B (IκB), leading to the release and nuclear translocation of NF-κB transcription factors. In the nucleus, NF-κB regulates the expression of genes involved in immune responses, inflammation, and cell survival.
These are just a few examples of the signaling pathways associated with CSF receptor activation. It's important to note that the specific signaling cascades and downstream effects can vary depending on the context and cell type. Additionally, cross-talk between different signaling pathways can occur, leading to complex and integrated cellular responses to CSF stimulation.
Understanding the intricacies of CSF receptor signaling pathways is essential for deciphering the mechanisms underlying hematopoiesis, immune regulation, and the therapeutic potential of targeting these pathways in various diseases.
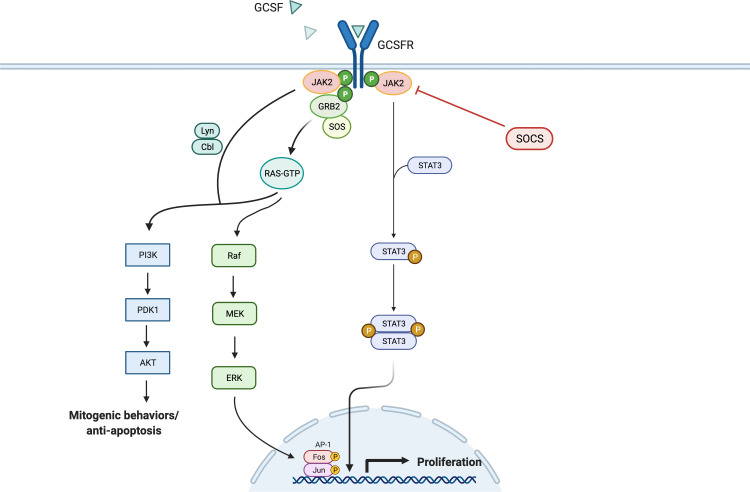 Fig.2 General overview of GCSFR signal pathways. (Park SD, et al., 2022)
Fig.2 General overview of GCSFR signal pathways. (Park SD, et al., 2022)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Weng S, Stoner SA, Zhang DE. Sex chromosome loss and the pseudoautosomal region genes in hematological malignancies. Oncotarget. 2016;7(44):72356-72372.
- Hercus TR, Broughton SE, Ekert PG, et al. The GM-CSF receptor family: mechanism of activation and implications for disease. Growth Factors. 2012;30(2):63-75. doi:10.3109/08977194.2011.649919
- Park SD, Saunders AS, Reidy MA, Bender DE, Clifton S, Morris KT. A review of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signaling and regulation with implications for cancer. Front Oncol. 2022;12:932608. Published 2022 Aug 11.
